Article contents
TRANSITIVE PRIMAL INFON LOGIC
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 March 2013
Abstract
Primal infon logic was introduced in 2009 in connection with access control. In addition to traditional logic constructs, it contains unary connectives p said indispensable in the intended access control applications. Propositional primal infon logic is decidable in linear time, yet suffices for many common access control scenarios. The most obvious limitation on its expressivity is the failure of the transitivity law for implication: 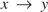 $x \to y$ and
$x \to y$ and 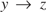 $y \to z$ do not necessarily yield
$y \to z$ do not necessarily yield 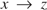 $x \to z$. Here we introduce and investigate equiexpressive “transitive” extensions TPIL and TPIL* of propositional primal infon logic as well as their quote-free fragments TPIL0 and TPIL0* respectively. We prove the subformula property for TPIL0* and a similar property for TPIL*; we define Kripke models for the four logics and prove the corresponding soundness-and-completeness theorems; we show that, in all these logics, satisfiable formulas have small models; but our main result is a quadratic-time derivation algorithm for TPIL*.
$x \to z$. Here we introduce and investigate equiexpressive “transitive” extensions TPIL and TPIL* of propositional primal infon logic as well as their quote-free fragments TPIL0 and TPIL0* respectively. We prove the subformula property for TPIL0* and a similar property for TPIL*; we define Kripke models for the four logics and prove the corresponding soundness-and-completeness theorems; we show that, in all these logics, satisfiable formulas have small models; but our main result is a quadratic-time derivation algorithm for TPIL*.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Association for Symbolic Logic 2013
References
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- 6
- Cited by


