Article contents
PROOF SYSTEMS FOR VARIOUS FDE-BASED MODAL LOGICS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 June 2019
Abstract
We present novel proof systems for various FDE-based modal logics. Among the systems considered are a number of Belnapian modal logics introduced in Odintsov & Wansing (2010) and Odintsov & Wansing (2017), as well as the modal logic KN4 with strong implication introduced in Goble (2006). In particular, we provide a Hilbert-style axiom system for the logic 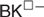 $BK^{\square - } $ and characterize the logic BK as an axiomatic extension of the system
$BK^{\square - } $ and characterize the logic BK as an axiomatic extension of the system 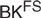 $BK^{FS} $. For KN4 we provide both an FDE-style axiom system and a decidable sequent calculus for which a contraction elimination and a cut elimination result are shown.
$BK^{FS} $. For KN4 we provide both an FDE-style axiom system and a decidable sequent calculus for which a contraction elimination and a cut elimination result are shown.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Association for Symbolic Logic 2019
References
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- 3
- Cited by



