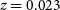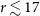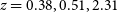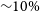1. Introduction
The broadband ultraviolet (UV) light (1000–3000 Å) from galaxies offers a unique window into their evolution. The far UV light (FUV; 1000–2000 Å) in normal star-forming galaxies is produced by intermediate-mass (2–5
![]() ${\rm M}_{\odot}$
) short-lived stars (
${\rm M}_{\odot}$
) short-lived stars (
![]() ${\leq} 1$
Gyr), and hence is a good tracer of the star formation rate (SFR; Kennicutt 1998; Mahajan et al. Reference Mahajan, Ashby, Willner, Barmby, Fazio, Maragkoudakis, Raychaudhury and Zezas2019). On the other hand, low-mass helium burning stars which evolve through the horizontal branch produce FUV emission in the more evolved elliptical galaxies (
${\leq} 1$
Gyr), and hence is a good tracer of the star formation rate (SFR; Kennicutt 1998; Mahajan et al. Reference Mahajan, Ashby, Willner, Barmby, Fazio, Maragkoudakis, Raychaudhury and Zezas2019). On the other hand, low-mass helium burning stars which evolve through the horizontal branch produce FUV emission in the more evolved elliptical galaxies (
![]() ${>}8-10$
Gyr old), resulting in a UV upturn in the spectra of such galaxies at wavelengths shorter than 2000 Å. In either case, the FUV emission can therefore be used as an age-dating tool to assess the evolution history for a variety of galaxies.
${>}8-10$
Gyr old), resulting in a UV upturn in the spectra of such galaxies at wavelengths shorter than 2000 Å. In either case, the FUV emission can therefore be used as an age-dating tool to assess the evolution history for a variety of galaxies.
The Indian multi-wavelength satellite AstroSat launched in 2015 (Singh et al. Reference Singh and Takahashi2014) greatly surpassed its predecessors in observing the UV sky. The Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UVIT; Tandon et al. Reference Tandon2017, Reference Tandon2020) on-board the AstroSat offers the highest spatial resolution of
![]() ${\lesssim}1.8^{\prime\prime}$
relative to similar missions such as the Swift–UVOT, XMM-OM and Galaxy evolution explorer mission Galex. With a
${\lesssim}1.8^{\prime\prime}$
relative to similar missions such as the Swift–UVOT, XMM-OM and Galaxy evolution explorer mission Galex. With a
![]() $28^{\prime}$
diameter field of view, UVIT is second only to Galex (
$28^{\prime}$
diameter field of view, UVIT is second only to Galex (
![]() $1.2^{\circ}$
), although the latter had a spatial resolution of
$1.2^{\circ}$
), although the latter had a spatial resolution of
![]() ${\sim} 5^{\prime\prime}$
. The large field of view together with the unprecedented resolution therefore makes UVIT a great tool for exploring the recent star formation history of galaxies in galaxy clusters.
${\sim} 5^{\prime\prime}$
. The large field of view together with the unprecedented resolution therefore makes UVIT a great tool for exploring the recent star formation history of galaxies in galaxy clusters.
The Coma cluster (
![]() ${\sim} 100\, h^{-1}$
Mpc,
${\sim} 100\, h^{-1}$
Mpc,
![]() $z=0.023$
) is one of the richest and the most well studied cluster of galaxies in the nearby Universe. Hence it is not surprising that this cluster has extensive panchromatic coverage from X-rays to the radio continuum. Prior to the launch of the AstroSat mission, the deepest UV observations (
$z=0.023$
) is one of the richest and the most well studied cluster of galaxies in the nearby Universe. Hence it is not surprising that this cluster has extensive panchromatic coverage from X-rays to the radio continuum. Prior to the launch of the AstroSat mission, the deepest UV observations (
![]() ${\sim} 26$
ks) of an off-centre field near the core of the Coma cluster were obtained by the Galex mission (Hammer et al. Reference Hammer2010). This region lies
${\sim} 26$
ks) of an off-centre field near the core of the Coma cluster were obtained by the Galex mission (Hammer et al. Reference Hammer2010). This region lies
![]() ${\sim} 1^{\circ}$
away from the core, and is linked with the secondary peak in the X-ray emission from the Coma cluster (Finoguenov, Briel, & Henry Reference Finoguenov, Briel and Henry2003; Neumann et al. Reference Neumann, Lumb, Pratt and Briel2003), associated with the infalling galaxy group NGC 4839 and several post-starburst galaxies (Poggianti et al. Reference Poggianti, Bridges, Komiyama, Yagi, Carter, Mobasher, Okamura and Kashikawa2004; Mahajan, Haines, & Raychaudhury Reference Mahajan, Haines and Raychaudhury2010).
${\sim} 1^{\circ}$
away from the core, and is linked with the secondary peak in the X-ray emission from the Coma cluster (Finoguenov, Briel, & Henry Reference Finoguenov, Briel and Henry2003; Neumann et al. Reference Neumann, Lumb, Pratt and Briel2003), associated with the infalling galaxy group NGC 4839 and several post-starburst galaxies (Poggianti et al. Reference Poggianti, Bridges, Komiyama, Yagi, Carter, Mobasher, Okamura and Kashikawa2004; Mahajan, Haines, & Raychaudhury Reference Mahajan, Haines and Raychaudhury2010).
Amongst others, the balloon-borne imaging FOCA instrument (2000 Å) was used to conduct a UV survey of the core of the Coma cluster with a spatial resolution of
![]() ${\sim} 20^{\prime\prime}$
which resulted in the first ever UV luminosity function for a cluster of galaxies (Donas, Milliard, & Laget Reference Donas, Milliard and Laget1991). Follow up observations of several other nearby clusters together with the Coma cluster showed that the UV luminosity functions are also well fitted by a Schechter function, and are similar to the ones obtained for the general ‘field’ (e.g. Cortese et al. Reference Cortese, Gavazzi, Iglesias-Paramo, Boselli and Carrasco2003). These observations indicate that the mechanisms responsible for quenching star formation of galaxies falling into clusters influence the giant and dwarf galaxies in a similar fashion, therefore preserving the shape of the luminosity function, albeit with different normalisation.
${\sim} 20^{\prime\prime}$
which resulted in the first ever UV luminosity function for a cluster of galaxies (Donas, Milliard, & Laget Reference Donas, Milliard and Laget1991). Follow up observations of several other nearby clusters together with the Coma cluster showed that the UV luminosity functions are also well fitted by a Schechter function, and are similar to the ones obtained for the general ‘field’ (e.g. Cortese et al. Reference Cortese, Gavazzi, Iglesias-Paramo, Boselli and Carrasco2003). These observations indicate that the mechanisms responsible for quenching star formation of galaxies falling into clusters influence the giant and dwarf galaxies in a similar fashion, therefore preserving the shape of the luminosity function, albeit with different normalisation.
In this work we utilise the merits of the UVIT to explore a region
![]() ${\sim} 5.5^{\prime}$
away (
${\sim} 5.5^{\prime}$
away (
![]() ${\sim} 0.7$
Mpc at
${\sim} 0.7$
Mpc at
![]() $z=0.023$
) from the core of the Coma cluster. The deviation from the core is necessitated by the technical requirements of the UVIT instruments. In our knowledge, this is the first statistical study of galaxies based on UVIT data, and hence a benchmark for the ones to follow from the arsenal of good quality data which is now becoming available.
$z=0.023$
) from the core of the Coma cluster. The deviation from the core is necessitated by the technical requirements of the UVIT instruments. In our knowledge, this is the first statistical study of galaxies based on UVIT data, and hence a benchmark for the ones to follow from the arsenal of good quality data which is now becoming available.
In the next section we describe the UV and optical data used in this work, followed by the properties of the detected UV sources in Section 3. In Section 4 we discuss some individual sources with distorted UV morphology, followed by a discussion of our findings in Section 5. We finally conclude with the summary of our work in Section 6. Throughout this work we use concordance
![]() $\Lambda$
cold dark matter cosmological model with
$\Lambda$
cold dark matter cosmological model with
![]() $H_0 = 70\ \mathrm{km\ s}^{-1}\ \mathrm{Mpc}^{-1}$
,
$H_0 = 70\ \mathrm{km\ s}^{-1}\ \mathrm{Mpc}^{-1}$
,
![]() $\Omega_\Lambda = 0.7$
and
$\Omega_\Lambda = 0.7$
and
![]() $\Omega_m = 0.3$
to calculate distances and magnitudes.
$\Omega_m = 0.3$
to calculate distances and magnitudes.
2. Data
2.1. UV observations and data processing
In this paper we utilise the data from the UVIT on-board the AstroSat (Kumar et al. Reference Kumar, Takahashi and Murray2012). The UVIT comprises two 35-cm Ritchey-Chrétien telescopes with one of them dedicated to the far ultraviolet (FUV; 1250–1830 Å) and the other split between the near ultraviolet (NUV; 1900–3040 Å) and the visible (VIS; 3040–5500 Å) channels, respectively. The raw data from the mission are processed by the Indian Space Science Data Centre (ISSDC) and the Level 1 as well as Level 2 (pre-processed events and images) from each instrument are provided to the users.
The data used for the Coma cluster used in this work were taken as part of the guaranteed time observations in cycle 6 taken over 17 orbits of the AstroSat (Observation ID: G06-077T01-9000001090; PI: K P Singh). Each orbit included simultaneous observations by VIS, FUV and X-ray instruments. The NUV channel could not be used due to the presence of a bright star in the field. The FUV observations were done in the broadband
![]() $\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter centred at 1541 Å (Tandon et al. Reference Tandon2017, Reference Tandon2020) with a total exposure time of 22669.5 s. The final science image required manual source-tracking techniques to determine the drift, as detailed below, due to the field having only a single source bright enough for tracking in the VIS channel, as well as fainter sources which were interfered with by electronic artefacts in the VIS image data. The VIS data are not recommended for scientific analysis and are primarily used for tracking the spacecraft. Figure 1 shows the position of the UVIT field relative to the x-ray centre (
$\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter centred at 1541 Å (Tandon et al. Reference Tandon2017, Reference Tandon2020) with a total exposure time of 22669.5 s. The final science image required manual source-tracking techniques to determine the drift, as detailed below, due to the field having only a single source bright enough for tracking in the VIS channel, as well as fainter sources which were interfered with by electronic artefacts in the VIS image data. The VIS data are not recommended for scientific analysis and are primarily used for tracking the spacecraft. Figure 1 shows the position of the UVIT field relative to the x-ray centre (
![]() $\alpha = 13:00:10.240$
and
$\alpha = 13:00:10.240$
and
![]() $\delta = 28:01:01.498$
; Rines et al. Reference Rines, Geller, Kurtz and Diaferio2003), along with the giant elliptical galaxy, NGC 4889.
$\delta = 28:01:01.498$
; Rines et al. Reference Rines, Geller, Kurtz and Diaferio2003), along with the giant elliptical galaxy, NGC 4889.

Figure 1. The UVIT field of view with the red circular region centred at
![]() $\alpha = 13:00:10.240$
and
$\alpha = 13:00:10.240$
and
![]() $\delta = 28:01:01.498$
, and having a radius of
$\delta = 28:01:01.498$
, and having a radius of
![]() $14.5^\prime$
analysed in this paper. The blue cross denotes the x-ray centre of the Coma cluster (
$14.5^\prime$
analysed in this paper. The blue cross denotes the x-ray centre of the Coma cluster (
![]() $\alpha = 12:59:31.900, \delta = 27:54:10.000$
; Rines et al. Reference Rines, Geller, Kurtz and Diaferio2003). The image is oriented such that North is up and east is on the left. The giant elliptical galaxy NGC 4889 is also shown for reference.
$\alpha = 12:59:31.900, \delta = 27:54:10.000$
; Rines et al. Reference Rines, Geller, Kurtz and Diaferio2003). The image is oriented such that North is up and east is on the left. The giant elliptical galaxy NGC 4889 is also shown for reference.

Figure 2. This sky plot shows the distribution of 1308 sources (blue points) detected in the UVIT’s FUV
![]() $\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter. The 134 sources with redshifts from the SDSS or NED are shown as red squares, and those also detected by GALEX are represented by (black crosses), respectively. This figure clearly shows that some UVIT detected sources are observed for the first time, while many UV sources lack redshift information.
$\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter. The 134 sources with redshifts from the SDSS or NED are shown as red squares, and those also detected by GALEX are represented by (black crosses), respectively. This figure clearly shows that some UVIT detected sources are observed for the first time, while many UV sources lack redshift information.
AstroSat UVIT is a unique telescope because it oscillates its pointing on the orthogonal UVIT image axis at a rate of a few arcseconds every second. These oscillations having an amplitude of a few arcminutes protect the detector components from bright objects. The original image field for the UVIT is then recovered from the effects of these ‘drifts’ by de-shifting and co-adding the count centroids of the detected sources, as a function of the pointing oscillations. For this work we processed the Level 1 FUV data with the CCDLAB software (Postma & Leahy Reference Postma and Leahy2017), following the procedure described in Postma & Leahy (Reference Postma and Leahy2021). The CCDLAB pipeline takes the L1 zip file as input and then performs various corrections on individual images from each orbit after extraction. The CCDLAB pipeline automatically corrects for the translational drift using the VIS data along with other procedures such as subtracting the flat field, detector corrections, and exposure array corrections, amongst others.
The corrected images are then co-aligned with manual intervention and stacked to create a deep field image. Following this, the automatic procedure for optimising the point source function of the sources was initiated in order to remove the residual drift effects from the image, yielding a final full width half maximum of
![]() $1.2^{\prime\prime}$
for this image. Finally, the world coordinate system (WCS) solution was obtained by mapping the pixel coordinates of sources in the image to the GAIA catalogue using the Astroquery utility (Ginsburg et al. 2019) through CCDLAB, and its implementation of the automated WCS-solver as detailed in Postma & Leahy (Reference Postma and Leahy2020). The image was then de-rotated to match the sky coordinates, thus eliminating the effect of the telescope’s field rotation, and used for science.
$1.2^{\prime\prime}$
for this image. Finally, the world coordinate system (WCS) solution was obtained by mapping the pixel coordinates of sources in the image to the GAIA catalogue using the Astroquery utility (Ginsburg et al. 2019) through CCDLAB, and its implementation of the automated WCS-solver as detailed in Postma & Leahy (Reference Postma and Leahy2020). The image was then de-rotated to match the sky coordinates, thus eliminating the effect of the telescope’s field rotation, and used for science.
The FUV source catalogue was created using the sextractor software (Bertin & Arnouts Reference Bertin and Arnouts1996). Sources were detected on a convolved version of the image (Gaussian kernel of FWHM
![]() $ = 4.0$
pixels) in order to prevent shredding of larger galaxies. Other de-blending and detection parameters used by sextractor were chosen after extensively testing a wide range of values and visually testing the processed image. The background was detected by sextractor in the ‘AUTO’ mode. The full set of sextractor parameters used for this image are provided in Table 1 in order to aid fellow UVIT users in processing similar imaging data. We detect 1308 sources in the UVIT
$ = 4.0$
pixels) in order to prevent shredding of larger galaxies. Other de-blending and detection parameters used by sextractor were chosen after extensively testing a wide range of values and visually testing the processed image. The background was detected by sextractor in the ‘AUTO’ mode. The full set of sextractor parameters used for this image are provided in Table 1 in order to aid fellow UVIT users in processing similar imaging data. We detect 1308 sources in the UVIT
![]() $\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter (Figure 2), which are analysed further in this paper.
$\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter (Figure 2), which are analysed further in this paper.
Table 1. Sextractor (version v1.2b14) parameters used for the analysis of the UVIT FUV image.

The integrated counts for all the 1308 sources identified in this image were normalised by the total integration time, and then converted to fluxes using the conversion factors provided by Tandon et al. (Reference Tandon2020). The measured flux was corrected for galactic extinction assuming a Milky way-like extinction curve (Calzetti et al. Reference Calzetti, Armus, Bohlin, Kinney, Koornneef and Storchi-Bergmann2000). Following Bianchi (Reference Bianchi2011) we assume
![]() $A_{FUV}=8.06 E(B-V)$
. The
$A_{FUV}=8.06 E(B-V)$
. The
![]() $E(B-V)$
values are obtained for positions of all the identified sources from https://irsa.ipac.caltech.edu/applications/DUST/. This resource provided the Schlegel et al. (Reference Schlegel, Finkbeiner and Davis1998) and Schlafly & Finkbeiner (Reference Schlafly and Finkbeiner2011) estimates for reddening excess, of which we employed the latter estimate of
$E(B-V)$
values are obtained for positions of all the identified sources from https://irsa.ipac.caltech.edu/applications/DUST/. This resource provided the Schlegel et al. (Reference Schlegel, Finkbeiner and Davis1998) and Schlafly & Finkbeiner (Reference Schlafly and Finkbeiner2011) estimates for reddening excess, of which we employed the latter estimate of
![]() $E(B-V)$
in this work. We however note that both estimates correlate very well for the sample studied in this work. The reddening excesses for these Coma cluster data are in the range
$E(B-V)$
in this work. We however note that both estimates correlate very well for the sample studied in this work. The reddening excesses for these Coma cluster data are in the range
![]() $0.0067 \leq E(B-V) \leq 0.0112$
with a median at
$0.0067 \leq E(B-V) \leq 0.0112$
with a median at
![]() $0.0090$
mag. The distribution of extinction-corrected fluxes and the corresponding FUV magnitude for all the UVIT sources are shown in Figure 3. This figure shows that our data spans almost three orders of magnitude in FUV flux, and a range of more than five magnitudes for the sources detected by the UVIT.
$0.0090$
mag. The distribution of extinction-corrected fluxes and the corresponding FUV magnitude for all the UVIT sources are shown in Figure 3. This figure shows that our data spans almost three orders of magnitude in FUV flux, and a range of more than five magnitudes for the sources detected by the UVIT.

Figure 3. The distribution of UVIT FUV flux corrected for the Milkyway extinction for all the 1308 sources analysed in this work. The top axis shows the AB magnitudes for the same.
2.2. Optical data
The SDSS photometric catalogue is complete to
![]() $r = 22.7$
mag.Footnote a The optical counterparts for 968/1308 UVIT sources were found in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS, data release 14) database, of which only 923 (
$r = 22.7$
mag.Footnote a The optical counterparts for 968/1308 UVIT sources were found in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS, data release 14) database, of which only 923 (
![]() ${\sim} 70$
%) fall within the SDSS completeness limit. We considered a maximum radius of
${\sim} 70$
%) fall within the SDSS completeness limit. We considered a maximum radius of
![]() $5^{\prime\prime}$
to find an optical counterpart for each UVIT source in our catalogue. Of these, 96.3% of the optical counterparts were found within
$5^{\prime\prime}$
to find an optical counterpart for each UVIT source in our catalogue. Of these, 96.3% of the optical counterparts were found within
![]() $3^{\prime\prime}$
of the UVIT source position.
$3^{\prime\prime}$
of the UVIT source position.
Amongst others, the SDSS photometric pipeline provides object type for most of the matched sources brighter than the magnitude completeness limit. Combining information from the SDSS and the NASA Extragalactic Database (NED)Footnote b we could identify 969/1308 objects: 114 stars, 852 galaxies and 3 quasi-stellar objects (QSO), respectively. However, only 957 of these sources meet the magnitude completeness limit for SDSS. We also note that the SDSS object type for some sources was modified based on visual inspection, spectroscopic information or additional data obtained from NED. Furthermore, spectroscopic redshifts for 95 sources were found in the SDSS database, while an additional 39 were obtained from NED. In Table 2 we show a sample of few rows from the full catalogue of 1308 UVIT sources detected in this image, the complete version of which is available online.
Table 2. The object ID, sky coordinates, UVIT flux and the uncertainty in the flux, object type (1: QSO; 3: galaxy; 6: star), r-band magnitude, plate, MJD and Fiber ID from SDSS, redshift and the source of redshift (0: Not available; 1: SDSS; 2: NED) for all the 1308 sources detected in our image. (A complete version of this table is available online here (Supplementary materials))


Figure 4. The distribution of 50% Petrosian radius as a function of extinction corrected r-band magnitude for the optical counterparts of our UVIT sources. The sources are separated into stars (grey asteriks), galaxies (red points) and quasars (black star) by using the SDSS classification. The Coma cluster galaxies are highlighted as blue triangles. The dot-dashed line represents the completeness limit for the SDSS photometric data.
In Figure 4, the Petrosian radius containing 50% of the total flux in the r-band (
![]() $R_{50}$
) is shown as a function of the extinction corrected r-band magnitude for all the optical counterparts, sub-classified into the Coma cluster galaxies, other galaxies, quasars and stars, respectively. The Coma cluster members have been identified assuming
$R_{50}$
) is shown as a function of the extinction corrected r-band magnitude for all the optical counterparts, sub-classified into the Coma cluster galaxies, other galaxies, quasars and stars, respectively. The Coma cluster members have been identified assuming
![]() $z_{Coma} = 0.023$
and velocity dispersion (
$z_{Coma} = 0.023$
and velocity dispersion (
![]() $\sigma_v$
) of
$\sigma_v$
) of
![]() $1000\ \mathrm{km\ s}^{-1}$
. These criteria yield 79 member galaxies within
$1000\ \mathrm{km\ s}^{-1}$
. These criteria yield 79 member galaxies within
![]() $\pm 3\sigma_v$
as members of the Coma cluster. All the other extended sources, with or without redshift, are addressed as ‘other galaxies’ henceforth, although it is possible that some of the fainter galaxies in this category might be members of the Coma cluster.
$\pm 3\sigma_v$
as members of the Coma cluster. All the other extended sources, with or without redshift, are addressed as ‘other galaxies’ henceforth, although it is possible that some of the fainter galaxies in this category might be members of the Coma cluster.
Figure 4 shows that most of the bright galaxies found in these UVIT data are members of the Coma cluster. These also happen to be the largest galaxies in our sample. Most of the stars brighter than
![]() $r \sim 20$
mag can be separated out from the galaxies in this plane. While one of the quasars coincides with stars, the second follows the galaxies, and the third one lies in the region occupied by the faint stars in this r-band magnitude-radius plane.
$r \sim 20$
mag can be separated out from the galaxies in this plane. While one of the quasars coincides with stars, the second follows the galaxies, and the third one lies in the region occupied by the faint stars in this r-band magnitude-radius plane.
It is also worth mentioning here that the three QSOs have
![]() $z = 0.383, 0.513$
and
$z = 0.383, 0.513$
and
![]() $2.315$
, respectively. While the last one has spectroscopic redshift available in the SDSS database, redshift for the other two were obtained from NED. The quasar B1257
$2.315$
, respectively. While the last one has spectroscopic redshift available in the SDSS database, redshift for the other two were obtained from NED. The quasar B1257
![]() $+$
280 (
$+$
280 (
![]() $z=2.315$
) shown in Figure 5 deserves a special mention, since this might be the highest redshift object observed by the UVIT to date. The multi-band optical image shows a blue star-like object, while the faint FUV emission at the edges show elongation in flux contours in the north-south direction. This QSO is known to be a Lyman
$z=2.315$
) shown in Figure 5 deserves a special mention, since this might be the highest redshift object observed by the UVIT to date. The multi-band optical image shows a blue star-like object, while the faint FUV emission at the edges show elongation in flux contours in the north-south direction. This QSO is known to be a Lyman
![]() $\alpha$
absorber (Garnett et al. Reference Garnett, Ho, Bird and Schneider2017).
$\alpha$
absorber (Garnett et al. Reference Garnett, Ho, Bird and Schneider2017).

Figure 5. The UVIT FUV (left) and FUV contours overlaid on the optical r-band image (right) of the quasar B1257
![]() $+$
280 (
$+$
280 (
![]() $z=2.315$
).
$z=2.315$
).
3. Properties of the detected FUV sources
The Coma field studied here has previously been observed with the Galex mission. So as a sanity check we compared our catalogue to the one created from Galex images. In order to do so, we made use of the processed images downloaded from the galexviewFootnote c page. The comparison images have an exposure time of 25656.55 s in NUV and 18620.45 s in the FUV band, respectively (Object ID: GI5_025001_COMA_0002). sextractor was used to identify the sources in the Galex images. We then searched for a Galex sources within
![]() $3^{\prime\prime}$
of each of the UVIT sources independently in the near and far UV catalogues. This resulted in 464 FUV and 599 NUV sources matched between the UVIT and Galex catalogues.
$3^{\prime\prime}$
of each of the UVIT sources independently in the near and far UV catalogues. This resulted in 464 FUV and 599 NUV sources matched between the UVIT and Galex catalogues.
The distributions of magnitudes of all the matched sources in the two GALEX wavebands are shown in Figure 6. Both stars and galaxies as identified in the previous section have well correlated FUV fluxes in the UVIT and the GALEX bands, albeit with the expected scatter which is a consequence of mismatched wavelength range covered by the three wavebands analysed here. We note that in the
![]() $FUV_{UVIT}$
–
$FUV_{UVIT}$
–
![]() $NUV_{Galex}$
plane, bright ‘stars’ are well separated from the galaxies. The best-fit least square relation between the UVIT and GALEX bands for these data as shown in Figure 6 are:
$NUV_{Galex}$
plane, bright ‘stars’ are well separated from the galaxies. The best-fit least square relation between the UVIT and GALEX bands for these data as shown in Figure 6 are:

Figure 6. The distribution of magnitude of GALEX NUV sources and (b) GALEX FUV sources plotted as a function of the FUV magnitude of the corresponding UVIT source, respectively. All magnitudes are corrected for extinction due to Milkyway. The red points denote galaxies, grey asterisks represent stars and QSOs are shown as stars, respectively. The dot-dashed line in both panels represents a perfect correlation, while the dashed lines represent the least square fit to the data along with
![]() $1\sigma$
deviation in it. Typical uncertainty along each axis is shown in the bottom right corner of the panels. This figure therefore shows that the FUV fluxes of the matched sources are consistent between the UVIT
$1\sigma$
deviation in it. Typical uncertainty along each axis is shown in the bottom right corner of the panels. This figure therefore shows that the FUV fluxes of the matched sources are consistent between the UVIT
![]() $\mathrm{BaF}_2$
band and both the wavebands of the GALEX mission. A marginal discrepancy of increasing magnitude in GALEX FUV, can be noticed towards the faint end, which is however well within
$\mathrm{BaF}_2$
band and both the wavebands of the GALEX mission. A marginal discrepancy of increasing magnitude in GALEX FUV, can be noticed towards the faint end, which is however well within
![]() ${\sim} 3\sigma$
for most of the sources.
${\sim} 3\sigma$
for most of the sources.
In Figure 6 we show that despite good general agreement between the UVIT FUV and GALEX bands, there are subtle discrepancies, particularly at the faint end. We note that the scatter is higher at the faint end in both the distributions. In fact, the standard deviation in the
![]() $FUV_{UVIT}$
–
$FUV_{UVIT}$
–
![]() $NUV_{Galex}$
correlation seems to be dictated by the faint end scatter. The correlation between
$NUV_{Galex}$
correlation seems to be dictated by the faint end scatter. The correlation between
![]() $FUV_{UVIT}$
and
$FUV_{UVIT}$
and
![]() $FUV_{Galex}$
is relatively better, but we observe a slight upturn in the distribution for galaxies fainter than
$FUV_{Galex}$
is relatively better, but we observe a slight upturn in the distribution for galaxies fainter than
![]() $FUV_{UVIT} \sim 22.6$
mag. The trend implies that these faint galaxies detected by both UVIT and Galex, are fainter in GALEX relative to UVIT. This might be a consequence of the poor resolution of GALEX relative to UVIT, but further investigation may be required if similar trends are observed in other UVIT fields as well. It should be noted, however, that the typical uncertainty in the GALEX bands is
$FUV_{UVIT} \sim 22.6$
mag. The trend implies that these faint galaxies detected by both UVIT and Galex, are fainter in GALEX relative to UVIT. This might be a consequence of the poor resolution of GALEX relative to UVIT, but further investigation may be required if similar trends are observed in other UVIT fields as well. It should be noted, however, that the typical uncertainty in the GALEX bands is
![]() ${\sim} 0.44$
and
${\sim} 0.44$
and
![]() $0.57$
mag in the FUV and NUV bands, respectively, which is an order of magnitude higher than the uncertainty of
$0.57$
mag in the FUV and NUV bands, respectively, which is an order of magnitude higher than the uncertainty of
![]() ${\sim} 0.03$
mag estimated for the UVIT
${\sim} 0.03$
mag estimated for the UVIT
![]() $\mathrm{BaF}_2$
band.
$\mathrm{BaF}_2$
band.
In Figure 7 we show the distribution of the UVIT sources in various optical, UV and composite colour-magnitude and colour-colour planes. Note that information in all wavebands is not available for all the sources, hence different number of sources are plotted in each of the four panels. The Coma cluster galaxies form a well defined sequence in the optical g-r vs r-band colour-magnitude plane (Figure 7(d)), but the other fainter galaxies show a larger scatter. On the other hand, all galaxies follow a continuous sequence in the plane mapped by the NUV-r colour and r-band magnitude (Figure 7(a)). It is interesting to note that most of the stars brighter than
![]() $r \sim 19$
mag span similar range of r-band magnitudes as the bright Coma cluster galaxies, yet have relatively bluer g-r, NUV-r and FUV-r colours.
$r \sim 19$
mag span similar range of r-band magnitudes as the bright Coma cluster galaxies, yet have relatively bluer g-r, NUV-r and FUV-r colours.

Figure 7. The colour-colour and colour–magnitude distributions for all UVIT sources along with their optical and GALEX counterparts, respectively in the (a)
![]() $NUV-r$
vs r-band magnitude, (b)
$NUV-r$
vs r-band magnitude, (b)
![]() $NUV-r$
vs
$NUV-r$
vs
![]() $FUV-r$
, (c)
$FUV-r$
, (c)
![]() $FUV-r$
vs
$FUV-r$
vs
![]() $g-r$
, and (d)
$g-r$
, and (d)
![]() $g-r$
vs r-band magnitude plane. The symbols are same as in Figure 4. The FUV magnitudes are from UVIT, while the NUV magnitudes are from the GALEX mission. Given the heterogeneous nature of the data plotted here, the number of data points plotted in each quadrant vary as mentioned in Section 2. The Coma cluster galaxies are distributed coherently in the brighter, redder region of the respective planes, while other galaxies are relatively fainter and bluer in comparison, with more scatter. It is notable that the other galaxies and stars are not easily distinguishable in all of these planes, particularly at the faint end with one exception. A handful of stars redder than
$g-r$
vs r-band magnitude plane. The symbols are same as in Figure 4. The FUV magnitudes are from UVIT, while the NUV magnitudes are from the GALEX mission. Given the heterogeneous nature of the data plotted here, the number of data points plotted in each quadrant vary as mentioned in Section 2. The Coma cluster galaxies are distributed coherently in the brighter, redder region of the respective planes, while other galaxies are relatively fainter and bluer in comparison, with more scatter. It is notable that the other galaxies and stars are not easily distinguishable in all of these planes, particularly at the faint end with one exception. A handful of stars redder than
![]() $NUV-r \sim 2$
mag and
$NUV-r \sim 2$
mag and
![]() $FUV-r \sim 5$
mag, are somewhat separated from galaxies (panels (a), (b) and (c)).
$FUV-r \sim 5$
mag, are somewhat separated from galaxies (panels (a), (b) and (c)).
The Coma cluster galaxies also follow a well defined sequence in the g-r vs FUV-r colour-colour plane (Figure 7(c)), and the NUV-r–FUV-r plane (Figure 7(b)), respectively. All other galaxies, although fainter than their Coma cluster counterparts, seem to follow the same correlation in the NUV-r vs FUV-r plane. Just like in panels (a) and (d), in the plane mapped by the NUV-r and FUV-r colours, a small subset of bright stars seems to follow a correlation just like the galaxies but have FUV-r colours redder by
![]() ${\sim} 2$
mag at fixed NUV-r colour, relative to the galaxies. As mentioned earlier, many of the objects at the faint end classified as stars by the SDSS photometric pipeline may be high-z quasars. Also, many of the ‘other’ galaxies falling in the same region of the colour-colour and colour-magnitude planes as the Coma cluster galaxies may also be member galaxies of the Coma cluster.
${\sim} 2$
mag at fixed NUV-r colour, relative to the galaxies. As mentioned earlier, many of the objects at the faint end classified as stars by the SDSS photometric pipeline may be high-z quasars. Also, many of the ‘other’ galaxies falling in the same region of the colour-colour and colour-magnitude planes as the Coma cluster galaxies may also be member galaxies of the Coma cluster.
In Figure 8 we show the distribution of various sources in the plane mapped by the UV colour and the r-band magnitude and the g-r colour, respectively. The difference in the r-band luminosity of the Coma cluster galaxies and other galaxies leads to a clear separation between the two sub-samples of galaxies in the r vs
![]() $FUV-NUV$
colour-magnitude plane. On the other hand, the Coma cluster galaxies form a tight sequence in the
$FUV-NUV$
colour-magnitude plane. On the other hand, the Coma cluster galaxies form a tight sequence in the
![]() $g-r$
vs
$g-r$
vs
![]() $FUV-NUV$
colour-colour plane (Figure 8(b)), an expected signature from the optical colour-magnitude diagram of clusters. We note however, that stars and quasars remain indistinguishable from galaxies in these planes.
$FUV-NUV$
colour-colour plane (Figure 8(b)), an expected signature from the optical colour-magnitude diagram of clusters. We note however, that stars and quasars remain indistinguishable from galaxies in these planes.

Figure 8. The distribution of all the UVIT sources having optical and GALEX counterparts in the (a) FUV-NUV vs r-band and (b) FUV-NUV vs g-r colour-colour plane, respectively. The symbols are same as in Figure 4. Most of the Coma cluster galaxies fall in well defined regions of the space dictated by their optical properties, while stars and quasars co-exist with the other, relatively fainter galaxies.
To summarise, this analysis shows that (i) the FUV flux from the UVIT
![]() $\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter data are well correlated with the GALEX bands, (ii) Coma cluster galaxies are much brighter, and hence well separated from the other galaxies in the image in almost all the colour-colour and colour-magnitude planes explored here, and (iii) stars and quasars have identical photometric properties as the other, relatively fainter galaxies.
$\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter data are well correlated with the GALEX bands, (ii) Coma cluster galaxies are much brighter, and hence well separated from the other galaxies in the image in almost all the colour-colour and colour-magnitude planes explored here, and (iii) stars and quasars have identical photometric properties as the other, relatively fainter galaxies.
4. FUV sources with unusual morphology
We found many galaxies with unconventional morphology in the UVIT FUV image by visualising the UVIT image simultaneously with the optical r-band image. Objects showing tails, rings or other features suggesting the impact of environment-related mechanism, and galaxies which showed morphology very different from their optical counterparts, were shortlisted and analysed further. The galaxies for which subsequent investigation showed that the ‘features’ were background objects, were then dropped, finally leaving a set of sixteen bright and seven faint galaxies with distorted morphology. Some of these galaxies have been subjects of other optical and ultraviolet studies in the literature (e.g. Yagi et al. Reference Yagi2010; Smith et al. Reference Smith2010), with most of them showing an ‘unusual’ morphology in the UV bands only. We describe each of them briefly below, incorporating relevant information from the literature where available. All the objects are listed in Table 3, and their UVIT FUV and optical r-band images are shown in Figures 9–15. The GMP identification in the first column of Table 3 is from Godwin et al. (Reference Godwin, Metcalfe and Peach1983). Redshift information is available only for the first sixteen bright galaxies with unusual FUV morphology in the Table. Where available, Table 3 also includes the stellar masses of galaxies from Mendel et al. (Reference Mendel, Simard, Palmer, Ellison and Patton2014) or the GSWLC, and HI-mass fraction estimated by applying artificial neural network on SDSS optical data (Teimoorinia, Ellison, & Patton Reference Teimoorinia, Ellison and Patton2017).
Table 3. The common name, sky coordinates and redshift for the objects with distorted morphology found in the FUV image. Where available, the last two columns show the stellar mass and the HI-to-stellar mass ratio of the objects. The last seven objects are optically faint galaxies without any redshift information.


Figure 9. This figure shows (left): the UVIT FUV image, and (right): the r-band optical image with FUV contours overlaid for (a) GMP 3016, (b) PGC 044679, and (c) GMP 2787, respectively from top to bottom. The contours are smoothed over 4 pixels and created such that the outermost contour is 2-3
![]() $\sigma$
above the typical background of the UVIT image. The arrow points towards the cluster centre. Images are oriented such that north is up and east is on the left of the image. These images evidently show the difference in morphology of the young, UV emitting stars and the generic distribution of other stellar populations in these galaxies. The impact of the cluster environment can also be noticed for galaxies which show UV emission away from the plane of the galaxy, often with no optical counterpart.
$\sigma$
above the typical background of the UVIT image. The arrow points towards the cluster centre. Images are oriented such that north is up and east is on the left of the image. These images evidently show the difference in morphology of the young, UV emitting stars and the generic distribution of other stellar populations in these galaxies. The impact of the cluster environment can also be noticed for galaxies which show UV emission away from the plane of the galaxy, often with no optical counterpart.

Figure 10. Same as Figure 9, but for (a) GMP 3523, (b) GMP 2910, and (c) NGC 4867.

Figure 11. Same as Figure 9, but for (a) NGC 4895, (b) GMP 2584, and (c) GMP 2559.

Figure 12. Same as Figure 9, but for (a) GMP 2347, (b) NGC 4907, and (c) GMP 2943 and GMP 2989.

Figure 13. Same as Figure 9, but for (a) GMP 3317, (b) GMP 3170, and (c) GMP 2956.

Figure 14. This figure shows the SDSS gri image of the galaxy GMP 2943 (left), and the same with UVIT FUV contours overlaid (right). Also, see Figure 12(c).

Figure 15. Same as Figure 9, but for (from top to bottom:) (a) GMP 2717, (b) Subaru ultra-diffuse galaxy, (c) Galaxy1, (d) GMP 2476, (e) GMP 2454, (f) GMP 2320 and (g) Galaxy2.
4.1. GMP 3016
This is an extremely blue, faint irregular galaxy as observed in the optical wavebands. Yagi et al. (Reference Yagi2010) have reported ‘fireball’ features, that is, extended H
![]() $\alpha$
emission following knots of blue stars (Yoshida et al. Reference Yoshida2008) from GMP 3016 (see the right panel of Figure 9(a)). On the other hand, Smith et al. (Reference Smith2010) found this to be a ‘less convincing case’ of a stripping galaxy in the combined NUV
$\alpha$
emission following knots of blue stars (Yoshida et al. Reference Yoshida2008) from GMP 3016 (see the right panel of Figure 9(a)). On the other hand, Smith et al. (Reference Smith2010) found this to be a ‘less convincing case’ of a stripping galaxy in the combined NUV
![]() $+$
FUV image obtained with Galex. Our UVIT image (Figure 9(a)) however, shows a linear structure in the northeastern part of the FUV image clearly extending towards GMP 3016. In FUV, this trail is detached from the galaxy and extends upto
$+$
FUV image obtained with Galex. Our UVIT image (Figure 9(a)) however, shows a linear structure in the northeastern part of the FUV image clearly extending towards GMP 3016. In FUV, this trail is detached from the galaxy and extends upto
![]() ${\sim} 26$
kpc in the northeast direction,Footnote d with the cluster centre
${\sim} 26$
kpc in the northeast direction,Footnote d with the cluster centre
![]() ${<} 200\, h^{-1}$
kpc away parallel to the direction of the alignment of knots. In our opinion, the morphology of the narrow structure extending in the northeast suggests that it is likely a part of GMP 3016, but without any optical counterpart.
${<} 200\, h^{-1}$
kpc away parallel to the direction of the alignment of knots. In our opinion, the morphology of the narrow structure extending in the northeast suggests that it is likely a part of GMP 3016, but without any optical counterpart.
4.2. PGC 044679
This is a barred S0 galaxy member of the Coma cluster (Lansbury, Lucey, & Smith Reference Lansbury, Lucey and Smith2014). The FUV image (Figure 9(b)) shows two discrete components, one centred at the galaxy’s nucleus and the other in the northeast. The nuclear component (C1 in Figure 9(b)) has an interesting morphology pointing in orthogonal directions, one of which points in the direction of the cluster centre which is at a distance of
![]() ${\sim} 256\, h^{-1}$
kpc from the galaxy. The second component C2, however, remains to be further investigated to confirm whether it also corresponds to PGC 044679, is a satellite galaxy or a random background object. Unlike GMP 3016, this is therefore one of our less convincing cases of multiple component UV emission. Table 3 shows that this galaxy is detected in HI (Table 3).
${\sim} 256\, h^{-1}$
kpc from the galaxy. The second component C2, however, remains to be further investigated to confirm whether it also corresponds to PGC 044679, is a satellite galaxy or a random background object. Unlike GMP 3016, this is therefore one of our less convincing cases of multiple component UV emission. Table 3 shows that this galaxy is detected in HI (Table 3).
4.3. GMP 2787
This is an irregular galaxy (
![]() $z=0.033;\ 9974\ \mathrm{km\ s}^{-1}$
), having radial velocity slightly above the maximum threshold considered here for selecting the members of the Coma cluster. It has a stellar mass of
$z=0.033;\ 9974\ \mathrm{km\ s}^{-1}$
), having radial velocity slightly above the maximum threshold considered here for selecting the members of the Coma cluster. It has a stellar mass of
![]() $9.39\,{\rm M}_\odot$
(Teimoorinia et al. Reference Teimoorinia, Ellison and Patton2017). This galaxy appears to be very faint in the Galex images. The UVIT image (Figure 9(c)) of this galaxy shows an irregular morphology, very different from the optical extent of the galaxy, and pointing in a direction away from the cluster centre which is
$9.39\,{\rm M}_\odot$
(Teimoorinia et al. Reference Teimoorinia, Ellison and Patton2017). This galaxy appears to be very faint in the Galex images. The UVIT image (Figure 9(c)) of this galaxy shows an irregular morphology, very different from the optical extent of the galaxy, and pointing in a direction away from the cluster centre which is
![]() ${\sim} 236\, h^{-1}$
kpc away.
${\sim} 236\, h^{-1}$
kpc away.
4.4. GMP 3523
This is a star-forming galaxy at
![]() $z=0.194$
with tail like features observed on the top and southwestern edge of the galaxy (Figure 10(a)). All the tail like features are invisible in the optical image, and may be tidal tail(s) of this galaxy, although this needs to be confirmed in further investigation. The southwestern extension was also seen in the Galex image (e.g. Donas, Milliard, & Laget Reference Donas, Milliard and Laget1995), but appeared as a fainter feature relative to the UVIT image.
$z=0.194$
with tail like features observed on the top and southwestern edge of the galaxy (Figure 10(a)). All the tail like features are invisible in the optical image, and may be tidal tail(s) of this galaxy, although this needs to be confirmed in further investigation. The southwestern extension was also seen in the Galex image (e.g. Donas, Milliard, & Laget Reference Donas, Milliard and Laget1995), but appeared as a fainter feature relative to the UVIT image.
4.5. GMP 2910
This is the most well studied of our sources with unusual FUV morphology. Several authors have reported extended emission associated with this post-starburst galaxy commonly known as D100 (
![]() $z=0.0177$
; Yagi et al. Reference Yagi, Komiyama, Yoshida, Furusawa, Kashikawa, Koyama and Okamura2007; Smith et al. Reference Smith2010; Yagi et al. Reference Yagi2010; Cramer et al. Reference Cramer, Kenney, Sun, Crowl, Yagi, Jáchym, Roediger and Waldron2019). This source was also reported as KUG
$z=0.0177$
; Yagi et al. Reference Yagi, Komiyama, Yoshida, Furusawa, Kashikawa, Koyama and Okamura2007; Smith et al. Reference Smith2010; Yagi et al. Reference Yagi2010; Cramer et al. Reference Cramer, Kenney, Sun, Crowl, Yagi, Jáchym, Roediger and Waldron2019). This source was also reported as KUG
![]() $1257+281$
in the Kiso Survey for UV-excess galaxies (Takase & Miyauchi-Isobe Reference Takase and Miyauchi-Isobe1993). The FUV emission observed in the UVIT image (Figure 10(b)) coincides well with the extended H
$1257+281$
in the Kiso Survey for UV-excess galaxies (Takase & Miyauchi-Isobe Reference Takase and Miyauchi-Isobe1993). The FUV emission observed in the UVIT image (Figure 10(b)) coincides well with the extended H
![]() $\alpha$
emission (Yagi et al. Reference Yagi, Komiyama, Yoshida, Furusawa, Kashikawa, Koyama and Okamura2007).
$\alpha$
emission (Yagi et al. Reference Yagi, Komiyama, Yoshida, Furusawa, Kashikawa, Koyama and Okamura2007).
GMP 2910 is rich in molecular (Jáchym et al. Reference Jáchym2017) and atomic gas (Teimoorinia et al. Reference Teimoorinia, Ellison and Patton2017), with a considerable HI-to-stellar mass fraction (
![]() ${>} 0.16$
; Table 3). The extended FUV emission points in the northeast direction almost perpendicular to the vector pointing in the direction of the cluster centre. The spectacular narrow tail observed with the Subaru telescope’s Suprime-Cam in the H
${>} 0.16$
; Table 3). The extended FUV emission points in the northeast direction almost perpendicular to the vector pointing in the direction of the cluster centre. The spectacular narrow tail observed with the Subaru telescope’s Suprime-Cam in the H
![]() $\alpha$
narrow band filter (see Figure 2 of Cramer et al. Reference Cramer, Kenney, Sun, Crowl, Yagi, Jáchym, Roediger and Waldron2019) is well aligned with the FUV feature observed with the UVIT.
$\alpha$
narrow band filter (see Figure 2 of Cramer et al. Reference Cramer, Kenney, Sun, Crowl, Yagi, Jáchym, Roediger and Waldron2019) is well aligned with the FUV feature observed with the UVIT.
This galaxy is only
![]() ${\sim} 240\, h^{-1}$
kpc away from the cluster centre, and hence likely a classic case of ram-pressure stripping. However, the narrow, linear structure emerging from the galaxy is difficult to explain via ram-pressure stripping alone. The other possibility is that the structure is formed by a dwarf galaxy or gas cloud which was disrupted due to ram-pressure stripping by the ICM, or tidal forces of GMP 2910 (Yagi et al. Reference Yagi, Komiyama, Yoshida, Furusawa, Kashikawa, Koyama and Okamura2007). In a recent study, Peluso et al. (Reference Peluso2022) explored the connection between active galactic nucleus (AGN) and ram-pressure stripping, in a sample of 115 ram-pressure stripped galaxies (also see, George et al. Reference George2019a). Peluso et al. (Reference Peluso2022) find that the incidence of AGN increases among ram-pressure stripped galaxies, relative to a stellar mass matched sample of cluster galaxies, thereby suggesting that GMP 2910, showing a Seyfert type 2 emission based on the emission-line diagnostic diagram (Baldwin, Phillips, & Terlevich Reference Baldwin, Phillips and Terlevich1981), may also harbour an AGN at its centre (see Table 4 of Peluso et al. Reference Peluso2022, also, Mahajan et al., Reference Mahajan, Haines and Raychaudhury2010).
${\sim} 240\, h^{-1}$
kpc away from the cluster centre, and hence likely a classic case of ram-pressure stripping. However, the narrow, linear structure emerging from the galaxy is difficult to explain via ram-pressure stripping alone. The other possibility is that the structure is formed by a dwarf galaxy or gas cloud which was disrupted due to ram-pressure stripping by the ICM, or tidal forces of GMP 2910 (Yagi et al. Reference Yagi, Komiyama, Yoshida, Furusawa, Kashikawa, Koyama and Okamura2007). In a recent study, Peluso et al. (Reference Peluso2022) explored the connection between active galactic nucleus (AGN) and ram-pressure stripping, in a sample of 115 ram-pressure stripped galaxies (also see, George et al. Reference George2019a). Peluso et al. (Reference Peluso2022) find that the incidence of AGN increases among ram-pressure stripped galaxies, relative to a stellar mass matched sample of cluster galaxies, thereby suggesting that GMP 2910, showing a Seyfert type 2 emission based on the emission-line diagnostic diagram (Baldwin, Phillips, & Terlevich Reference Baldwin, Phillips and Terlevich1981), may also harbour an AGN at its centre (see Table 4 of Peluso et al. Reference Peluso2022, also, Mahajan et al., Reference Mahajan, Haines and Raychaudhury2010).
4.6. NGC 4867
This is a typical S0 galaxy in the Coma cluster (
![]() $z=0.016$
), around 1.6 kpc (
$z=0.016$
), around 1.6 kpc (
![]() $5^{\prime\prime}$
) from the most dominant galaxy at the centre. NGC 4867 (seen as component C1 in Figure 10) shows FUV emission extending towards west and southeast, but invisible in the optical image. A weak feature also appears to extend towards another FUV source C2 towards the left, which has no optical counterpart. The western tail from C1 seem to be extending towards NGC 4864 (
$5^{\prime\prime}$
) from the most dominant galaxy at the centre. NGC 4867 (seen as component C1 in Figure 10) shows FUV emission extending towards west and southeast, but invisible in the optical image. A weak feature also appears to extend towards another FUV source C2 towards the left, which has no optical counterpart. The western tail from C1 seem to be extending towards NGC 4864 (
![]() $z=0.022$
; component C3), which is also a Coma cluster member, separated in redshift space by 1800 km s–1 from NGC 4867. Hence, it is possible that the two galaxies are gravitationally influencing each other. It is notable that the cluster centre lies at a distance of
$z=0.022$
; component C3), which is also a Coma cluster member, separated in redshift space by 1800 km s–1 from NGC 4867. Hence, it is possible that the two galaxies are gravitationally influencing each other. It is notable that the cluster centre lies at a distance of
![]() ${\sim} 200\, h^{-1}$
kpc eastward of this galaxy. The third galaxy (component C4) in the image panel is a background object at
${\sim} 200\, h^{-1}$
kpc eastward of this galaxy. The third galaxy (component C4) in the image panel is a background object at
![]() $z=0.283$
, but shows an interesting UV morphology.
$z=0.283$
, but shows an interesting UV morphology.
4.7. NGC 4895
NGC 4895 (
![]() $z=0.0283$
) comprises multiple components in the FUV (Figure 11(a)). While the dominant component (C1) in centred at the galaxy’s nucleus, the northwestern component C3 is a blue foreground star observed in the multi-band SDSS image. The relatively smaller, northeastern component C2 however, does not have an optical counterpart. The two extraplanar concentrations in southwest and southeast (C4 and C5, respectively) are likely background objects, with no optical counterparts available in the SDSS database. Hence, it will be interesting to explore the latter three in follow-up observations. We also note that the major axis of this galaxy is orthogonal to the direction of the cluster centre. Nisbet & Best (Reference Nisbet and Best2016) found this massive galaxy (log
$z=0.0283$
) comprises multiple components in the FUV (Figure 11(a)). While the dominant component (C1) in centred at the galaxy’s nucleus, the northwestern component C3 is a blue foreground star observed in the multi-band SDSS image. The relatively smaller, northeastern component C2 however, does not have an optical counterpart. The two extraplanar concentrations in southwest and southeast (C4 and C5, respectively) are likely background objects, with no optical counterparts available in the SDSS database. Hence, it will be interesting to explore the latter three in follow-up observations. We also note that the major axis of this galaxy is orthogonal to the direction of the cluster centre. Nisbet & Best (Reference Nisbet and Best2016) found this massive galaxy (log
![]() $M*/M_{\odot} = 11.21$
) to be hosting a low-ionisation nuclear emission-line region (LINER) type AGN.
$M*/M_{\odot} = 11.21$
) to be hosting a low-ionisation nuclear emission-line region (LINER) type AGN.
4.8. GMP 2584
This edge-on S0 galaxy in the Coma cluster, also known as PGC 044784, shows a central FUV emission reported here for the first time (Figure 11(b)). The FUV emission is tilted in the direction of the cluster centre towards northwest relative to the optical disk of the galaxy.
4.9. GMP 2559
Also known as PGC 044789 and IC4040, this is a well studied blue, Sd type spiral galaxy in the Coma cluster. It is known to be an HI-deficient galaxy, having asymmetric HI distribution, such that most of the HI gas lies in the south-eastern part of the galaxy, while the northwestern part appears depleted (Bravo-Alfaro et al. Reference Bravo-Alfaro, Cayatte, van Gorkom and Balkowski2000). The major axis of this galaxy is almost orthogonal to the cluster centre. GMP 2559 exhibits an HI tail extending towards south-east (Miller, Hornschemeier, & Mobasher Reference Miller, Hornschemeier and Mobasher2009; Chen et al. Reference Chen2020), almost coincident with the extraplanar FUV emission as shown in Figure 11(c). It is also noteworthy that the three ‘knots’ of star-forming region seen extending towards southwest in the UVIT image are also observed in the H
![]() $\alpha$
emission (see Figure 2 of Chen et al. Reference Chen2020), but not in the radio continuum.
$\alpha$
emission (see Figure 2 of Chen et al. Reference Chen2020), but not in the radio continuum.
4.10. GMP 2347
This early-type spiral galaxy in the Coma cluster shows a central FUV component (C1), along with an off-centre component C2. The latter might be a dwarf galaxy merging with GMP 2347. This galaxy is
![]() ${\sim} 0.45$
Mpc away from the cluster centre. Another faint galaxy GMP 2333 (component C3) can also be seen in the northeast direction relative to the galaxy in Figure 12(a). In the absence of redshift information, however, it is not possible to test if this faint blue galaxy is interacting with GMP 2347 or is a member of the Coma cluster.
${\sim} 0.45$
Mpc away from the cluster centre. Another faint galaxy GMP 2333 (component C3) can also be seen in the northeast direction relative to the galaxy in Figure 12(a). In the absence of redshift information, however, it is not possible to test if this faint blue galaxy is interacting with GMP 2347 or is a member of the Coma cluster.
4.11. NGC 4907
This face-on barred spiral galaxy in the Coma cluster, also known as GMP 2441, shows distinct FUV emission, unlike the symmetric spiral arms observed in the optical waveband. This is a LINER galaxy (Mahajan et al. Reference Mahajan, Haines and Raychaudhury2010; Toba et al. Reference Toba2014). Figure 12(b) shows that unlike the optical, the UVIT FUV image shows clear asymmetry between the northeast and southwestern regions of the galaxy. It is possible that gas is being pushed to the northeastern face as galaxy moves towards the cluster centre
![]() ${\sim} 0.44$
Mpc away. Another interesting feature is the C-shaped hole seen in the FUV emission surrounding the bar at the centre. This cavity may be a consequence of the bar suppressing star formation in the centre just like in Messier 95 (George et al. Reference George, Joseph, Mondal, Subramanian, Subramaniam and Paul2019b).
${\sim} 0.44$
Mpc away. Another interesting feature is the C-shaped hole seen in the FUV emission surrounding the bar at the centre. This cavity may be a consequence of the bar suppressing star formation in the centre just like in Messier 95 (George et al. Reference George, Joseph, Mondal, Subramanian, Subramaniam and Paul2019b).
4.12. GMP 2943 and 2989
GMP 2943 (C1 in Figure 12(c)) is a distorted spiral galaxy in the Coma cluster, whose optically-red nuclear region is observed below the blue spiral arms which take on a spider-like morphology in the optical image as shown in Figure 14. However, in the FUV image this galaxy appears to be a face-on spiral, much unlike its optical facade.
GMP 2989, which is also a Coma cluster member, is also seen alongside GMP 2943 in the image (Figure 12(c)) as C2. This spiral galaxy has its major axis pointed along the vector pointing in the direction of the cluster centre. GMP 2943 and 2989 are
![]() ${\sim} 1380\ \mathrm{km\ s}^{-1}$
away in redshift, hence unlikely to be interacting with each other, but within
${\sim} 1380\ \mathrm{km\ s}^{-1}$
away in redshift, hence unlikely to be interacting with each other, but within
![]() ${\sim} 0.45$
Mpc from the cluster centre. GMP 2989 is also the only bonafide AGN host galaxy (see Figure 19) amongst the galaxies with unusual FUV morphology discussed in this section.
${\sim} 0.45$
Mpc from the cluster centre. GMP 2989 is also the only bonafide AGN host galaxy (see Figure 19) amongst the galaxies with unusual FUV morphology discussed in this section.
4.13. GMP 3317
GMP 3317 appears as a small, red, faint spheroid in the optical image, very close to a bright star. Not much is known about this distant galaxy (
![]() $z=0.2748$
). However, the FUV image inevitably shows that this is likely a much larger galaxy, only whose nucleus is observed in the optical images. Interestingly though, there appears to be a hole in the FUV emission surrounding the nuclear region as seen in Figure 13(a).
$z=0.2748$
). However, the FUV image inevitably shows that this is likely a much larger galaxy, only whose nucleus is observed in the optical images. Interestingly though, there appears to be a hole in the FUV emission surrounding the nuclear region as seen in Figure 13(a).
4.14. GMP 3170
This Coma cluster galaxy is only
![]() ${\sim} 0.04$
Mpc from the cluster centre, and hence very likely experiencing the hostile environmental mechanisms. Besides the central component C1 in Figure 13(b), one can clearly see a tail of FUV blobs (components C2, C3 and C4) in the direction perpendicular to the vector pointing towards the cluster centre. Although follow-up spectroscopic observations are required to confirm our speculation that the blobs are connected to GMP 3170.
${\sim} 0.04$
Mpc from the cluster centre, and hence very likely experiencing the hostile environmental mechanisms. Besides the central component C1 in Figure 13(b), one can clearly see a tail of FUV blobs (components C2, C3 and C4) in the direction perpendicular to the vector pointing towards the cluster centre. Although follow-up spectroscopic observations are required to confirm our speculation that the blobs are connected to GMP 3170.
4.15. GMP 2956
This S0 Coma cluster galaxy lies at a distance of
![]() ${\sim} 0.31$
Mpc from the cluster centre. The FUV emission appears to be divided into at least two components: C1 is centred at the core of the galaxy, while the component C2 does not show any obvious optical counterpart. C2 also appears to be tilting in the northeast direction away from the direction of the cluster centre.
${\sim} 0.31$
Mpc from the cluster centre. The FUV emission appears to be divided into at least two components: C1 is centred at the core of the galaxy, while the component C2 does not show any obvious optical counterpart. C2 also appears to be tilting in the northeast direction away from the direction of the cluster centre.
4.16. Optically-faint candidates
Besides the above mentioned galaxies, we also detected a few optically faint galaxies for which redshift information is not available, but their FUV morphology is markedly different from the optical image. These galaxies are listed at the bottom of Table 3, shown in Figure 15, and are briefly described below.
GMP 2717: This faint irregular galaxy shows an extended emission pointing opposite to the cluster centre on the southwestern side of the image.
Subaru-UDG: This ultra-diffuse galaxy (UDG) was first reported by Yagi et al. (Reference Yagi, Koda, Komiyama and Yamanoi2016) in their Subaru imaging survey of UDGs in the Coma cluster region. The FUV extent of the galaxy is evidently larger than its optical size.
Galaxy 1: This is also an irregular low-surface brightness galaxy, which is much larger in FUV relative to the optical extent.
GMP 2476: This is component C1 in Figure 15(d), and like other faint dwarf galaxies, appears to be much smaller in the optical image. Also seen in the field GMP 2457 which shows nuclear FUV emission (component C2) and an off-centre component C3. The entire system is aligned normal to the vector pointing in the direction of the cluster centre.
GMP 2454: This faint dwarf galaxy appears as a small, red spheroid in the multi-band SDSS data, but shows a distinct double-object morphology in the FUV image.
GMP 2320: Only the nuclear region of this dwarf galaxy seems to be observable in the optical image, while the larger extent is apparent in the FUV data. The point source in the southeastern corner may be a star unrelated to the galaxy.
Galaxy 2: This dwarf galaxy shows a very interesting morphology in the FUV image, but interestingly appears as two separate faint spheroidal objects in the optical data. A distinct tail of FUV emitting blobs can also be observed extending towards southwest of the field.
In summary, at least 13 of the 23 galaxies discussed in this section are Coma cluster members likely to be experiencing ram-pressure stripping. Although gravitational influence of the neighbouring galaxies may also have contributed to their unusual FUV morphology, it is worth noting that all of them are
![]() ${\lesssim}0.5\, h^{-1}$
Mpc of the centre of the Coma cluster. The seven low-surface brightness dwarf galaxies will be explored further in future work.
${\lesssim}0.5\, h^{-1}$
Mpc of the centre of the Coma cluster. The seven low-surface brightness dwarf galaxies will be explored further in future work.
5. Discussion
The aim of this paper is to analyse the sources detected in our deep FUV UVIT data for the central region of the Coma cluster. In order to do so, we have employed the NUV and FUV data from the GALEX mission, and optical photometric and spectroscopic data from the SDSS as well. We have presented various statistical properties of the sources detected in our data, classifying them into Coma cluster members, other galaxies, stars and quasars, respectively, where possible. In the following, we compare our data and findings with the existing literature, and further discuss the properties of the galaxies having unusual morphology in the FUV band.
5.1. Phase space distribution in Coma cluster
The phase space diagram mapped by the distance of a galaxy to the cluster centre normalised by
![]() $r_{200}$
Footnote e and the line-of-sight velocity of the galaxy scaled by the velocity dispersionFootnote f is shown in Figure 16. This figure shows that most of the Coma cluster galaxies having distorted UV morphologies are far away from the cluster centre, in spatial as well as velocity space. This suggests that these galaxies have recently entered the cluster, and are experiencing the impact of the intra-cluster medium (ICM) for the first time.
$r_{200}$
Footnote e and the line-of-sight velocity of the galaxy scaled by the velocity dispersionFootnote f is shown in Figure 16. This figure shows that most of the Coma cluster galaxies having distorted UV morphologies are far away from the cluster centre, in spatial as well as velocity space. This suggests that these galaxies have recently entered the cluster, and are experiencing the impact of the intra-cluster medium (ICM) for the first time.

Figure 16. This figure shows the distribution of all galaxies (grey asterisks) and those with distorted UV morphology (blue points) in the phase space around the Coma cluster centre. It is evident that most of the UV galaxies lie away from the cluster core in spatial as well as velocity space.

Figure 17. This figure shows the distribution of (a) log SFR, (b) sSFR, (c) log
![]() $M^*$
and (d)
$M^*$
and (d)
![]() $A_{FUV}$
for the galaxies matched to our UVIT sources in the GSWLC database. The solid black lines are for all the sources, while the dotted blue line represents the Coma cluster members, respectively.
$A_{FUV}$
for the galaxies matched to our UVIT sources in the GSWLC database. The solid black lines are for all the sources, while the dotted blue line represents the Coma cluster members, respectively.
5.2. Spectroscopic properties of UVIT sources
We found 88 galaxies from our UVIT sample in the GALEX-SDSS-WISE Legacy catalogue (GSWLC henceforth; Salim et al. Reference Salim2016), 79 of which are members of the Coma cluster. The GSWLC provides estimates of physical properties for
![]() ${\sim} 700000$
galaxies in the Galex footprint, also observed by the SDSS. The physical properties of galaxies are obtained by fitting the UV and optical spectral energy distribution following a Bayesian methodology. In Figure 17 we show the distributions of SFR, stellar mass (
${\sim} 700000$
galaxies in the Galex footprint, also observed by the SDSS. The physical properties of galaxies are obtained by fitting the UV and optical spectral energy distribution following a Bayesian methodology. In Figure 17 we show the distributions of SFR, stellar mass (
![]() $M^*$
), SFR/
$M^*$
), SFR/
![]() $M^*$
and extinction in the FUV band (
$M^*$
and extinction in the FUV band (
![]() $A_{FUV}$
), for all the matched galaxies and the Coma cluster members, respectively.
$A_{FUV}$
), for all the matched galaxies and the Coma cluster members, respectively.
In Figure 18 we show the SFR of the matched GSWLC galaxies as a function of their stellar mass. It is well known that the SFR of galaxies correlate well with their stellar mass, such that more massive galaxies have higher SFR relative to their lower mass counterparts. In a recent work, Roberts & Parker (Reference Roberts and Parker2020) have used a Bayesian-based regression approach on the SDSS data release 12 data to find the main sequence relationship for star-forming field galaxies as
![]() $\rm{log\,SFR} = 0.55\times {\rm log}\,M^*-5.7$
. This relationFootnote g is shown for reference as a dotted line in Figure 18, along with the UVIT galaxies, and galaxies with unusual FUV morphology found in the GSWLC catalogue. Most of our UVIT detected galaxies are found in the region occupied by the passive galaxies (log sSFR
$\rm{log\,SFR} = 0.55\times {\rm log}\,M^*-5.7$
. This relationFootnote g is shown for reference as a dotted line in Figure 18, along with the UVIT galaxies, and galaxies with unusual FUV morphology found in the GSWLC catalogue. Most of our UVIT detected galaxies are found in the region occupied by the passive galaxies (log sSFR
![]() $< {-}11$
yr-1; where, sSFR
$< {-}11$
yr-1; where, sSFR
![]() $\equiv$
SFR/
$\equiv$
SFR/
![]() $M^*$
) in the SFR-
$M^*$
) in the SFR-
![]() $M^*$
space, evidently showing that star formation activity is suppressed in the cluster environment, even for UV-bright galaxies. We also note that nine of the twelve galaxies with unusual FUV morphology are found below the field main sequence relation, in the region occupied by passive galaxies in the sample of Roberts & Parker (Reference Roberts and Parker2020). These authors however, found their ram-pressure stripping candidates to lie above the main sequence, where only three of our distorted galaxies make an appearance (Roberts & Parker Reference Roberts and Parker2020, see their Figure 7). This analysis suggests that beside ram-pressure stripping galaxies, unusual FUV morphology may be found among transitional galaxy populations. We also note that the low-surface brightness dwarf galaxies do not make an appearance on this plot due to lack of spectroscopic data.
$M^*$
space, evidently showing that star formation activity is suppressed in the cluster environment, even for UV-bright galaxies. We also note that nine of the twelve galaxies with unusual FUV morphology are found below the field main sequence relation, in the region occupied by passive galaxies in the sample of Roberts & Parker (Reference Roberts and Parker2020). These authors however, found their ram-pressure stripping candidates to lie above the main sequence, where only three of our distorted galaxies make an appearance (Roberts & Parker Reference Roberts and Parker2020, see their Figure 7). This analysis suggests that beside ram-pressure stripping galaxies, unusual FUV morphology may be found among transitional galaxy populations. We also note that the low-surface brightness dwarf galaxies do not make an appearance on this plot due to lack of spectroscopic data.

Figure 18. This figure shows the distribution of all UVIT detected galaxies found in the GSWLC catalogue (black points), and Coma cluster galaxies with unusual morphology (blue asterisks) in the stellar mass–SFR space. The dot-dashed line represents the main sequence of star-forming field galaxies (Roberts & Parker Reference Roberts and Parker2020). While three distorted galaxies lie
![]() ${\lesssim}0.5$
dex away from the main sequence, in the region where ram-pressure stripping candidates are expected to lie (see Figure 7 of Roberts & Parker Reference Roberts and Parker2020), majority of the galaxies with unusual morphology populate the region of this space expected to be inhabited by the red sequence and normal star-forming galaxies of the Coma cluster.
${\lesssim}0.5$
dex away from the main sequence, in the region where ram-pressure stripping candidates are expected to lie (see Figure 7 of Roberts & Parker Reference Roberts and Parker2020), majority of the galaxies with unusual morphology populate the region of this space expected to be inhabited by the red sequence and normal star-forming galaxies of the Coma cluster.

Figure 19. This figure shows the distribution of 48 UVIT detected galaxies found in the GSWLC catalogue (grey asterisks), and those with distorted morphology (blue points) in the BPT plane. The solid and dot-dashed lines mark the limiting criteria to distinguish between star-forming and AGN galaxies, respectively. The galaxies inhabiting the region between these two lines are known as composites, that is, part of their emission comes from an AGN-like component. We note that 18 and 17 galaxies respectively classify as star-forming and composites, while the remaining 13 as AGN. While amongst the galaxies with distorted UV morphology, five are star-forming, two are composite and one is an AGN.
Recently, Chen et al. (Reference Chen2020) presented high spatial resolution HI and deep 1.4GHz continuum data for 20 galaxies which are being ram-pressure stripped (RPS) in the Coma cluster. Three of these galaxies (GMP 2910, GMP 2559 and GMP 3016) are also part of our UVIT data. While GMP 2910 and GMP 2559 exhibit RPS tails matching their H
![]() $\alpha$
observations (Smith et al. Reference Smith2010; Yagi et al. Reference Yagi2010), GMP 3016 does not show RPS tails in the radio continuum.
$\alpha$
observations (Smith et al. Reference Smith2010; Yagi et al. Reference Yagi2010), GMP 3016 does not show RPS tails in the radio continuum.
There are 48 galaxies matched with the GSWLC, and having good signal-to-noise in all four emission lines (H
![]() $\alpha$
, [NII], [OIII] and H
$\alpha$
, [NII], [OIII] and H
![]() $\beta$
) in the SDSS database, which allows us to distinguish the active galactic nuclei (AGN) from the star-forming galaxies using the Baldwin et al. (Reference Baldwin, Phillips and Terlevich1981) criteria. The Baldwin, Phillip, Terlevich, popularly known as the BPT diagram is shown in Figure 19, with the galaxies with distorted UV morphology highlighted where possible. This space can be further divided into the regions occupied by star-forming, AGN and composites (i.e. galaxies with a weak AGN-like emission component) using the well used criteria put forward by Kauffmann et al. (Reference Kauffmann2003) and Kewley et al. (Reference Kewley, Dopita, Sutherland, Heisler and Trevena2001). As shown in Figure 19, we find that 18 UVIT sources with optical spectra are star-forming galaxies, 17 are composites and the remaining 13 are AGN host galaxies. Amongst the galaxies with unusual UV morphology, five are star-forming galaxies, two are found in the region occupied by the composite galaxies, and one is an AGN. Since star-forming galaxies are in general comparable in number to the composite galaxies, it would be interesting to explore the FUV emission in AGN host galaxies for a similar, larger sample in future.
$\beta$
) in the SDSS database, which allows us to distinguish the active galactic nuclei (AGN) from the star-forming galaxies using the Baldwin et al. (Reference Baldwin, Phillips and Terlevich1981) criteria. The Baldwin, Phillip, Terlevich, popularly known as the BPT diagram is shown in Figure 19, with the galaxies with distorted UV morphology highlighted where possible. This space can be further divided into the regions occupied by star-forming, AGN and composites (i.e. galaxies with a weak AGN-like emission component) using the well used criteria put forward by Kauffmann et al. (Reference Kauffmann2003) and Kewley et al. (Reference Kewley, Dopita, Sutherland, Heisler and Trevena2001). As shown in Figure 19, we find that 18 UVIT sources with optical spectra are star-forming galaxies, 17 are composites and the remaining 13 are AGN host galaxies. Amongst the galaxies with unusual UV morphology, five are star-forming galaxies, two are found in the region occupied by the composite galaxies, and one is an AGN. Since star-forming galaxies are in general comparable in number to the composite galaxies, it would be interesting to explore the FUV emission in AGN host galaxies for a similar, larger sample in future.
We conclude this discussion by summarising some of the limitations of the data analysed in this paper. Our UVIT data are limited to the FUV band only. The NUV band was not operated due to the presence of bright point sources in the field. Instead, we have used the NUV data from GALEX. The large difference in the resolution and the sensitivity of the two instruments, however, made a comparison of the FUV and NUV emission from the galaxies difficult. We wish to point out that since this is the first time that this field has been observed and analysed to such a depth in the FUV waveband, many interesting sources detected in the UVIT field lack redshift information, and require follow-up optical observations to throw more light on their origin and properties.
6. Summary
In this paper, we have examined a deep FUV image of the central region of the Coma cluster, observed by the UVIT on-board the Indian multi-wavelength satellite mission AstroSat. For the sources detected by both missions, we find a good correlation between the flux derived from the UVIT
![]() $\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter and the two GALEX wavebands. The UVIT fluxes of the detected sources (galaxies, stars and quasars) span two orders of magnitude in flux. We find that most of the galaxies brighter than
$\mathrm{BaF}_2$
filter and the two GALEX wavebands. The UVIT fluxes of the detected sources (galaxies, stars and quasars) span two orders of magnitude in flux. We find that most of the galaxies brighter than
![]() $r \sim 17$
mag are members of the Coma cluster, and occupy the bright end of the distributions in all colour-magnitude and, red end in the colour-colour space, respectively. Amongst others, we have also detected three quasars, one of which at
$r \sim 17$
mag are members of the Coma cluster, and occupy the bright end of the distributions in all colour-magnitude and, red end in the colour-colour space, respectively. Amongst others, we have also detected three quasars, one of which at
![]() $z=2.315$
is likely the farthest object observed by the UVIT so far.
$z=2.315$
is likely the farthest object observed by the UVIT so far.
Furthermore, we investigated sources with unusual FUV morphology, twenty three of which are discussed in detail here. Amongst others, we have identified several new candidate galaxies having unusual FUV morphology, many of which could be members of the Coma cluster. New, spectroscopic data are however needed to confirm this hypothesis. Our analysis indicates that distorted FUV sources may have recently entered the Coma cluster, and hence undergoing stripping events under the influence of the cluster-related environmental mechanisms. While five of these galaxies could be classified as star-forming on the basis of their emission line properties, two are found to be composites and one is an AGN.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study of a galaxy cluster field being carried out with the UVIT data. Hence, despite several limitations mentioned in the previous section, this work provides an idea of the finesse with which UVIT has captured the features of nearby extra-galactic objects, and a flavour of the problems which, together with the multi-band archival data may be addressed using the UVIT. In order to facilitate this, we have also provided detailed information for data handling and reduction for fellow UVIT users who intend to work with similar data.
Supplementary material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/pasa.2022.45.
Acknowledgements
S. Mahajan was funded by the INSPIRE Faculty award (DST/INSPIRE/04/2015/002311) and the SERB Research Scientist (SRS) award (SB-SRS/2020-21/56/PS), Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India. K. P. Singh thanks the Indian National Science Academy for support under the INSA Senior Scientist Programme. Authors are very grateful to Prof. S. Tandon for his valuable comments on earlier versions of this manuscript. We are very grateful to the anonymous reviewer for their constructive critique which helped in improving this manuscript.
This publication uses data from the AstroSat mission of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), archived at the ISSDC. UVIT project is a result of collaboration between IIA (Bengaluru), IUCAA (Pune), TIFR (Mumbai), several centres of ISRO, and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). This research has made use of the NASA/IPAC Infrared Science Archive, which is funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and operated by the California Institute of Technology. The topcat software (Taylor Reference Taylor, Shopbell, Britton and Ebert2005) was used for some of the analysis presented in this paper.