No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Automatic detection of cataclysmic variables from SDSS images
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 June 2023
Abstract
Investigating rare and new objects have always been an important direction in astronomy. Cataclysmic variables (CVs) are ideal and natural celestial bodies for studying the accretion process of semi-detached binaries with accretion processes. However, the sample size of CVs must increase because a lager gap exists between the observational and the theoretical expanding CVs. Astronomy has entered the big data era and can provide massive images containing CV candidates. CVs as a type of faint celestial objects, are highly challenging to be identified directly from images using automatic manners. Deep learning has rapidly developed in intelligent image processing and has been widely applied in some astronomical fields with excellent detection results. YOLOX, as the latest YOLO framework, is advantageous in detecting small and dark targets. This work proposes an improved YOLOX-based framework according to the characteristics of CVs and Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) photometric images to train and verify the model to realise CV detection. We use the Convolutional Block Attention Module to increase the number of output features with the feature extraction network and adjust the feature fusion network to obtain fused features. Accordingly, the loss function is modified. Experimental results demonstrate that the improved model produces satisfactory results, with average accuracy (mean average Precision at 0.5) of 92.0%, Precision of 92.9%, Recall of 94.3%, and 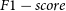 $F1-score$ of 93.6% on the test set. The proposed method can efficiently achieve the identification of CVs in test samples and search for CV candidates in unlabeled images. The image data vastly outnumber the spectra in the SDSS-released data. With supplementary follow-up observations or spectra, the proposed model can help astronomers in seeking and detecting CVs in a new manner to ensure that a more extensive CV catalog can be built. The proposed model may also be applied to the detection of other kinds of celestial objects.
$F1-score$ of 93.6% on the test set. The proposed method can efficiently achieve the identification of CVs in test samples and search for CV candidates in unlabeled images. The image data vastly outnumber the spectra in the SDSS-released data. With supplementary follow-up observations or spectra, the proposed model can help astronomers in seeking and detecting CVs in a new manner to ensure that a more extensive CV catalog can be built. The proposed model may also be applied to the detection of other kinds of celestial objects.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2023. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the Astronomical Society of Australia



