No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 December 2024
We present a comprehensive analysis of simultaneous, long-term observations of blazar S5 0716+714, covering optical/UV, X-ray, and 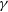 $\gamma$-ray wavelengths. All available observations of the source by Swift-UVOT/XRT and Fermi-LAT till January 2023 were used, and the spectra were fitted using power-law/log-parabola functions. A detailed correlation study between the best-fit parameters were performed, and our results suggest that the spectral changes observed during high flux states could be associated with the spectral energy distribution shifting towards the blue end. The flux distribution predominantly shows a log-normal/double log-normal behaviour, whereas the index distribution indicates a Gaussian or double Gaussian nature. As a Gaussian variation in the index of a power-law spectrum will result in a log-normal variation in the flux, the observed log-normal variability in blazars may be associated with Gaussian variation in the spectral indices. The observed normal/log-normal variations in indices/fluxes can again be interpreted through bluer when brighter behaviour of the source. Furthermore, the broadband SED during two distinct flux states can be successfully fitted by considering synchrotron, synchrotron self-Compton, and external Compton emission processes. The flux enhancement of the source is predominantly associated with an increase in the bulk Lorentz factor. Additionally, we find that the model curves corresponding to variations in the Lorentz factor have the potential to explain the observed correlations between the spectral parameters. Our study thereby concludes that the spectral variations of blazar S5 0716+714 are primarily associated with changes in the bulk Lorentz factor of the jet.
$\gamma$-ray wavelengths. All available observations of the source by Swift-UVOT/XRT and Fermi-LAT till January 2023 were used, and the spectra were fitted using power-law/log-parabola functions. A detailed correlation study between the best-fit parameters were performed, and our results suggest that the spectral changes observed during high flux states could be associated with the spectral energy distribution shifting towards the blue end. The flux distribution predominantly shows a log-normal/double log-normal behaviour, whereas the index distribution indicates a Gaussian or double Gaussian nature. As a Gaussian variation in the index of a power-law spectrum will result in a log-normal variation in the flux, the observed log-normal variability in blazars may be associated with Gaussian variation in the spectral indices. The observed normal/log-normal variations in indices/fluxes can again be interpreted through bluer when brighter behaviour of the source. Furthermore, the broadband SED during two distinct flux states can be successfully fitted by considering synchrotron, synchrotron self-Compton, and external Compton emission processes. The flux enhancement of the source is predominantly associated with an increase in the bulk Lorentz factor. Additionally, we find that the model curves corresponding to variations in the Lorentz factor have the potential to explain the observed correlations between the spectral parameters. Our study thereby concludes that the spectral variations of blazar S5 0716+714 are primarily associated with changes in the bulk Lorentz factor of the jet.