No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Theoretical Entities in Statistical Explanation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 February 2022
Extract
The ideas in this paper are based on an analysis of statistical explanation that uses the information transmitted by a theory. Consider a theory that specifies a probability distribution on the events of some domain, where for purposes of analysis we divide the variables that describe the domain into two sets: [M], a set of variables whose values are to be explained, and [S], a set of variables whose values are used to explain the values of the variables in [M]. The information transmitted by the theory is
(1)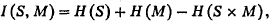
where H(S) and H(M) are the uncertainties of the events in [S] and [M], respectively, and H(S x M) is the uncertainty of the joint events.
To illustrate this idea, consider the problem of explaining medical symptoms such as fever, coughing, skin rash and abdominal pain.
- Type
- Symposium: Theoretical Entities in Statistical Explanation
- Information
- PSA: Proceedings of the Biennial Meeting of the Philosophy of Science Association , Volume 1970 , 1970 , pp. 3 - 26
- Copyright
- Copyright © Philosophy of Science Association 1970


