No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Using machine learning to investigate the populations of dusty evolved stars in various metallicities
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 August 2024
Abstract
Mass loss is a key property to understand stellar evolution and in particular for low-metallicity environments. Our knowledge has improved dramatically over the last decades both for single and binary evolutionary models. However, episodic mass loss although definitely present observationally, is not included in the models, while its role is currently undetermined. A major hindrance is the lack of large enough samples of classified stars. We attempted to address this by applying an ensemble machine-learning approach using color indices (from IR/Spitzer and optical/Pan-STARRS photometry) as features and combining the probabilities from three different algorithms. We trained on M31 and M33 sources with known spectral classification, which we grouped into Blue/Yellow/Red/B[e] Supergiants, Luminous Blue Variables, classical Wolf-Rayet and background galaxies/AGNs. We then applied the classifier to about one million Spitzer point sources from 25 nearby galaxies, spanning a range of metallicites (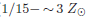 ). Equipped with spectral classifications we investigated the occurrence of these populations with metallicity.
). Equipped with spectral classifications we investigated the occurrence of these populations with metallicity.
Keywords
- Type
- Contributed Paper
- Information
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union , Volume 18 , Symposium S361: Massive Stars Near and Far , May 2022 , pp. 454 - 459
- Creative Commons
- This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution licence (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted re-use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of International Astronomical Union
Footnotes
contact: [email protected]



