No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Photometric Structure and Star Formation in Blue Compact Dwarf Galaxies
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 August 2006
Extract
The star-formation history and chemodynamical evolution of Blue Compact Dwarf (BCD) galaxies are central issues in dwarf galaxy research. In spite of being old in their vast majority, BCDs resemble in many aspects unevolved low-mass galaxies in the early universe. They are gas-rich (Hi mass fraction of typically > 30%) and metal-deficient (7.1 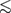 12+log(O/H)
12+log(O/H) 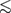 8.3) extragalactic systems, undergoing intense star-forming (SF) activity within an underlying low-surface brightness (LSB) host galaxy.
8.3) extragalactic systems, undergoing intense star-forming (SF) activity within an underlying low-surface brightness (LSB) host galaxy.
- Type
- Contributed Papers
- Information
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union , Volume 2 , Symposium S235: Galaxy Evolution Across the Hubble Time , August 2006 , pp. 327
- Copyright
- Copyright © International Astronomical Union 2007


