Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 January 2023
Photoelectric effect of dust grains by UV radiation is an important process for disk heating, but as a disk evolves, the amount of dust grains decreases. Photoeaporation is a disk dispersal process, which is caused by high-energy radiation. We perform a set of photoevaporation simulations solving hydrodynamics with radiative transfer and non-equilibrium chemistry in a self-consistent way. We run a series of simulations with varying the dust-to-gas mass ratio in a range 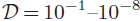 . We show that H2 pumping and X-ray heating mainly contribute to the disk heating in case of
. We show that H2 pumping and X-ray heating mainly contribute to the disk heating in case of 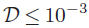 and photoelectric effect mainly heats the gas in
and photoelectric effect mainly heats the gas in 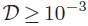 cases. The mass-loss profile changes significantly with respect to the main heating process. The outer disk is more efficiently dispersed when photoelectric effect is the main heating source.
cases. The mass-loss profile changes significantly with respect to the main heating process. The outer disk is more efficiently dispersed when photoelectric effect is the main heating source.