No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 August 2024
Long gamma-ray bursts (LGRBs) and superluminous supernovae (SLSNe) are expected to result from massive star deaths. However to date, there has been no direct observational measurement of their cloud collapse timescales nor progenitor lifetimes to help constrain their mass. Our analyses of z 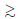 2 LGRB afterglow spectra and Hubble Space Telescope images find a higher fraction of host galaxies that are interacting, have a close companion, and/or may have experienced a recent galaxy ‘fly by’ as compared to the general z
2 LGRB afterglow spectra and Hubble Space Telescope images find a higher fraction of host galaxies that are interacting, have a close companion, and/or may have experienced a recent galaxy ‘fly by’ as compared to the general z 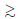 2 galaxy population. A smaller set of z
2 galaxy population. A smaller set of z 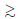 2 SLSNe suggests a similar result. Under the hypothesis that galaxy interactions induce cloud collapse and star formation near their closest approach, we explore measurements of the host and companion galaxy velocities and separations at the time of the LRGB/SLSN event as a direct physical means to measure the timescale of cloud collapse plus progenitor star lifetime.
2 SLSNe suggests a similar result. Under the hypothesis that galaxy interactions induce cloud collapse and star formation near their closest approach, we explore measurements of the host and companion galaxy velocities and separations at the time of the LRGB/SLSN event as a direct physical means to measure the timescale of cloud collapse plus progenitor star lifetime.