No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 June 2020
By considering a modified version of the evolutionary population synthesis (EPS) model for stellar populations (SPs) comprising binary stars, the retrieved galaxy and HII-region parameters/properties differ from the case of neglecting binary stars. The retrieved age, stellar metallicity and mass of galaxies increase (e.g. ∼ 0.2 dex when using spectral fitting algorithm), whilst the star formation rate decreases (∼0.2 dex). The radiation fields from intermediate-age SPs with binary stars could be potentially important ionizing sources in HII regions. Under this possibility, the theoretical division between star forming galaxy and AGN on the diagnostic diagrams would move towards the up-right corner and the retrieved gaseous metallicity would decrease.
Our prediction for the birth rate of binary neutron stars in SPs ranges from 10−9 to 10−6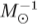 ${\M {^\minus 1_\odot}} $ yr−1 when the kick velocity is from 0 to 190 km s−1.
${\M {^\minus 1_\odot}} $ yr−1 when the kick velocity is from 0 to 190 km s−1.