Introduction
Questionnaire surveys are widely used by health researchers. Methods of questionnaire administration include post, telephone, on-line and face to face. Researchers select the method used based on their assessment of the population of interest and the issue being studied. It is important that an adequate or a good response rate is achieved from a sample of participants who are representative of the population of interest as this will help to reduce non-response bias, increase data reliability (larger sample size) and help achieve the researchers’ aims (Asch et al., Reference Asch, Jedrziewski and Christakis1997). In some populations, achieving good response rates may be harder than in others. Recognised hard to reach groups include people with poor literacy, low socio-economic status, members of minority ethnic groups, young males, the elderly and those who may be particularly sensitive to the research in question (Freimuth and Mettger, Reference Freimuth and Mettger1990). Many studies have reported low levels of response from such groups and the incurring high costs that are associated with their recruitment (Stoop, Reference Stoop2004; O'Hegarty et al., Reference O'Hegarty, Pederson, Thorne, Caraballo, Evans, Athey and McMichael2010).
Numerous methods have been put forward to increase response rates with hard to reach groups. For example, a study of chronic musculoskeletal pain in an ethnic minority population in Greater Manchester showed an increase in the response rate from 35% to postal questionnaires in a South Asian population to 75% using interviews with the non-responders, a response rate comparable to that in White subjects following the initial sending of the questionnaire (Allison et al., Reference Allison, Ahmad, Brammah, Symmons and Urwin2003). A postal questionnaire on acculturation and pain prevalence among South Asian groups in the United Kingdom that included a link worker visit to non-responders to offer assistance in completing the questionnaire achieved a response rate of 51%. However, a study in inner London in which Bangladeshi subjects were sent a Bengali questionnaire achieved a response rate of only 17% despite using a Bengali health worker to hand deliver second copies of the questionnaires to the initial non-responders (MacCarthy and Craissati, Reference MacCarthy and Craissati1989; Palmer et al., Reference Palmer, Macfarlane, Afzal, Esmail, Silman and Lunt2007).
We planned a study, The Tower Hamlets Pain Study (TOPAS), to compare the population burden of chronic pain in White British/Irish and Bangladeshi residents in Tower Hamlets, the third most economically deprived part of the United Kingdom, where many people do not speak English, and literacy levels are poor (Tower Hamlets Public Health Report, 2007). In the 2001 census, the population of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets was 196 106, of whom 45% were White British/Irish, 33% were Bangladeshi, 6% African/Caribbean and 16% were other ethnic groups (2001 Census, 2008). The Bangladeshi community in Tower Hamlets is the largest outside of Bangladesh.
In this article, we describe and compare two separate pilots of the TOPAS study in which we collected data on the prevalence and health impact of chronic pain in Tower Hamlets with White and Bangladeshi residents. We discuss the initial use of a postal survey and the resultant response rate, followed by a description of other methods tested to improve response rates in a deprived and ethnically diverse borough. In addition, we describe a nested randomised-controlled trial (RCT) of hand-addressed versus printed-address envelopes to test whether personalising mail had an effect on the response rates as suggested by the Cochrane review (Edwards et al., Reference Edwards, Roberts, Clarke, DiGuiseppi, Wentz, Kwan, Cooper, Felix and Pratap2007).
Method
We carried out both pilots in two general practices located in the most economically deprived and ethnically diverse parts of Tower Hamlets. Practice one was located in the Spitalfields and Banglatown ward and practice two in the Shadwell ward. Out of 32 483 local authority wards in the United Kingdom, these are the 639th and 808th most deprived (Index of Multiple Deprivation, 2007). The population of ‘Spitalfields and Banglatown’ is 58% Bangladeshi and that of Shadwell is 49% Bangladeshi (2001 Census LBTH Ward Profiles – Spitalfields and Banglatown, 2008; 2001 Census LBTH Ward Profiles – Shadwell, 2008). Many of the adult Tower Hamlets Bangladeshi population do not speak English and/or are illiterate; the majority are from Sylhet, a rural province in the North East of Bangladesh. They speak Sylheti, a dialect of Bengali that has no official written form. Those educated in Bangladesh will usually be able to read Bengali. We translated our postal questionnaires into Bengali and produced phonetic translations into Sylheti for use by the researchers in face-to-face interviews and over the telephone (Choudhury et al., submitted). We will describe the methods of our original pilot study first.
Pilot one
Postal questionnaire with telephone reminders by practice receptionists
Only a third of the Tower Hamlets population are aged over 45 compared with 40% nationally (Key Statistics for Local Authorities in England and Wales, 2008). To ensure sufficient responses from older residents, we selected two random samples of participants from each practice register. The first included 175 participants aged 18–35 and the second included 175 participants aged 36 and above, 700 in total across both practices. Practices then excluded participants who had an established patho-physiological diagnosis for their chronic pain, or a terminal illness or anyone whom they wanted to exclude at their discretion. The practices sent each remaining participant a 12-page questionnaire by post with a covering letter on their practice-headed notepaper. If the participants appeared to have a Bangladeshi surname, the practice sent both English and Bengali versions of the questionnaire (Figure 1). The work on this was carried out in August 2006.

Figure 1 Questionnaire content (Census, 2001; EuroQol Group, 1990; Goldberg and Williams, Reference Goldberg and Williams1991; Melzack, Reference Melzack1975; Mumford et al., Reference Mumford, Bavington, Bhatnagar, Hussain, Mirza and Naraghi1991; Smith et al., Reference Smith, Penny, Purves, Munro, Smith, Grimshaw, Wilson and Chambers1997; Von Korff et al., Reference Von Korff, Ormel, Keefe and Dworkin1992)
Participants were given the option of completing the questionnaire themselves or calling the research centre at the Centre for Health Sciences to arrange for a researcher to help them complete it either face to face or over the telephone. We had two bilingual researchers: one female and one male (Yasmin Choudhury and Iqbal Hussain). Non-responders to the initial mailing received a reminder telephone call from practice reception staff approximately two weeks after the initial mail out. In this call, participants were given the options of declining to participate, being sent another questionnaire, completing the questionnaire over the telephone with a researcher and finally completing the questionnaire with a researcher's help at their general practice or at their home.
The questionnaire was administered in Sylheti for those Bangladeshis who were unable to complete it in English, and completed in English on their behalf by the study researchers. Our target from this intensive approach to data collection was to achieve a 30% response rate. This target response rate was lower than customary in epidemiological studies and reflects the anticipated difficulty in survey work in this environment. While recognising that this may be inadequate to make observations on absolute rate of chronic pain, it would allow us to make comparisons between the Bangladeshi and the White populations of Tower Hamlets if response rates were similar in both groups and confounding is adequately accounted for. We chose postal questionnaire surveys because this is the most practical and economical method for data collection on prevalence rates of chronic pain from large samples.
Pilot two
Two-page questionnaire with a telephone follow-up by research assistants
Following a poor response rate of 12% (79/653) in pilot one, we piloted a second data collection approach in the same two practices, using two separate questionnaire surveys. This took place in the beginning of 2007. We first condensed the 12-page questionnaire to two pages as previous studies have shown shorter questionnaires to yield a higher response than longer ones (Bogen, Reference Bogen1996; Edwards et al., Reference Edwards, Roberts, Clarke, DiGuiseppi, Pratap, Wentz and Kwan2002; Nakash et al., Reference Nakash, Hutton, Jørstad-Stein, Gates and Lamb2006). The questionnaire focused on the presence and locality of chronic pain, and included simple demographic data to estimate the prevalence of chronic pain in the different ethnic groups. We posted the questionnaire to two fresh random samples of 350 participants from each of the two practices after making exclusions as described for pilot one. The covering letter detailed the following options for participants if they did not want to or were unable to complete the questionnaire:
-
• to opt out of the study entirely;
-
• to be contacted by one of the study researchers to arrange for some help in completing the questionnaire either over the telephone or in person.
In the covering letter, all participants were informed that if we had not heard from them within two weeks, they would receive a brief telephone call from the researchers involved with the study, to determine whether they had received the letter and questionnaire and to find out whether they were willing to take part in the study. These calls were made from the general practices, not from the research centre, to ensure that patient-identifiable information was kept within the practice. If subjects were willing to take part they completed the short questionnaire over the telephone with a researcher. Follow-up of postal surveys via telephone is said to help increase response rates (Sibbald et al., Reference Sibbald, Addington-Hall, Brenneman and Freeling1994; Brogger et al., Reference Brogger, Bakke, Eide and Gulsvik2003). All telephone calls and telephone administration of the questionnaires were made in the language with which the participants were most comfortable.
RCT comparing the impact of hand-written or word-processed addressed envelopes on the response rate
Within this second pilot, we nested a RCT exploring the impact of hand-written envelopes versus word-processed addresses in window envelopes on the response rate to the short postal questionnaire study. A previous systematic review found that hand-written envelopes received a slightly higher response rate than word-processed envelopes (Edwards et al., Reference Edwards, Roberts, Clarke, DiGuiseppi, Wentz, Kwan, Cooper, Felix and Pratap2007). The use of hand-addressed envelopes adds a personal touch and is less likely to be perceived by individuals as junk mail (McCoy and Hargie, Reference McCoy and Hargie2007). We wanted to test whether this personalised approach worked to increase the response rate with our study population. Subjects were randomly allocated to two groups using a web-based random number programme (Haahr, Reference Haahr1998). The sample size was determined by the primary aim of the second pilot. To show an increased response rate from 20% to 30%, however, with 80% power at the 5% significance level requires 314 subjects in each group. This is approximately the number of people we intended to approach in this second pilot.
Face-to-face questionnaire administration in general practice waiting rooms
To assess the comparative health impact of chronic pain on White and Bangladeshi subjects, we administered the original 12-page questionnaire, used in pilot one, to participants sampled from the waiting rooms of our two pilot practices. In each practice, we set a target of 40 questionnaires; this is the number per practice we anticipated needed for the main study (Choudhury et al., submitted).
To obtain a representative sample of the population in terms of age, ethnicity and gender, we used quota sampling (Clarke-Carter, Reference Clarke-Carter2010). We sampled according to the age and ethnicity distribution of the population. We estimated the ethnic breakdown using 2001 census data for the ward in which the practice was located. We had equal numbers of males and females. Participants were approached, as appropriate, in the waiting areas of general practices by either a male or a female bilingual (Sylheti and English) researcher who explained the study to them and asked whether they were willing to take part. Posters in the waiting rooms in both English and Bengali provided details of the study so that participants were aware that they might be approached. Each participant was given a brief information sheet to read, the study questionnaire and an envelope to seal and return their completed questionnaires to a box provided at the reception area, to the researchers or to the study team in a freepost envelope. A separate room was made available within the practices for those participants who required assistance in completing the questionnaire to complete the questionnaire with the researcher.
Results (Table 1)
Pilot one
Postal questionnaire with telephone reminders by practice receptionists
Of those participants who were initially sent the questionnaire (n = 653), 21 (3%) had moved or changed practice. When telephoned by the practice receptionists many non-respondents reported not having received the questionnaire. We also found that the freepost address we provided for return of the questionnaire resulted in some confusion, with some participants reporting they thought the return address was incorrect as it did not include a street name or postcode and subsequently decided that it was not prudent for them to complete or return the questionnaire.
Table 1 Results of the two pilots

The overall response rate was 12% (79/653): 9% (62/653) after the initial mail out and a further 3% following telephone reminders, with three of these being done face to face with participants. Of the responders, 49% (39/79) were male, 29% (23/79) were Bangladeshi, 48% (38/79) White British/Irish and 23% (18/79) of other ethnic groups; 59% (47/79) reported chronic pain.
Pilot two
Two-page questionnaire with telephone follow-up by research assistants
We sent 642 participants a postal questionnaire (312 from practice one and 330 from practice two); 4% (27/642) of these participants had moved or changed practice, leaving 615 contactable participants.
The overall response rate was 37% (240/642); 16% (104/642) of the questionnaires were returned after the initial mail out and a further 21% (136/642) were completed over the telephone with a researcher. Of the responders, 41% (98/240) were male, 47% (112/240) were Bangladeshi, 31% (74/240) White British/Irish and 21% (51/240) from other ethnic groups; 52% (125/240) reported chronic pain.
RCT comparing the influence of hand-written versus word-processed envelopes on the response rate
Out of the total 642 participants sent the short questionnaire, 321 (156 from practice one and 165 in practice two) were randomly assigned to receive hand-written envelopes and the remaining 321 to receive word-processed envelopes from the two practices.
We received 56/321 (17%) responses from those receiving hand-written envelopes and 46/321 (14%) responses from those who had received word-processed addressed in window envelopes (95% confidence interval (CI) for difference: −2% to 9%; Figure 2).
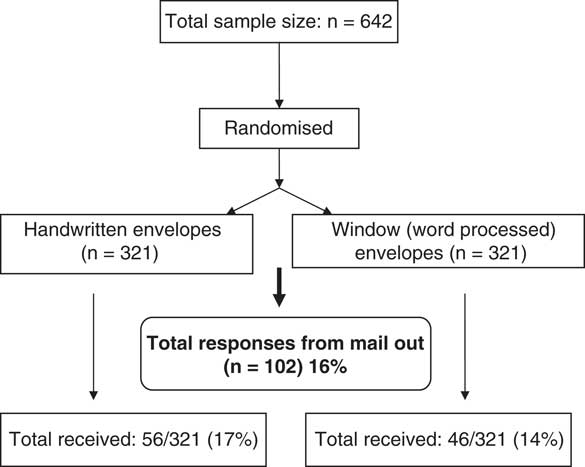
Figure 2 Flow chart for a randomised-controlled trial: handwritten-addressed envelopes versus word-processed addressed (window) envelopes
Our estimate of the effect of hand-addressed envelopes on response is entirely consistent with previous RCTs, with the relevant pooled odds ratio (OR) from a recent Cochrane review being OR 1.37 (95% CI 0.95, 1.98).
Face-to-face questionnaire administration in general practice waiting rooms
We recruited 78 of our target of 80 participants from the two general practices. Of these, 28/78 (36% were male and 50/78 (64%) were Bangladeshi); 37/78 (47%) reported chronic pain. With the exception of our shortfall of two patients, we achieved the planned quota sample in each practice.
Discussion
The use of several methods to test response rates has provided some insight into the factors that could affect responses when conducting postal surveys in hard to reach populations such as a deprived and ethnically diverse area. The use of two or more different modes of data collection has been noted to improve the response rate. Dillman et al. (Reference Dillman, Phelps, Tortora, Swift, Kohrell, Berck and Messer2009: 16) measured this in their study and found that ‘response rates can be improved by this sequential offering of survey modes. This is particularly apparent when response to the first mode is fairly low’.
Pilot one
Postal questionnaires and telephone reminders from receptionists
A previous postal survey carried out in Tower Hamlets did achieve a response rate of 46%, higher than in many similar studies, possibly due to the study participants being familiar with the study centre and its researchers (Ahmed et al., Reference Ahmed, Rahman and Hull1997). When originally planning this research, we had planned for a response rate of 30%. Our actual response rate of 12%, even after quite intensive follow-up, was much lower. Drawing reliable conclusions from these data would have been challenging. Factors contributing to the poor response as felt by the researchers working on the study include failure of material to arrive with the addressee, poor literacy, too lengthy a questionnaire, difficulty contacting non-responders and time constraints on practice staff. In our case, the questionnaire was 12 pages long and there were participants in our sample who could not read either English or Bengali. Additionally, the practice receptionists were fitting the reminder telephone calls to non-responders around their normal work, and did not have the capacity to conduct the volume of calls generated by the low response rate. They also reported sometimes finding it difficult to reach the person to whom the questionnaire had been sent and sometimes being unable to get through to anyone at all, especially if their telephone number was unattainable, which was the case with 13% of potential respondents.
Pilot two
Two-page questionnaire with telephone follow-up by research assistants
This approach was more successful. We partly attribute this to condensing our 12-page questionnaire to two pages and in allowing the telephone calls to non-responders being made by the projects’ researchers rather than the practice reception staff, which generated a higher response rate; both researchers had more knowledge of the study and so were able to explain it better to participants and more able to concentrate solely on making telephone calls and completing the questionnaire over the telephone. This also possibly resulted in better quality data due to the higher level of training and interest of researchers. This method also cut out the extra procedural stage of the practice receptionists needing to contact the project researchers before a questionnaire could be completed.
Despite the improvements in the response rate resulting from this approach, difficulties with incorrect telephone numbers and in reaching the correct person were unchanged. Maintaining confidentiality of patient data is an important ethical issue in medical research. In our first pilot, we achieved this by using practice staff to contact non-responders. In the second pilot, with the agreement of the local research ethics committee, researchers were given access to names and contact details of the subjects at participating practices, from where they made the telephone calls. This approach allowed us to obtain good data on the prevalence of chronic pain in a hard to reach group; this would not otherwise have been possible.
RCT: hand-written versus word-processed addressed envelopes
We did not find a statistically significant benefit from using hand-written in preference to window envelopes. Although the trend was towards an improved response rate from hand-written envelopes, even if this had been statistically significant, this advantage was too small to justify the additional time and expense for this study. This finding concurs with the conclusion of the Cochrane review on this point (Edwards et al., Reference Edwards, Roberts, Clarke, DiGuiseppi, Wentz, Kwan, Cooper, Felix and Pratap2007) and that of Wunder and Wynn (Reference Wunder and Wynn1988) and McCoy and Hargie (Reference McCoy and Hargie2007) who also came to similar conclusions.
Face-to-face questionnaire administration in general practice waiting rooms
As this was primarily a survey of those attending a general practice, it was difficult to recruit young men aged 18–35, who are less likely to attend general practices, although through much time and effort, we did manage to achieve our target for this group. The face-to-face approach enabled us to collect a wider range of data on patients than using any other methods, for example postal or telephone surveys.
Strengths and limitations
This study enabled the use of a range of methods to test response rates to postal questionnaires in hard to reach populations. By performing two pilots, we were able to assess what methods worked and did not work with our study population. Furthermore, the use of random sampling to test our various approaches (excluding waiting room survey) added to the representativeness of the study population.
Although the process of contacting non-responders through telephone calls can help generate more responses to surveys, it is still a costly and lengthy procedure particularly when the level of non-response is high. The data collected face to face through the waiting room survey will not generally be representative of the study population, but nonetheless does provide researchers with the opportunity to collect more in-depth data for surveys from some sample of the population, and our quota sampling at least achieved representativeness with respect to age, sex and ethnicity.
Lessons for the future
There are numerous factors that can contribute to the response rate of postal questionnaires and as Bogen states, ‘researchers have manipulated many different features of surveys in their attempts to understand the factors that affect survey participation’ (1996: 1). Strategies known to improve response rates to postal questionnaires include offering monetary incentives, pre-notification, follow-up contact, shorter questionnaires, personalising correspondence, use of recorded or special delivery letter, telephone follow-up and direct contact with the researcher (Wunder and Wynn, Reference Wunder and Wynn1988; Edwards et al., Reference Edwards, Roberts, Clarke, DiGuiseppi, Pratap, Wentz and Kwan2002; Edwards et al., Reference Edwards, Roberts, Clarke, DiGuiseppi, Wentz, Kwan, Cooper, Felix and Pratap2007; McCoy and Hargie, Reference McCoy and Hargie2007). Few, if any, researchers use all of these techniques. Although we had used some of these in our first pilot, we have clearly shown that the combination of a short questionnaire and follow-up telephone interviews is superior to longer questionnaires and telephone reminders.
Contrary to expectation, personalising the correspondence by using hand-written rather than window envelopes did not produce a statistically significant improvement in the response rates to our study (although a 3% difference may be clinically important in other studies and circumstances). It generates additional labour and time. As window envelopes are substantially less time consuming to prepare, we recommend that they be used in preference to hand-addressed envelopes. This came as something of a relief to the research team, who would otherwise have needed to hand address over 4000 envelopes for the main study.
Although using short postal questionnaires, followed by telephone interviews for non-responders has provided more data on the comparative prevalence of chronic pain, it does not allow us to collect detailed data on the comparative health impact of chronic pain in the Bangladeshi and White populations. The more detailed and comparative data were from the data generated in the general practices of waiting rooms. Researchers need to arm themselves with an arsenal of various methodologies, which can be utilised to maximise responses to surveys. Although it may appear costly and time consuming, these strategies can produce more effective and successful results, thus ultimately proving to be better value for money. It is important when undertaking research with hard to reach groups that the characteristics of the study population are carefully looked at and considered into the initial design phase of the study. This will allow the researcher to identify the most appropriate method(s) to achieve successful data collection.
Acknowledgements
We thank the two practices who took part in the pilot and all those involved with the study design and the study itself.
Ethical Approval: The Tower Hamlets Pain Study (TOPAS) was approved by the East London and the City Research Ethics Committee.
Funding: This work was supported by the Arthritis Research Campaign.
YC and IH were involved in the data collection and YC drafted the manuscript. SP designed the study and AR helped with the design of the waiting room survey. SE contributed to the design of the study. MU was primarily responsible for the study design and was the Principal Investigator for the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.





