Introduction
There is a crisis of low morale among General Practitioners (GPs) in the UK National Health Service (NHS), at a time when their resources and attributes are most required to lead on the significant changes outlined in the NHS 5 Year Forward View (NHS England, 2016). The latest British Medical Association (BMA) tracker survey (BMA, 2016) revealed that 73% of GPs describe their workload as unmanageable (twice the number compared with consultants); 71% of doctors are suffering or at risk of burnout; 45% have considered working part time; 42% retiring early and 25% leaving the profession entirely. The reasons for this are multiple and include increasing volume and complexity of workload, the secondary to primary care shift, recruitment and retention challenges, changes in other services such as community nursing, mental health and care homes creating additional pressure on general practice, increasing non-patient facing administrative duties and a declining trajectory of NHS GP funding (Baird et al., Reference Baird, Charles, Honeyman, Maguire and Das2016).
The picture is also reflective of a global trend toward increasing work pressures and growing dissatisfaction among physicians and other healthcare workers, linked to rising prevalence of stress and burnout (Spickard et al., Reference Spickard, Gabbe and Christensen2002). Stress and burnout are related but distinct concepts. Burnout is measured using the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI), which has subscales for emotional exhaustion, depersonalization (cynicism) and personal accomplishment (professional efficacy), while stress is assessed using measures, such as the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ) and Perceived Stress Scale (PSS). In a longitudinal study of UK doctors, McManus et al. (Reference McManus, Winder and Gordon2002) demonstrated that increases in stress resulted in increased emotional exhaustion, while increases in emotional exhaustion contributed to increased stress. Personal accomplishment also increased stress both directly and indirectly, by increasing emotional exhaustion, while depersonalization reduced stress, possibly due to ego-defense mechanisms.
Studies using the MBI provide further evidence of a rapidly developing crisis in NHS general practice. A study of 564 UK GPs in 2012 found high levels of emotional exhaustion in 46% of respondents, depersonalization in 42% and low levels of personal accomplishment in 34% (Orton et al., Reference Orton, Orton and Pereira Gray2012). An online survey of 2230 UK GPs in 2015, using the same tool, showed a worsening picture with emotional exhaustion affecting 74% of respondents and a conclusion that 50% of GPs were at risk of burnout (Matthews-King, Reference Matthews-King2015). Considerable evidence shows that physician burnout can increase medical errors and adversely affect patient care (Prins et al., Reference Prins, van der Heijden, Hoekstra-Weebers, Bakker, van de Wiel, Jacobs and Gazendam-Donofrio2009; Shanafelt and Dyrbye, Reference Shanafelt and Dyrbye2012). There is also evidence that burnout may contribute to even greater work demands – a longitudinal study revealed that GPs who attempted to gain emotional distance from their patients as a way of coping with exhaustion, evoked demanding and threatening behaviour from their patients (Bakker et al., Reference Bakker, Schaufeli, Sixma, Bosveld and Dierendonck2000). GP commentators have urged that, rather than waiting to address such problems as they arise, it would be wiser to tackle GP burnout before it causes harm to self and others (Jones and Davies, Reference Jones and Davies2016) and that ‘until medical professional bodies recognise the size of the burnout problem and start taking action, physicians can only help themselves’ (Lee et al., Reference Lee, Medford and Halim2015, p. 106).
A seemingly promising means by which GPs might ‘help themselves’ is by cultivating mindfulness skills. Mindfulness refers to a way of paying attention, without judgement to one’s moment-by-moment awareness. It is a skill that can be developed through a range of formal and informal practices, which have been demonstrated to cultivate clear thinking, equanimity and compassion and lead to greater emotional balance and well-being (Ludwig and Kabat-Zinn, Reference Ludwig and Kabat-Zinn2008). The clinical evidence base for its use is strongest for patients with recurrent depression who are in remission, for which mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) has been approved for over 10 years and shown to be equivalent in efficacy, and so an alternative to, ongoing antidepressant medications (Kuyken et al., Reference Kuyken, Hayes, Barrett, Byng, Dalgleish and Kessler2015). There is also an increasing evidence base for its use as an intervention to address the high levels of stress and burnout in a variety of healthcare professionals (Shapiro et al., Reference Shapiro, Astin, Bishop and Cordova2005), including those working in primary care (Martin Asuero et al., Reference Martin Asuero, Rodriguez Blanco, Pujol-Ribera, Berenguera and Moix2013; Aranda Auserón et al., Reference Aranda Auserón, Elcuaz Viscarret, Fuertes Goñi, Güeto Rubio, Pascual Pascual and Sainz de Murieta García de Galdeano2017), as well as medical students (Warnecke et al., Reference Warnecke, Quinn, Ogden, Towle and Nelson2011) and UK midwives (Warriner et al., Reference Warriner, Hunter and Dymond2016). With regard to GPs specifically, pilot studies from the United States have demonstrated reduced indicators of job burnout, depression, anxiety and stress (Fortney et al., Reference Fortney, Luchterhand, Zakletskaia, Zgierska and Rakel2013), and a study of Dutch GPs showed that a mindfulness intervention was feasible and significantly reduced depersonalization in the active group (Verweij et al., Reference Verweij, Waumans, Smeijers, Lucassen, Donders, van der Horst and Speckens2016). US GPs who rated themselves as more mindful were found to engage in more patient-centred consultations and have more satisfied patients (Beach et al., Reference Beach, Roter, Korthuis, Epstein, Sharp, Ratanawongsa, Cohn, Eggly, Sankar, Moore and Saha2013). As yet, there is insufficient evidence to determine whether this approach could provide an effective form of self-help for NHS GPs at risk of burnout.
Aim
The purpose of this study was to explore, for the first time, whether a modified MBCT course has the potential to reduce stress and burnout in NHS GPs.
Methods
Design
We used an uncontrolled before and after study design.
Inclusion/exclusion criteria
We included all NHS GPs attending an eight-week mindfulness course, starting in May 2016.
Intervention
The course was a modified version of the MBCT course approved by National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) for prevention of depressive relapse (NICE, 2009). The eight weekly 2-h sessions adhered closely to the MBCT protocol, with one main difference: the homework (completed between sessions) was less time-consuming to facilitate compliance among the GP cohort and used the Mindfulness: A Practical Guide to Finding Peace in a Frantic World book (Williams and Penman, Reference Williams and Penman2011) as the homework text (i.e. designed for a non-clinical cohort, in contrast to the NICE approved MBCT course, which is designed for patients with recurrent depression. The few course components in MBCT which were designed to address the depressive cohort were also modified for the non-clinical cohort). The course was delivered by NP, a full-time GP Principal who has trained to teach MBCT through the Oxford Mindfulness Centre, Oxford University, with the support of a trainee mindfulness teacher. NP adheres to the Good Practice Guidelines for teaching mindfulness-based courses as developed by the UK Network for Mindfulness-Based Teacher Trainers. The course was offered to GPs in two Clinical Commissioning Group areas in South East England as an eight-week evening course in May and June 2016.
Outcome measures
Burnout and stress were measured using the MBI (Maslach and Jackson, Reference Maslach and Jackson1981) and PSS (Cohen et al., Reference Cohen, Kamarck and Mermelstein1983). The MBI consists of 22 questions that assess three aspects of professional burnout syndrome: emotional exhaustion, depersonalization and personal accomplishment. Respondents record how often they experience job-related feelings using a seven-point Likert scale ranging from ‘Never’ to ‘Every day’. Three scores are computed for each respondent, one for each aspect of burnout. The PSS is a validated scale used widely to measure the perception of stress. We used the validated 10-item version. Respondents record how often they felt a certain way during the past month using a five-point Likert scale ranging from ‘Never’ to ‘Very Often’. Higher scores indicate greater perceived stress. Participants were also asked to provide their age, gender and number of years in practice and to respond to open-ended questions on their experiences of the mindfulness course.
Procedure
Participants completed the questionnaires online using the secure Qualtrics® system. We sent out a link to the questionnaire by email two weeks before the start of the course, and then four weeks (T2) and three months (T3) after the end of the course.
Data analysis
Descriptive statistics were computed for each measure at baseline and follow-up; the change from baseline was also computed. Tests for normality of the data were performed and distributional plots assessed. The paired t-test was used to analyze the change from baseline and follow-up. All quantitative analyses were conducted using SAS version 9.3. Responses to open-ended questions were read by one member of the team and themes arising from the text were identified. The themes were then reviewed by a second member of the team and consensus reached by discussion. Data analyses were conducted by T.P.-H. and K.H.-W. who were not involved in the delivery of the intervention and had no contact with participants.
Ethical issues
A participant information sheet and consent form was embedded in the online questionnaire as a cover page. Participants were informed that they were free to decide whether or not to take part and that anonymity would be maintained. A unique identification number was used to match participants’ baseline and follow-up questionnaires. We also provided a contact telephone number in case of questions. All data were stored securely in accordance with the Data Protection Act.
Results
Of the 22 GPs enrolled for the study, all completed baseline assessments and 21 completed the assessment at T2. Compliance was very high, all respondents completed at least six of the eight weekly mindfulness sessions; most GPs (86%) attended seven or eight sessions (Figure 1).
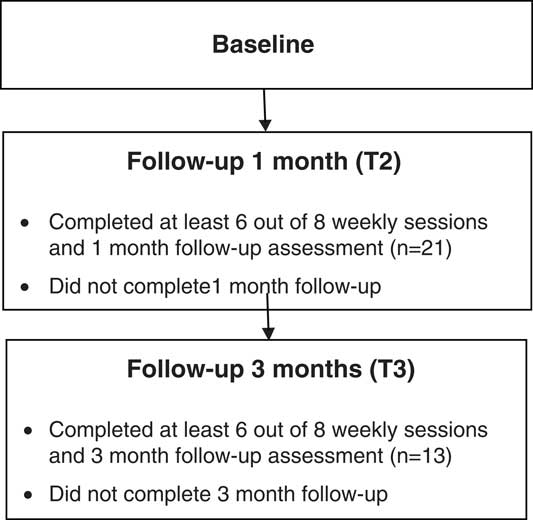
Figure 1 Participant flow diagram
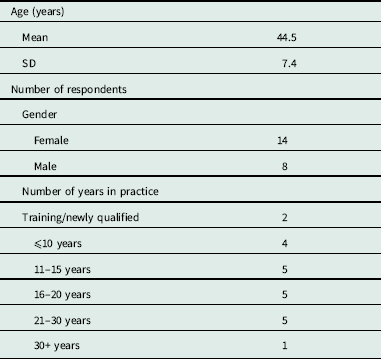
The mean age of GPs enrolled on the study was 44.5 (SD=7.4). The number of years in practice varied; two GPs were newly qualified or still in training, while the majority had more than 10 years in practice (73%). Participant characteristics at baseline are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Participants characteristics at baseline
MBI burnout scores of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization were significantly lower at T2 compared with baseline (P<0.001 and P=0.0421, respectively). There was a large change in emotional exhaustion scores during the study, the mean score was 11.5 points lower at T2 compared with baseline (95% confidence interval 6.75–16.3 points). Depersonalization scores also decreased by 2.62 points (95% confidence interval 0.103–5.13) at T2 compared with baseline, and PSS scores at T2 were significantly lower than those seen at baseline (P<0.001); there was a drop of 6.48 points (95% confidence interval 4.09–8.86).
Completed questionnaires were obtained from 13 participants at T3. The large reduction in MBI burnout scores of emotional exhaustion at T2 were maintained at T3, the mean score was significantly lower at T3 compared with baseline (P=0.0024), the mean reduction was 12.85 points (95% confidence interval 5.52–20.17). PSS scores were significantly lower at T3 compared with baseline (P<0.001), replicating the pattern seen at T2, the mean score was 8.69 points lower (95% confidence interval 5.57–11.8). MBI personal accomplishment scores were significantly higher at T3 compared with baseline (P<0.001); there was an increase of 4.32 points at T3 (95% confidence interval 2.44–6.18). Outcome scores at each survey are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Outcome scores at each survey with comparison to baseline
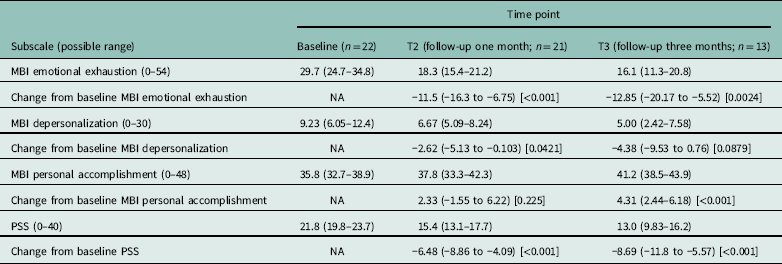
MBI=Maslach Burnout Inventory; PSS=Perceived Stress Scale; NA=not applicable.
Values shown are mean score (95% CI) [P-value].
Table 3 shows outcome scores at each survey for participants who completed all follow-up assessments. Personal accomplishment scores at T2 showed larger increases from baseline (mean change=3.62, n=13) when compared with all participants (mean change=2.33, n=21) who completed the first follow-up assessment. In addition, there was a statistically significant increase in personal accomplishment at T3 which was not evident at T2, and a reduction in variability at T3.
Table 3 Outcome scores at each survey for participants completing both follow-up assessments (n=13)

MBI=Maslach Burnout Inventory; PSS=Perceived Stress Scale; NA=not applicable.
Values shown are mean score.
Plots are presented separately below for all participants who completed baseline and the T2 assessment (n=21), and all participants who completed all three assessments (n=13) for comparison (Figures 2 and 3).
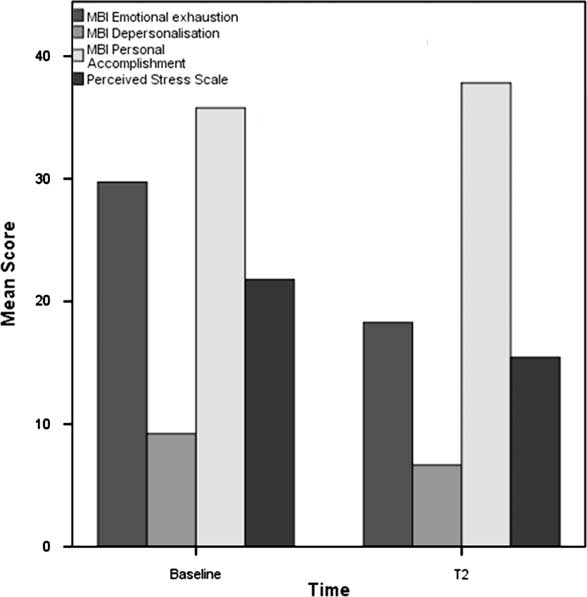
Figure 2 Mean outcome score assessed at baseline and follow-up one month after the course (T2) (all participants). MBI=Maslach Burnout Inventory.
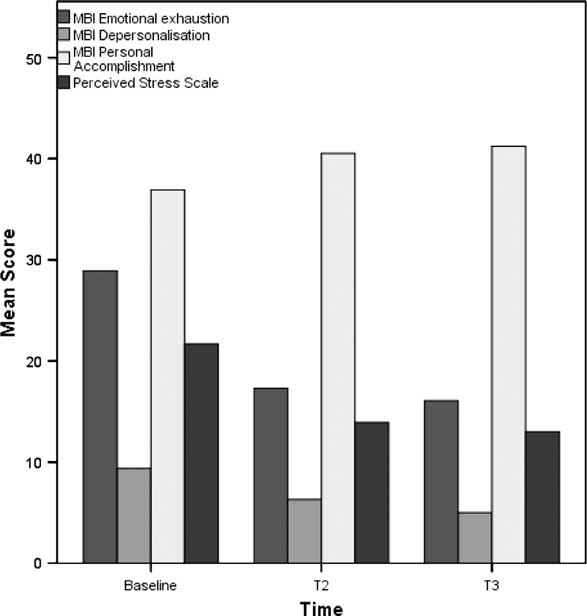
Figure 3 Mean outcome score assessed at baseline, follow-up one month after the course (T2) and follow-up three months after the course (T3) for participants completing both follow-up assessments (n=13). MBI=Maslach Burnout Inventory.
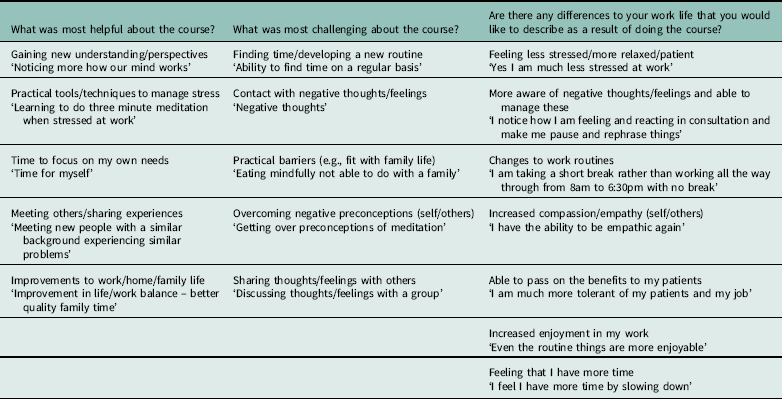
GP responses to open-ended questions revealed a wide range of benefits of the course, including gaining new understanding/perspectives and learning practical tools/techniques to manage stress. Participants also provided information on challenges encountered in developing mindfulness practice, such as difficulties finding time/developing a new routine, or overcoming negative preconceptions. GPs described differences to their work-life since attending the course, such as feeling less stressed/more relaxed and experiencing increased compassion for self and others. Themes and example responses are provided in Table 4.
Table 4 Themes arising from GP responses to open-ended questions, with example quotes
Participants were also asked to respond to the following Yes/No questions: ‘Would you recommend a mindfulness course to a colleague?’, ‘Has doing this mindfulness course increased your awareness of mindfulness as a therapeutic option for your patients?’ and ‘Are you more likely to recommend such a course for appropriate patients?’ For all three questions 100% of participants responded ‘Yes’ (n=21).
Discussion
This is, to our knowledge, the first study to explore potential benefits of a mindfulness course for reducing stress and burnout in NHS GPs. Findings are promising: compliance with the intervention was very high and scores on validated measures of stress and burnout were significantly improved at one-month follow-up compared with baseline. Furthermore, this improvement was maintained at three-month follow-up. Participants reported a wide range of benefits of the course and all respondents indicated that they would recommend a similar course to colleagues and patients. These findings are particularly noteworthy given the well-documented pressures facing NHS GPs, many of whom are leaving the profession as a result. Notwithstanding the need for effective policy and management responses to this urgent issue, our findings indicate that mindfulness meditation could help to mitigate some of the adverse impacts on GP well-being.
It is important to acknowledge that this is a small preliminary evaluation and a larger scale randomized-controlled trial will be needed before definitive conclusions can be drawn. The findings presented here support the case for such a trial and provide valuable information for designing a future study. For example, GP responses to open-ended questions indicate that the course helped them to manage work pressures, feel more relaxed, enjoy their work and experience greater empathy and compassion (for self, colleagues and patients). Participants also valued having time to focus on their own needs and share experiences with others in a similar situation. These benefits could be examined further in future research, by including validated measures of compassion, emotional expression and work-related outcomes (e.g., job satisfaction/work engagement); potential benefits for patients (e.g., increased satisfaction with the consultation) could also be examined. Participants reported that sharing thoughts and feelings could be challenging and they found it difficult to find time to practice the mindfulness exercises. Future research could identify approaches to address these challenges – for example, by examining the ways in which participants successfully integrate mindfulness practice into daily routines.
Analyses reported here reveal a different pattern of results for participants who completed both follow-up assessments, compared to all participants who completed the first follow-up. In particular, those completing both follow-up assessments showed larger increases in personal accomplishment. This highlights a potential bias in the T3 results; those who remained in the study may not be representative of the group and this potential response bias should be borne in mind when interpreting the results. The potential influence of personal accomplishment on completion of outcome measures could also be examined in future research. In addition, our pattern of results suggests a different relationship between personal accomplishment, emotional exhaustion and stress than previously reported by McManus et al. (Reference McManus, Winder and Gordon2002). In this longitudinal study of UK doctors, personal accomplishment increased emotional exhaustion and stress, while in the current study increased personal accomplishment at follow-up was associated with reductions in both emotional exhaustion and stress. Studies examining interrelationships between the MBI subscales have yielded mixed results. For example, Taris et al. (Reference Taris, Le Blanc, Schaufeli and Schreurs2005) reviewed evidence in relation to three models proposing causal relationships between the MBI dimensions. None of the seven studies reviewed provided convincing support for any causal order proposed so far. Taris et al. (Reference Taris, Le Blanc, Schaufeli and Schreurs2005) also conducted analyses on combined data from two longitudinal studies of Dutch oncology care providers and teachers (n=1185). Findings revealed that high levels of emotional exhaustion were associated with high levels of depersonalization over time across both samples. Further, higher levels of depersonalization led to higher levels of emotional exhaustion and lower levels of personal accomplishment. Baseline correlations between the MBI constructs also indicated that personal accomplishment was inversely correlated with both emotional exhaustion and depersonalization.
There have been two other studies looking at the effects of a mindfulness intervention on burnout in GPs specifically (Fortney et al., Reference Fortney, Luchterhand, Zakletskaia, Zgierska and Rakel2013; Verweij et al., Reference Verweij, Waumans, Smeijers, Lucassen, Donders, van der Horst and Speckens2016) and studies reporting benefits of mindfulness in combined groups of primary care (including medical and non-medical) professionals (Martin Asuero et al., Reference Martin Asuero, Rodriguez Blanco, Pujol-Ribera, Berenguera and Moix2013; Aranda Auserón et al., Reference Aranda Auserón, Elcuaz Viscarret, Fuertes Goñi, Güeto Rubio, Pascual Pascual and Sainz de Murieta García de Galdeano2017), though none before in the NHS. The changes from baseline scores on the MBI parameters emotional exhaustion and depersonalization were of a much greater magnitude in our study than in the previous GP studies. We found a 38% reduction in emotional exhaustion compared with a 17% reduction in the US study (Fortney et al., Reference Fortney, Luchterhand, Zakletskaia, Zgierska and Rakel2013) from a similar baseline level, and a reduction in depersonalization of 28% compared with 18%. These differences may be explained by the duration of intervention (only four weeks in the US study, compared with eight weeks in the current study), or to therapist effects (in our study all classes were led by a GP, which was not the case in the other studies). Another explanation may arise from the fact that we used a modified MBCT course, which incorporated one week dedicated to self-compassion. As noted above, increased compassion for self and others was one of the main themes arising from the qualitative analysis, suggesting that this was an important benefit for GPs. Further work could examine the impacts of increased self-compassion on GP well-being and consider whether such ‘soft’ factors may prove crucial in empowering the GP workforce to successfully rise to the extreme challenges that they currently face in the NHS. The recently published evaluation of a mindfulness programme in Spanish primary care professionals also incorporated self-compassion. Compared to control participants, doctors and nurses attending an eight-week Mindfulness and Self-Compassion Programme, demonstrated improvements in mindfulness, perceived stress, self-kindness and emotional fatigue (Aranda Auserón et al., Reference Aranda Auserón, Elcuaz Viscarret, Fuertes Goñi, Güeto Rubio, Pascual Pascual and Sainz de Murieta García de Galdeano2017). Future research could examine which of the mindfulness programmes evaluated to date is most effective for reducing stress and burnout in GPs.
A further potential limitation of the current study is that GPs were recruited from only two Clinical Commissioning Group areas in South East England. Survey findings have revealed that GPs across the UK National Health Service face similar challenges in relation to stress and burnout and our baseline scores are in line with these national data (e.g., BMA, 2016). However, future studies could examine to what extent the findings of the current study are replicated in other areas of the United Kingdom.
In summary, our results provide support for benefits of mindfulness in an NHS GP cohort. This is a brief, practical intervention, which NHS GPs found acceptable and which has been demonstrated to improve depression and anxiety in other populations. We encourage further research to examine impacts on GP well-being, work-related outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the advice and support provided by Professor Patricia Wilson, University of Kent.
Financial Support
A small grant was provided by the Royal College of General Practitioners South East Thames Faculty (£1498). The funder was not involved in the conduct of the research.
Conflicts of Interest
None.
Ethical Standards
Ethical approval was granted by the School of Sociology, Social Policy and Social Research (SSPSSR) Ethics Committee, University of Kent.










