Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 January 2013
The crystal structure of the spinel polymorph of Fe2SiO4, synthesized at high temperature (900°C) and high pressure (70 kbar), was studied by the Rietveld analysis of X-ray powder diffraction data collected with a Guinier-Hägg camera. The compound is cubic, space group 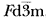 , with cell dimension: a= 8.2413(6) Å, V= 559.8(1) Å3, Z= 8, Cell Wt. = 1630.2, Dx= 4.835 g·cm−3, Do= 4.75 g·cm−3. The figure of merit is F10= 92(0.011, 10). The final R value is RF= 0.058. The crystal has a mixed normal-inverse spinel structure. The site occupancy refinement showed that 37.9% of the silicon was found in the octahedral site (M site), while 18.9% of the iron occupied the tetrahedral site (T site). Due to the larger displacement of Si4+ion by Fe2+ion, the positional parameter of oxygen atom (0.3689) is smaller than that of X-ray single crystal structure (0.3658), and the average Si-O bond (1.697(1)Å) is longer and Fe-O bond (2.112(1)Å) is shorter than those of X-ray single crystal structure.
, with cell dimension: a= 8.2413(6) Å, V= 559.8(1) Å3, Z= 8, Cell Wt. = 1630.2, Dx= 4.835 g·cm−3, Do= 4.75 g·cm−3. The figure of merit is F10= 92(0.011, 10). The final R value is RF= 0.058. The crystal has a mixed normal-inverse spinel structure. The site occupancy refinement showed that 37.9% of the silicon was found in the octahedral site (M site), while 18.9% of the iron occupied the tetrahedral site (T site). Due to the larger displacement of Si4+ion by Fe2+ion, the positional parameter of oxygen atom (0.3689) is smaller than that of X-ray single crystal structure (0.3658), and the average Si-O bond (1.697(1)Å) is longer and Fe-O bond (2.112(1)Å) is shorter than those of X-ray single crystal structure.