Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 February 2009
It is the purpose of the following pages to reconsider the basic problem of induction. According to Hume the concomitance of A with B on one or more occasions gives no valid presumption that A will be accompanied by B on any other occasion. The data of experience may give rise to an association of ideas or set up mental habits, but they provide no reasonable grounds for expecting similar concomitances or sequences in future. If this is correct, we have no starting point for the formation of any valid opinions about matters of fact; we remain ice-bound in a region of total scepticism.
1 Vide: Treatise on Probability, Ch. 22.
2 Vide: Foundations of Geometry and Induction, pp. 266–281.
page 41 note 1 Theory of Probability, p. 353.
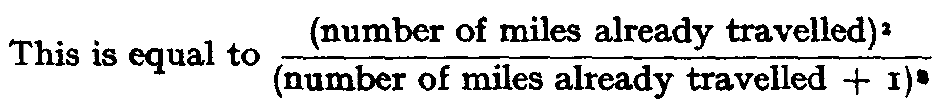
page 43 note 1 For a full treatment of the matter here briefly discussed in this paragraph, see Mind (1942, January).
page 44 note 1 Pp. 3–5.
page 45 note 1 Scientific Inference, pp. 37–41.
page 45 note 2 A power is used since each place in the set is distinctive.
page 51 note 1 An example of a generalization from only one instance by the Method of Agreement is the conclusion drawn from the observed bending of light rays on the famous occasion in 1919. We did not say that that bit of light might have bent, but other bits of light may behave quite differently. Owing to the extreme precision of the characteristics of light, we regard light, wherever it occurs, as the recurrence of an identical complex of properties, and are therefore confident in generalizing about its reaction to a neighbouring mass from one crucial instance.