This paper contains supplementary material that can be found online at http://journals.cambridge.org
Introduction
Since the mid 1990s a variety of priority setting concepts have been designed to guide policy and help reap maximum benefit in a world of limited conservation resources (Balmford, Reference Balmford, Norris and Pain2002; Caro, Reference Caro2010; Gauthier et al., Reference Gauthier, Debussche and Thompson2010). Often employing different taxa and/or criteria, these have been either coarse-scale and global in reach (e.g. Global Biodiversity Hotspots, Myers et al., Reference Myers, Mittermeier, Mittermeier, Da Fonseca and Kent2000; Centres of Plant Diversity, WWF & IUCN 1994–1997; Endemic Bird Areas, Stattersfield et al., Reference Stattersfield, Crosby, Long and Wege1998), or more fine-scale and regional, (e.g. Important Bird Areas, Fishpool & Evans, Reference Fishpool and Evans2001; Important Plant Areas, Anderson, Reference Anderson2002, Plantlife International, 2004; Important Mammal Areas, Linzey, Reference Linzey2002; Prime Butterfly Areas, van Swaay & Warren, Reference Van Swaay and Warren2003). Others (e.g. Key Biodiversity Areas) are sites of global importance for conservation of biodiversity and yet aimed at the site-scale (Langhammer et al., Reference Langhammer, Bakarr, Bennun, Brooks, Clay and Darwall2007), with the irreplaceability and vulnerability of species the main criteria.
Tanzania is widely regarded as being the most important country in mainland Africa for biodiversity and biological endemism, with the continent's highest mountain, deepest lakes and two globally significant biodiversity hotspots, the Eastern Arc Mountains and the Albertine Rift (Burgess et al., Reference Burgess, Lovett, Rodgers, Kilahama, Davenport, Butynski, Mittermeier, Gil, Hoffmann, Pilgrim, Brooks, Mittermeier, Lamoreux and da Fonseca2004a, Reference Burgess, D'amico Hales, Underwood, Dinerstein, Olson and Itoua2004b). However, Tanzania has the second highest rate of forest loss in sub-Saharan Africa (FAO, 2005) and, despite considerable conservation investment and a large amount of land nominally under protection, natural habitats and biodiversity continue to be lost at a significant rate (e.g. Rovero et al., Reference Rovero, Mtui, Kitegile and Nielsen2012). For a developing nation of such global natural resource importance, priority setting is an essential conservation tool.
A range of general national-level priority setting analyses has been carried out in Tanzania. The African Mammal Databank undertook an environmental suitability and species occurrence analysis (Boitani et al., Reference Boitani, Corsi, De Biae, D'inzillo Carranza, Ravagli and Reggiani1999), although extrapolations were based on species habitat suitability rather than species occupancy. No distinction was made at the subspecies level, and the extent and number of occupied protected areas was overestimated. The European Commission subsequently used these data to assess 31 protected areas in Tanzania for mammal, bird, amphibian and habitat irreplaceability (Hartley et al., Reference Hartley, Nelson, Mayaux and Grégoire2007), and IUCN's Gap Analysis evaluated whether protected areas safeguard biodiversity and how much biodiversity falls outside them (Langhammer et al., Reference Langhammer, Bakarr, Bennun, Brooks, Clay and Darwall2007). More specifically, the Alliance for Zero Extinction (Ricketts et al., Reference Ricketts, Dinerstein, Boucher, Brooks, Butchart and Hoffmann2005) aimed to identify sites that contain at least 95% of a known population of one or more Critically Endangered or Endangered species. In Africa, 76 sites and 122 species were identified and Tanzania had the most (eight) Alliance for Zero Extinction sites, seven of which are based on amphibians. However, because of the nature of the Alliance for Zero Extinction process there is a bias towards sites that have been better investigated, and thus the list for Tanzania is neither topical nor complete. Currently, the Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund is identifying Key Biodiversity Areas across the Eastern Afromontane Biodiversity Hotspot, including in Tanzania, but this work is not yet complete (BirdLife, 2012). At the species level there have been only two national analyses, the 77 Important Bird Areas of Tanzania (Baker & Baker, Reference Baker and Baker2002) and a partial identification of the nation's Important Plant Areas (McClean et al., Reference Mcclean, Doswald, Kuper, Sommer, Barnard and Lovett2006).
Primates are one of the most threatened and charismatic groups. The taxon is largely forest-dependent and Tanzania hosts eight endemic species. This represents 29% of its total primate species, a figure second only to Madagascar. Usually, it is the rare primate species that are less well studied, and this rarity is attributed to ecological specialization (Doherty & Harcourt, Reference Doherty and Harcourt2004). In Tanzania, however, the two rarest species are not obligate specialists (Davenport et al., Reference Davenport, De Luca, Bracebridge, Machaga, Mpunga, Kibure and Abeid2010; Nowak & Lee, Reference Nowak and Lee2011) and as little is known about their distribution and conservation status as about that of the more common species. With the exception of a species list recently constructed as part of a photographic atlas of East African primates (Reference De Jong and ButynskiDe Jong & Butynski, 2012) and a few site-specific primate lists (e.g. Rovero et al., Reference Rovero, Marshall, Jones and Perkin2009), Tanzania lacks a complete annotated list of its species (and subspecies/races) of diurnal and nocturnal primates, or a nationwide dataset of primate distribution and status. We provide here the first complete annotated list of Tanzanian primates, including diurnal and nocturnal species and subspecies. We also present a novel concept synonymous with Important Bird Areas, which we have called Priority Primate Areas, based on our compilation and comprehensive nationwide analysis of distributions and status. We identify these Priority Primate Areas to facilitate a focus on the range-restricted and threatened primate species and subspecies that will most benefit from conservation at the site-level. The intention is to quantify at a national scale the immediacy and precedence of threats to a group that has both considerable conservation relevance and charismatic appeal, thus identifying conservation gaps, providing ‘watch lists’ of priority sites and taxa using globally consistent criteria (Langhammer et al., Reference Langhammer, Bakarr, Bennun, Brooks, Clay and Darwall2007), and ensuring there is an objective, empirical and ranked plan to protect all of Tanzania's primates.
Specifically, we aim to (1) identify major populations and subpopulations of all primate species and subspecies in Tanzania, (2) rank species and subspecies according to their irreplaceability, vulnerability and conservation status (and anticipating future taxonomic change), (3) identify priority sites for conservation of primates on the basis of number of species present and rank, (4) provide a minimum critical list of sites whose protection would ensure the conservation of all of Tanzania's primates, (5) complement other taxa-specific analyses such as Important Bird Areas, (6) identify gaps in knowledge and conservation at a national scale, thus limiting duplication of conservation effort, and (7) provide a concept (Priority Primate Areas) that could be adopted internationally to prioritize implementation of the conservation of primate taxa. Primates are often flagship species (Caro, Reference Caro2010); by identifying and quantifying priority sites for primates in Tanzania we hope to ameliorate resource allocation problems facing government and conservation organizations (Rondinini et al., Reference Rondinini, Wilson, Biotani, Grantham and Possingham2006; Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Mcbridge, Bode and Possingham2006) and focus conservation attention on Tanzania's unique primate fauna and the habitats in which they dwell.
Methods
Species list
A full species list of the diurnal and nocturnal primates of Tanzania was drawn up (Table 1). We followed the taxonomy of Grubb et al. (Reference Grubb, Butynski, Oates, Bearder, Disotell, Groves and Struhsaker2003), and referred to Groves (Reference Groves2007) for Lophocebus johnstoni, Kingdon (Reference Kingdon1997) and Groves (Reference Groves, Wilson and Reeder2005) for Cercocebus sanjei, Davenport et al. (Reference Davenport, Stanley, Sargis, De Luca, Mpunga, Machaga and Olson2006) for Rungwecebus kipunji, Groves (Reference Groves2001, Reference Groves, Wilson and Reeder2005) for Chlorocebus pygerythrus, and Rahm (Reference Rahm, Napier and Napier1970), Napier (Reference Napier1985) and Kingdon (Reference Kingdon1997) for Colobus angolensis sharpei. Primate taxonomy is developing, occasionally contentious, and compounded by concepts such as superspecies and clines, and by personal interpretation. It is not our intention here to enter into taxonomic debate. Tanzanian primates also experience high levels of hybridization, such as between the baboons Papio anubis and Papio cynocephalus on the Tanzania–Kenya border (Alberts & Altmann, Reference Alberts and Altmann2001) and the several inter- and intraspecific Cercopithecine hybrid zones (Detwiler et al., Reference Detwiler, Burrell and Jolly2005), including Cercopithecus mitis albogularis and Cercopithecus mitis stuhlmanni in Ngorongoro and Lake Manyara, and Cercopithecus ascanius schmidti and Cercopithecus mitis doggetti in Gombe National Park (Detwiler, Reference Detwiler, Glenn and Cords2002). Although we recognize the presence of hybrids we did not include them in the analysis. We recognize two forms of Galagoides rondoensis, based on recent data (Perkin et al., unpubl. data).
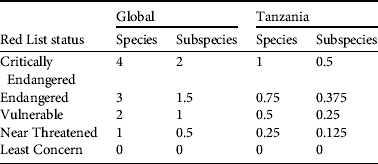
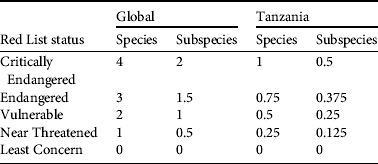
Table 1 List of primate species and subspecies in Tanzania, with their Red List status at the global (IUCN, 2012b) and national levels (see text for sources). Endemic taxa are in bold (note that national and global assessments are the same when a taxon is endemic).

Species scores
For each species and subspecies IUCN (2012b) proscriptions were applied. Following IUCN (2003) we also made assessments of the extinction risk of Tanzanian national populations of species and subspecies, as such evaluations were previously lacking. We thus assigned regional Red List categories to all Tanzanian taxa if the national status merited a classification higher than the global status (Table 1). Nationwide primate distributions were compiled from the literature, online databases, local expert knowledge and personal observations from our combined experience in Tanzania. Databanks included the IUCN Red List (IUCN, 2012b), the Primate Information Network factsheets (Primate Info Net, 2011), the African Mammals Databank (1999), the Tanzania Mammal Atlas Project (2013), the Pictorial Guide to Living Primates (2013), Tanzania National Parks websites and grey literature, although these mainly provided extent of occurrence estimates rather than occupancy.
Site list
A list of discrete sites in which species occur was compiled (Fig. 1). This followed the Alliance for Zero Extinction definition (Ricketts et al., Reference Ricketts, Dinerstein, Boucher, Brooks, Butchart and Hoffmann2005): ‘an area with a definable boundary within which the character of habitats, biological communities, and/or management issues have more in common with each other than they do with those in adjacent areas.’ Thus, sites such as Tongwe East (Forest Reserve) and Ugalla River (Game Reserve), and Kitulo (National Park) and Mt Rungwe (Nature Reserve) were treated separately, although contiguous, because of their different protected area status and hence management. Protected area data came from Protected Planet (2013), the Tanzania Ministry of Natural Resources and Tourism, and Tanzania National Parks. Areas to which species were introduced (Rubondo Island for Pan troglodytes and Colobus guereza, and Ngezi Forest, Pemba, for Procolobus kirkii), were not included although we recognize that these sites may contribute to species’ conservation and genetic and behavioural diversity.

Fig. 1 Location of the 62 sites considered in the ranking analysis of Priority Primate Areas.
Taxon conservation score
To rank sites it was first necessary to assign conservation scores to each taxon so that a summed score based on taxon presence could be applied. The taxon conservation score is a sum of a taxon's irreplaceability and vulnerability. For irreplaceability we modified the index used by the European Community (Hartley et al., Reference Hartley, Nelson, Mayaux and Grégoire2007), calculating 1/n (maximum = 1), where n = the number of sites in which a taxon occurs. To this site occupancy score we added a value reflecting the percentage of a taxon's total range that falls within Tanzania (maximum = 2.5; Table 2); this gives a proxy for percentage of the total population within Tanzania, data that are unavailable for most taxa. Thus taxon irreplaceability score = (1/n) + (% range score). We calculated a taxon vulnerability score using global Red List data (IUCN, 2012b) and our recommended Tanzanian Red List status (maximum = 4; Table 3), and the current population trend for each taxon. The latter was quantified according to whether the Tanzanian population is decreasing (0.5), stable or assumed stable (0), increasing (−0.5) or unknown (−0.25). Thus vulnerability score = Red List score + population trend score. Summing the scores of taxon irreplaceability and vulnerability produces an overall taxon conservation score (maximum total = 8).
Table 2 Scores assigned to the percentage of the total range of a primate species or subspecies that falls within Tanzania, for the calculation of the taxon conservation score (see text for details).

Site scores
A matrix was compiled of the 62 sites identified (Fig. 1) and occupancy by primates (Supplementary Table S1). The taxon conservation scores for primates at each site were summed, producing total site scores for nocturnal, diurnal and all (combined nocturnal and diurnal) species and all taxa (Supplementary Tables S2 & S3, respectively). Sites were then ranked according to their taxon scores: all species, nocturnal species, diurnal species, all taxa, nocturnal taxa and diurnal taxa. To derive a ranked list of Priority Primate Areas two simple complementarity analyses were performed, one by taxa frequency and the other by site rank. For the former we began with the site in each category that had the highest number of taxa and then added the next site that would add more taxa. This was continued until a list of Priority Primate Areas for species and taxa had been produced. For the latter we began with the site that ranked highest and subsequent complementary sites were added consecutively from the site rank list that added more species (Howard et al., Reference Howard, Davenport, Kigenyi, Viskanic, Baltzer and Dickinson2000; Brugiere, Reference Brugière2012).
Results
We recognize 27 species of primates in Tanzania (15 diurnal and 12 nocturnal species) and 43 taxa (26 diurnal and 17 nocturnal) including subspecies (Table 1). Of these, four are endemic diurnal primate species (C. sanjei, R. kipunji, Procolobus gordonorum and P. kirkii), four are endemic nocturnal species (Galagoides orinus, G. rondoensis, Galagoides sp. nov. and Galagoides zanzibaricus), and four are endemic diurnal subspecies (Chlorocebus pygerythrus nesiotes, Erythrocebus patas baumstarki, Colobus angolensis subsp. nov. and Colobus guereza caudatus). The list includes two species that are categorized on the IUCN Red List as Critically Endangered, five as Endangered, two as Near Threatened and 18 as Least Concern (IUCN, 2012b). At the subspecies level two are categorized as Critically Endangered, three as Endangered, four as Vulnerable, one as Data Deficient and 19 as Least Concern (IUCN, 2012b). At the national level two species are categorized as Critically Endangered, eight as Endangered, three as Vulnerable, two as Near Threatened and 11 as Least Concern, and at national subspecies level, two as Critically Endangered, one as Endangered, four as Vulnerable, one as Near Threatened, two as Not Evaluated and 13 as Least Concern (IUCN, 2012b). We assigned putative Red List categories (IUCN, 2003) for 11 taxa; the relevant justifications are given in Table 1.
The comparative rankings of each taxon are illustrated in Tables 4–5. The taxon conservation scores produced the same top six primates irrespective of whether the analysis was at the species or taxon level. These were R. kipunji, G. rondoensis, C. sanjei, P. gordonorum, P. kirkii and Galagoides sp. nov. Of the 62 sites identified as being of importance for conservation of primates 57 are officially or nominally protected (nine national parks; six nature reserves; 34 forest reserves, including four proposed nature reserves; seven game reserves; and one conservation area). The other five sites are either privately managed or have no protection status.
On application of the taxon conservation scores to the 62 sites, a matrix was drawn up illustrating the Priority Primate Areas across Tanzania according to all diurnal and nocturnal species and all diurnal and nocturnal taxa (Supplementary Tables S2–S3). When all primates are considered, either at the species level or species and subspecies level, the sites that emerged to be most important are Kilombero Nature Reserve, Udzungwa Mountains National Park and Uzungwa Scarp Forest Reserve, with Kitulo National Park and Mt Rungwe Nature Reserve in joint fourth place (Fig. 2). If diurnal and nocturnal primates are treated separately, Mahale Mountains National Park is placed fourth for diurnal taxa (Fig. 3). The nocturnal primates produced a different assessment. At both the species and all taxa levels, Saadani National Park, Pande Game Reserve, and Pugu/Kazimzumbwe, Chitoa, Litipo, Rondo, Ruawa and Ziwani Forest Reserves all illustrated the importance of Tanzania's coastal forests for galago taxa (Fig. 4).

Fig. 2 Top-ranking sites for (a) all primate species and (b) all taxa (i.e. species and subspecies). All species: 1, Kilombero Nature Reserve*†; 2, Udzungwa Mts National Park†; 3, Uzungwa Scarp Forest Reserve†; 4=, Mt Rungwe Nature Reserve*†; 4=, Kitulo National Park*†; 6, Saadani National Park; 7, Mahale National Park; 8=, Pande GR*†; 8=, Pugu/Kazimzumbwe Forest Reserve*†; 10, Magombera†. All taxa: 1–5, as above; 6, Mahale National Park; 7, Magombera; 8, Jozani-Chwaka Bay National Park†; 9, Minziro Forest Reserve; 10=, Kiwengwa-Pongwe Forest Reserve†; 10=, Uzi and Vundwe Islands†. *Critically Endangered species; †endemic species present.

Fig. 3 Top-ranking sites for (a) diurnal primate species and (b) taxa (i.e. species and subspecies). Diurnal species: 1, Kilombero Nature Reserve*†; 2=, Udzungwa Mts National Park†; 2=, Uzungwa Scarp Forest Reserve†; 4, Mahale National Park; 5=, Mt Rungwe Nature Reserve*†; 5=, Kitulo National Park*†; 7, Magombera†; 8, Gombe National Park; 9, Jozani-Chwaka Bay National Park†; 10=, Kiwengwa-Pongwe Forest Reserve†; 10=, Uzi/Vundwe Islands†. Diurnal taxa: 1–5=, as above; 7, Gombe National Park; 8, Magombera; 9, Jozani-Chwaka Bay National Park; 10, Minziro Forest Reserve. *Critically Endangered species; †endemic species present.

Fig. 4 Top-ranking sites for (a) nocturnal primate species and (b) taxa (i.e. species and subspecies). Nocturnal species: 1, Saadani National Park; 2=, Pande GR*†; 2= Pugu/Kazimzumbwe Forest Reserve*†; 4=, Ruawa Forest Reserve; 4=, Chitoa Forest Reserve; 4=, Litipo Forest Reserve*†; 4=, Rondo Forest Reserve*†; 4=, Ziwani Forest Reserve*†; 9, Udzungwa Mts National Park†; 10, Kilombero Nature Reserve†. Nocturnal taxa: 1, Udzungwa Mts National Park; 2, Saadani National Park; 3, Kilombero Nature Reserve; 4=, Amani Forest Reserve; 4=, Mkungwe Forest Reserve; 4=, Nilo Nature Reserve; 7, Selous GR; 8=, Pande GR; 8=, Pugu/Kazimzumbwe Forest Reserve; 10=, Mt Rungwe Nature Reserve† 10=, Kitulo National Park†. *Critically Endangered species; †endemic species present.
To derive an applied and ranked list of priority areas for conservation of primates, two sets of Priority Primate Areas were determined based on the two complementarity analyses. For both the taxa frequency analysis and the site rank analysis, a list of nine sites (with possible alternatives) was identified for the 27 primate species, and 14 sites (with alternatives) for the 43 primate taxa (Tables 6–7). Seven Priority Primate Areas were identified separately for the 15 diurnal species, eight for the 12 nocturnal species, 11 for the 26 diurnal taxa, and 10 for the 17 nocturnal taxa.
Discussion
Given that endemism of primates in Tanzania is 29.6% at species level and 28.6% at species and subspecies level combined, with the highest number of threatened primate taxa in mainland Africa, the country is of global conservation significance. However, Tanzania still faces substantial challenges, with a growing human population, ever pressing needs for development and growth, and an increasingly fragmented and human-dominated landscape. Prioritization of conservation interventions is thus of particular importance for a nation with such a responsibility. Because of their diversity, broad appeal and taxonomic tractability, birds have often been used as effective indicators of biodiversity and habitat health (Howard et al., Reference Howard, Viskanic, Davenport, Kigenyi, Baltzer and Dickinson1998), although cross-taxon congruence has been less reliable, in part because of birds' greater mobility (Tsushabe et al., Reference Tsushabe, Kalema, Byaruhanga, Asasira, Ssegawa and Balmford2006). Despite their charismatic qualities and evolutionary proximity to humans, primates have been less of a focus for priority setting and less often used as surrogate taxa for broader conservation needs. This priority setting for primates is the first such national analysis, and offers an objective, quantifiable protocol for the identification of Priority Primate Areas. We have developed this method both to provide the means to replicate the process of prioritizing sites important for primates in other countries and to help focus national conservation priorities in Tanzania.
There were a number of challenges, and compromises made, in designing this system, the foremost being how best to define a site. We concluded that an area must have a definable boundary within which the character of habitats, biological communities, and/or management issues have more in common with each other than they do with those in adjacent areas. Conservation must be pragmatic. However, it is clear that prioritization of forest sites can change as lesser known areas are investigated (Burgess et al., Reference Burgess, Butynski, Cordeiro, Doggart, Fjeldså and Howell2007; Davenport et al., Reference Davenport, Mpunga and Machaga2007). That notwithstanding, the correlation between site rankings and degree of survey effort (Doggart et al., Reference Doggart, Perkin, Kiure, Fjeldsa, Poynton and Burgess2006) is less of an issue with smaller taxonomic groups such as primates.
There are a number of sites in Tanzania where primate species have been introduced, notably Rubondo Island in Lake Victoria (P. troglodytes and C. guereza), Ngezi Forest on Pemba Island and Masingini Forest on Zanzibar (Unguja) Island (P. kirkii). We made the decision not to include sites where species had been introduced, although in some instances this was difficult to prove. For example, it is not known whether vervets are indigenous to Zanzibar but there is no irrefutable evidence to the contrary. It is the case that introductions are different to reintroductions on the basis that reintroductions are a valid conservation tool. However, although P. kirkii were introduced to Masingini (Silkiluwasha, Reference Silkiluwasha1981) it is unclear if they were there formerly. Therefore, we omitted P. troglodytes and C. guereza in Rubondo and P. kirkii in Ngezi and, as we have no evidence of their former presence in Masingini, we omitted them at this site too. For the same reason we retained vervets in the analysis.
Our study highlighted eight species of particular conservation concern in Tanzania: R. kipunji, G. rondoensis, C. sanjei, P. kirkii, P. gordonorum, Galagoides sp. nov., P. troglodytes and G. orinus. We also assigned a threat category to a number of taxa that had not previously been designated (Table 1). However, our main aim was to identify all key primate sites in Tanzania, to prioritize conservation intervention and facilitate the role of primates as flagship or umbrella species (Caro, Reference Caro2011) for the conservation of key habitats. The list of Priority Primate Areas identified differs according to whether species and subspecies, and diurnal or nocturnal taxa are considered (Supplementary Tables S2–S3). Top-ranking sites for diurnal taxa are in the Udzungwa Mountains, Southern Highlands, Zanzibar archipelago, two forested western national parks (Gombe and Mahale), and the north-western forest of Minziro within the Guinea-Congo biome. The top-ranking sites for nocturnal taxa, although also including the Udzungwa Mountains and Southern Highlands, predominantly include sites in the coastal forest zone from the East Usambaras in the north to the south-eastern Lindi forests, as well as the Selous Game Reserve in south-central Tanzania. There is, therefore, little overlap in the importance of sites for diurnal and nocturnal primate species, suggesting that the former cannot be used as a surrogate for the latter.
Forests are of most relevance for conservation of primates and are ranked accordingly in our analyses. This is in contrast to many Important Bird Areas, where savannah and wetland habitats are often equally important. However, 44 of the 62 Priority Primate Areas are also Important Bird Areas or parts of them. Highest ranking in the Priority Primate Areas are the species-rich forests of the Eastern Arc Mountains, the Southern Highlands, including Mt Rungwe and Livingstone Mountains, and the northern ranges incorporating Kilimanjaro, Mt Meru (Arusha National Park) and Ngorongoro. However, because of their soils, rainfall and drainage, forested areas are also important for agriculture and forest products, and are therefore often zones of the greatest human–primate conflict.
Based on recent reports of accelerating forest loss, sites needing particular conservation attention include the forest reserves of Chome, East Usambaras, Ilole, Mbizi, Milo, Uzungwa Scarp and Ziwani, and the unprotected forests of Magombera, Mbuzi, Uzi and Vundwe Islands (Davenport et al., Reference Davenport, Mpunga and Machaga2007; Nowak et al., Reference Nowak, Perkin and Jones2009; Nowak & Lee, Reference Nowak and Lee2011; Rovero et al., Reference Rovero, Mtui, Kitegile, Nielsen and Jones2010, Reference Rovero, Mtui, Kitegile and Nielsen2012). The coastal forests of Pugu and Kazimzumbwe (two of four forests in the Dar es Salaam greenbelt; Monga & Gwegime, Reference Monga and Gwegime2011) are subjected to high human disturbance because of their proximity to Dar es Salaam and the city's demand for charcoal and timber. However, these forests are potentially manageable as an urban recreational and educational asset. In general however, the charcoal industry is growing rapidly and is a major threat to forests nationwide. Remote locations, such as the Lindi forests (Perkin et al., Reference Perkin, Samuel and Gwegime2011), are safer from these pressures but often receive little management attention as a result.
Of the 62 Priority Primate Areas only five (Ilole, Madehani, Magombera, Mbuzi and Uzi and Vundwe Islands) have no official protection status. However, this gives a misleading impression because few forest reserves in Tanzania are actively managed in any way. Game Reserve management usually depends on the zeal of individual concession holders. Thus not all of the Priority Primate Areas we propose are equal in terms of conservation management. Although a national park should be considered safer than a forest reserve, few protected areas are managed adequately and adjacent human density can be an important factor determining conservation success (Wittemeyer et al., Reference Wittemeyer, Elsen, Bean, Burton and Brashares2008).
The critical subset of Priority Primate Areas (Tables 6–7) attempts to rationalize through complementarity the full list of areas and demonstrates how selective targeting could conserve Tanzania's primates. The protection of just nine sites, totalling 8,679 km2, would protect all 27 of Tanzania's primate species. This subset includes six national parks (Kilimanjaro, Kitulo, Mahale, Saadani, Udzungwa and Jozani-Chwaka Bay), one nature reserve (Kilombero) and two forest reserves (Minziro and Mgambo). The addition of just three forest reserves (Rondo, Kilulu Hill and Ngezi) and two game reserves (Grumeti and Biharamulo) results in a list of 14 Priority Primate Areas comprising 10,561 km2 (1.1%) of Tanzania's total land area, the conservation of which would ensure the protection of all 43 of Tanzania's primate taxa (species and subspecies). We believe therefore that adoption of the Priority Primate Area system as a guiding concept could help focus efforts to conserve primates in Tanzania, and also globally.
Table 4 The comparative ranking of each primate species based on the taxon conservation score (maximum = 8; see text for details).

Table 5 The comparative ranking of each primate taxon (i.e. species or subspecies) based on the taxon conservation score (maximum = 8; see text for details).

Table 6 Minimum critical set of Priority Primate Areas, based on complementarity analyses (see text for further details), for all, diurnal and nocturnal species. The sites are those that would at a minimum need to be protected to conserve at least one population of each of Tanzania's primate species.

* NR, Nature Reserve; NP, National Park; FR, Forest Reserve
Table 7 Minimum critical set of Priority Primate Areas, based on complementarity analyses (see text for further details), for all, diurnal and nocturnal taxa (i.e. species and subspecies). The sites are those that would at a minimum need to be protected to conserve at least one population of each of Tanzania's primate taxa.

* NR, Nature Reserve; NP, National Park; FR, Forest Reserve; GR, Game Reserve
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Wildlife Conservation Society. We are grateful to the following people for information and assistance: Liz Baker, Simon Bearder, Tom Butynski, Tim Caro, Anthony Collins, Daniela De Luca, Kate Detwiler, Nike Doggart, Richard Estes, Charles Foley, Trevor Jones, Yvonne de Jong, Alex Lobora, Jonathan Kingdon, Sophy Machaga, Noah Mpunga, Arafat Mtui, Alex Piel, the late Alan Rodgers, Francesco Rovero, Bill Stanley, Fiona Stewart and Tom Struhsaker.
Biographical sketches
Tim Davenport's research interests include biogeography, exploration, herpetology, human impacts, orchidology, primatology and protected areas. Kate Nowak studies primate and elephant behaviour and the use of refuge habitats in flooded and montane forests. Andrew Perkin studies the phylogeography, bioacoustics and taxonomy of galagos with a focus on forested landscapes, and hyrax and elephant shrew diversity.