Article contents
Multiconfigurational Carbon-Group V Pair Defects in Silicon
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 February 2011
Abstract
In addition to a new configuration of the previously reported multistable carbon-phosphorus pair, we report on two new multiconfìgurational defects in electron irradiated silicon doped, with arsenic and antimony. These defects are also identified as interstitial carbon-substitutional group V pairs, (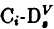 ). We identified two different types of metastability for
). We identified two different types of metastability for 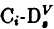 . Type I is similar to the bistable carbon-carbon pair defect for which a bond switching mechanism has been reported [1]. Type II is similar to donor-acceptor pairs in silicon which show electrostatically driven metastability [2,3]. The three
. Type I is similar to the bistable carbon-carbon pair defect for which a bond switching mechanism has been reported [1]. Type II is similar to donor-acceptor pairs in silicon which show electrostatically driven metastability [2,3]. The three 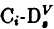 pairs have many similar features, but also show surprising donor related differences. In this paper we will discuss the general features of these defects.
pairs have many similar features, but also show surprising donor related differences. In this paper we will discuss the general features of these defects.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1990
References
- 6
- Cited by


