Article contents
High-Purity Germanium Technology for Gamma-Ray and X-Ray Spectroscopy
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 February 2011
Abstract
High-purity germanium (HPGe) for gamma-ray spectroscopy is a mature technology that continues to evolve. Detector size is continually increasing, allowing efficient detection of higher energy gamma rays and improving the count rate and minimum detectable activity for lower energy gamma rays. For low-energy X rays, entrance window thicknesses have been reduced to where they are comparable to those in Si(Li) detectors. While some limits to HPGe technology are set by intrinsic properties, the frontiers have historically been determined by the level of control over extrinsic properties. The point defects responsible for hole trapping are considered in terms of the “standard level” model for hole capture. This model originates in the observation that the magnitude and temperature dependence of the cross section for hole capture at many acceptors in germanium is exactly that obtained if all incident s-wave holes were captured. That is, the capture rate is apparently limited by the arrival rate of holes that can make an angular-momentum-conserving transition to a s ground state. This model can also be generalized to other materials, where it may serve as an upper limit for direct capture into the ground state for either electrons or holes. The capture cross section for standard levels σS.L. is given by
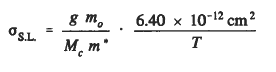
where g is the degeneracy of the ground state of the center after capture, divided by the degeneracy before capture. Mc is the number of equivalent extrema in the band structure for the carrier being captured, mo is the electronic mass, m* is the effective mass, and T is the temperature in degrees Kelvin.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1993
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


