Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 February 2011
Low-temperature magneto-luminescence studies are used to examine the in-plane valence-band dispersion in GaAs/GaPAs strained-layer-superlattice structures. The results provide a direct observation of valence-band mixing effects in strained-layer systems.
Theoretical and experimental studies of the effect of valence-band mixing upon the magneto-transport properties and magneto-luminescence data for GaAs/AlGaAs latticed-matched superlattices have been recently reported.[1–] Due to the presence of the 2D-quantum well, the valence-band degeneracy between the light-hole and heavy-hole bands at 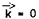 is removed. These studies show, however, that the lowest energy valence-band mass is still strongly dependent upon
is removed. These studies show, however, that the lowest energy valence-band mass is still strongly dependent upon 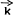 due to valence-band mixing. On the other hand, because of the large biaxial compression in strained-layer-super lattices (SLS), valence-band mixing effects should be minimal.[8–9] Recent magneto-transport measurements[10] on p-type InGaAs/GaAs SLS structures have provided information regarding nonparabolic valence-bands in these structures.
due to valence-band mixing. On the other hand, because of the large biaxial compression in strained-layer-super lattices (SLS), valence-band mixing effects should be minimal.[8–9] Recent magneto-transport measurements[10] on p-type InGaAs/GaAs SLS structures have provided information regarding nonparabolic valence-bands in these structures.