Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 February 2011
Volatile and thermally stable nickel complexes have been prepared by the reaction of fluorine substituted, nickel β–diketonates with neutral (poly)oxygen and (poly)nitrogen donor ligands.
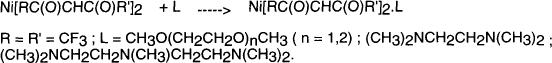
These complexes, which have low melting points, have been applied as precursors in MOCVD experiments directed on nickel and nickel oxide deposition. Investigations into the deposition of NiO in porous YSZ via particle precipitation MOCVD, for the development of an anode for a planar Solid Oxide Fuel Cell, are reported.