Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 February 2011
High resolution transmission electron microscopy techniques have been used to obtain information on the contrast, spatial distribution, size and annealing behaviour of the damaged regions produced within individual collision cascades by heavy ion (As, Sb and Bi) bombardment (10–120 KeV) of silicon with 1.0 × 1011 – 6.0 × 1011 ions cm−2. The fraction of the theoretical cascade volume occupied by a heavily damaged region steadily increased as the average deposited energy density 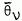 within the cascade increased. At high energy densities, the visible damage produced in the main cascade consisted of a single, isolated damaged region. With decreasing values of
within the cascade increased. At high energy densities, the visible damage produced in the main cascade consisted of a single, isolated damaged region. With decreasing values of 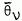 (i.e. increasing ion implant energies), there was an increasing tendency for multiple damaged regions to be produced within the main cascade.
(i.e. increasing ion implant energies), there was an increasing tendency for multiple damaged regions to be produced within the main cascade.