Article contents
Atomic Defects in Intermetallic Compounds and Diffusion Processes
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 February 2011
Abstract
For the understanding of the properties of the technically important intermetallic compounds as transition metal aluminides and silicides the understanding of atomic defect properties is pivotal. From recent positron lifetime studies high or low values for the effective vacancy formation enthalpy 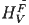 were found for close-packed or for more open-structured bcc type compounds, respectively, which can be well understood theoretically. In B2-FeAl the vacancy migration enthalpy
were found for close-packed or for more open-structured bcc type compounds, respectively, which can be well understood theoretically. In B2-FeAl the vacancy migration enthalpy 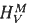 could be additionally derived at high temperatures from vacancy equilibration processes. It is shown here by a study on B2-FeAl in comparison to the positron annihilation experiments that the thermal formation and migration of defects can be specifically investigated by time-dependent length-change experiments at high temperatures by the defect equilibration behavior after temperature changes. With the present data on vacancy formation and migration the wide variation of the transition-metal self-diffusivities in intermetallic compounds can be understood.
could be additionally derived at high temperatures from vacancy equilibration processes. It is shown here by a study on B2-FeAl in comparison to the positron annihilation experiments that the thermal formation and migration of defects can be specifically investigated by time-dependent length-change experiments at high temperatures by the defect equilibration behavior after temperature changes. With the present data on vacancy formation and migration the wide variation of the transition-metal self-diffusivities in intermetallic compounds can be understood.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1998
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by


