Article contents
Study of Mo selenisation process on different Mo substrates
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 January 2011
Abstract
In the present work we studied the influence of selenisation temperature, Se vapour pressure and duration of the process on the properties of MoSe2 layer formed on Mo-foil and on sputtered Mo layers on soda lime and Mo-on-ITO glasses. We found that MoSe2 layer thickness (dL) on Mo-foil depended linearly on selenisation time. The thickness of MoSe2 layer on Mo-foil (dL) depended on Se vapour pressure as a function 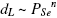 , where n ≈ 0.5. The same dependence was also found for sputtered Mo layers in low Se vapour pressure region of 13 – 133 Pa. MoSe2 layer thickness depended on the origin of Mo layer which is related with the density of Mo layer: MoSe2 on Mo foil was thicker than on sputtered Mo. All the MoSe2 layers were full of cracks if Se vapour pressure was higher than 1333 Pa. All tested MoSe2 layers showed p-type conductivity.
, where n ≈ 0.5. The same dependence was also found for sputtered Mo layers in low Se vapour pressure region of 13 – 133 Pa. MoSe2 layer thickness depended on the origin of Mo layer which is related with the density of Mo layer: MoSe2 on Mo foil was thicker than on sputtered Mo. All the MoSe2 layers were full of cracks if Se vapour pressure was higher than 1333 Pa. All tested MoSe2 layers showed p-type conductivity.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2009
References
- 4
- Cited by


