No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 February 2011
Surface superstructures (reconstructed structures) have been observed by many authors. However, it is not easy to confirm that a superstructure does exist at an interface between two solid layers. The present paper reports a direct observation, by a grazing incidence x-ray diffraction technique with use of synchrotron radiation, of superstructures at the interface. Firstly, the boron-induced 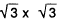 R30° reconstruction at the Si interface has been investigated. At the a Si/Si(111) interface, boron atoms at 1/3 ML are substituted for silicon atoms, thus forming a
R30° reconstruction at the Si interface has been investigated. At the a Si/Si(111) interface, boron atoms at 1/3 ML are substituted for silicon atoms, thus forming a 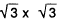 R30° lattice. Even at the interface between a solid phase epitaxial Si(111) layer and a Si(111) substrate, the boron-induced
R30° lattice. Even at the interface between a solid phase epitaxial Si(111) layer and a Si(111) substrate, the boron-induced 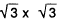 R30° reconstruction has been also observed. Secondly, SiO2/Si(100)-2×l interfacial superstructures have been investigated. Interfacial superstructures have been only observed in the samples of which SiO2 layers have been deposited with a molecular beam deposition method. Finally, the interfaces of MOCVD-grown AIN/GaAs(100) have been shown to have 1×4 and 1×6 superstructures.
R30° reconstruction has been also observed. Secondly, SiO2/Si(100)-2×l interfacial superstructures have been investigated. Interfacial superstructures have been only observed in the samples of which SiO2 layers have been deposited with a molecular beam deposition method. Finally, the interfaces of MOCVD-grown AIN/GaAs(100) have been shown to have 1×4 and 1×6 superstructures.