No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 July 2011
We conduct first-principles total-energy density functional calculations to study the interaction of H2 on ZnO surfaces. Four surface models of Zn-terminated (0001)-, O-terminated (0001)-, 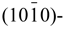 , and
, and 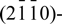 oriented ZnO planes in the presence of H2 are evaluated. The relative stability of four different surface models is examined as a function of the chemical potentials of oxygen and hydrogen. We find that only surfaces of O-terminated (0001)-oriented ZnO models exhibit active sites for the dissociation of H2, which in turn enables the formation of water from dissociative chemisorption of 2H on the O-terminated ZnO(0001) surface. The surface energy of O-terminated ZnO(0001) surface in the presence of water was found to be negative under the O-rich and H-rich condition. The findings agree with the experimental observations that ZnO epitaxial layers are easily etched by hydrogen at typical growth temperatures.
oriented ZnO planes in the presence of H2 are evaluated. The relative stability of four different surface models is examined as a function of the chemical potentials of oxygen and hydrogen. We find that only surfaces of O-terminated (0001)-oriented ZnO models exhibit active sites for the dissociation of H2, which in turn enables the formation of water from dissociative chemisorption of 2H on the O-terminated ZnO(0001) surface. The surface energy of O-terminated ZnO(0001) surface in the presence of water was found to be negative under the O-rich and H-rich condition. The findings agree with the experimental observations that ZnO epitaxial layers are easily etched by hydrogen at typical growth temperatures.