Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 October 2020
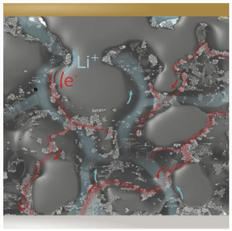
Electrochemical energy-storage systems such as supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries require complex intertwined networks that provide fast transport pathways for ions and electrons without interfering with their energy density. Self-assembly of nanomaterials into hierarchical structures offers exciting possibilities to create such pathways. This article summarizes recent research achievements in self-assembled zero-dimensional, one-dimensional, and two-dimensional nanomaterials, ordered pore structure materials, and the interfaces between these. We analyze how self-assembly strategies can create storage architectures that improve device performance toward higher energy densities, longevity, rate capability, and device safety. At the end, the remaining challenges of scalable low-cost manufacturing and future opportunities such as self-healing are discussed.