Mechanophores are compounds that respond to an externally applied mechanical force by undergoing chemical changes. In some cases, this response alters the fluorescence characteristics of these motifs. Embedding these molecules into polymers has tremendous industrial appeal for synthesizing luminescent (light-emitting) polymers that can then be used to develop precise stress sensors and visual detectors of stress and strain.
The traditional approach to achieving this goal has relied on weak chemical bonds that are broken when the molecules are mechanically stressed, leading to luminescence. This approach, however, suffers from a number of disadvantages: the chemical bond cleavage requires high activation energy, is irreversible, and can also be induced by light or heat, rather than mechanical force alone, making it less specific. A research team led by Christoph Weder at the University of Fribourg and Yoshimitsu Sagara, an assistant professor at Hokkaido University, has now overcome these limitations. In a recently published report in ACS Central Science (doi:10.1021/acscentsci.9b00173), they describe a new class of blue, green, and red light-emitting mechanophores, which when combined with a polymer, yield thin films that emit white light when mechanically stressed. Importantly, since these systems do not rely on breaking chemical bonds, they involve a low activation energy, are reversible, and respond only to a mechanical force stimulation.
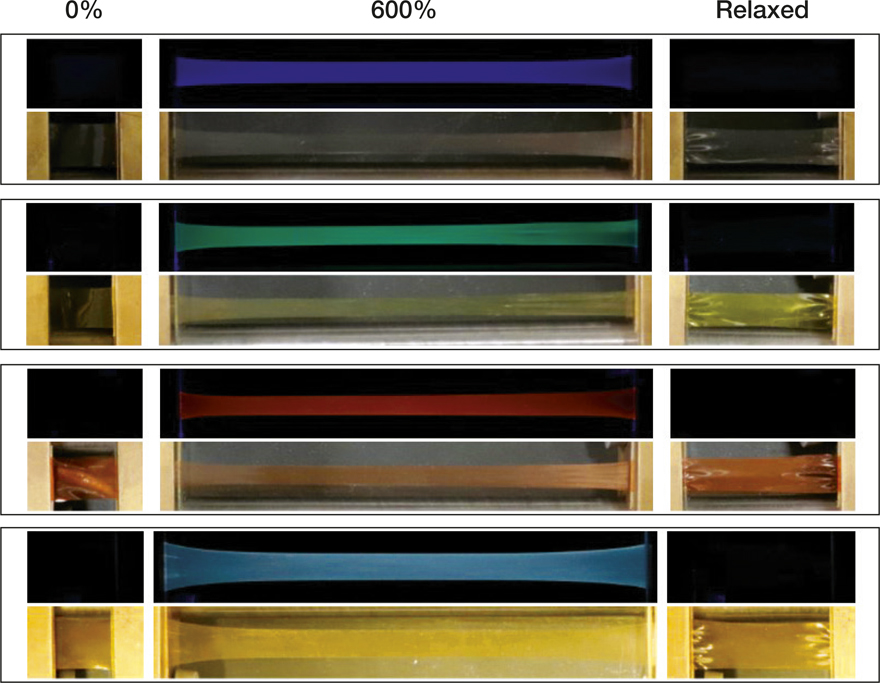
Photographs showing the mechanoresponsive luminescence behavior of blue-, green-, red-, and white-light-emitting polymer films upon deformation. In each panel, top rows show images taken under 365-nm ultraviolet light excitation and bottom rows show images taken in room light. Percentages represent applied strain. Credit: American Chemical Society.
The demonstration employed light-emitting molecules called rotaxanes, a terminology that derives from their shapes that resemble dumb-bells. According to Weder, the key aspect of this approach is that it allows tailoring the properties of the rotaxane-based mechanophores on demand in a simple and predictive manner.
“We chose to demonstrate this by tackling white mechanofluorescence as a difficult-to-achieve target: this goal requires the combination of three mechanofluorophores with predefined emission colors and similar mechanoresponse,” Weder says. In the polymer, obtaining white mechanofluorescene was possible because their approach enabled a straightforward integration of any given chromophore pair without affecting the mechanoresponse. “This allowed us to select three emitters that we knew from small molecule studies would in combination afford white light, and integrate them into this platform,” Weder says.
The research team synthesized rotaxanes that had a light-emitting group, or luminophore, located close to a chemical unit that served the role of a “quencher” by swiftly accepting the excited electron. In the “off-state,” the close proximity of the luminophore and the quencher ensures that the luminescence is quenched. However, when the molecule is mechanically deformed, the luminophore unit is displaced away from the quencher.
If the molecule is now excited with ultraviolet photons, the subsequent absorption and electronic transition leads to detectable luminescence, thereby allowing direct visual detection of mechanical stress. This is the “on-state” of the molecule with the emitted color being blue, green, or red depending upon the luminophore unit employed. Releasing the stress brings the molecules into their original off-state and quenches the luminescence. Mixing the three systems together, the team was able to realize white-light emitting mechanically responsive polymer films.
Maxwell J. Robb, an assistant professor of chemistry at the California Institute of Technology, is excited about this discovery and feels that the findings have overcome a major obstacle in the field of polymer mechanochemistry. Robb says the report “expands on their recent breakthrough innovation of fluorescence-switching rotaxane-based supramolecular mechanophores that require unusually low activation energy. The team now demonstrates that the fluorescence color can be tailored by incorporating different luminophores into the rotaxane structure to ultimately enable a white-light-emitting material that retains the same sensitivity to mechanical force.” Robb highly recommends the videos that accompany the article, found under Supporting Information at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acscentsci.9b00173.


