No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 February 2010
Let Cn be the n-dimensional complex number space of the complex variables z1,…, zn and 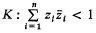 be the unit hypersphere. Further, let G be the group of all holomorphic automorphisms of K, then G is a n(n + 2)-dimensional real Lie group. In [3] the author has proved that for any P∈∂K (the boundary of K) there exists a decomposition of G in the form
be the unit hypersphere. Further, let G be the group of all holomorphic automorphisms of K, then G is a n(n + 2)-dimensional real Lie group. In [3] the author has proved that for any P∈∂K (the boundary of K) there exists a decomposition of G in the form 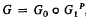 , where G0 is the group of all analytic rotations about the origin and
, where G0 is the group of all analytic rotations about the origin and 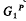 is a 2n-dimensional real Lie group, whose underlying topological space is K, which acts transitively on K and P is a fixed point of all elements of
is a 2n-dimensional real Lie group, whose underlying topological space is K, which acts transitively on K and P is a fixed point of all elements of 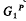 .
.