Article contents
DIOPHANTINE APPROXIMATION ON MANIFOLDS AND LOWER BOUNDS FOR HAUSDORFF DIMENSION
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 November 2017
Abstract
Given 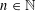 $n\in \mathbb{N}$ and
$n\in \mathbb{N}$ and 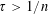 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}>1/n$, let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}>1/n$, let 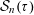 ${\mathcal{S}}_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F})$ denote the classical set of
${\mathcal{S}}_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F})$ denote the classical set of  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$-approximable points in
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$-approximable points in 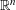 $\mathbb{R}^{n}$, which consists of
$\mathbb{R}^{n}$, which consists of 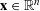 $\mathbf{x}\in \mathbb{R}^{n}$ that lie within distance
$\mathbf{x}\in \mathbb{R}^{n}$ that lie within distance 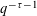 $q^{-\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}-1}$ from the lattice
$q^{-\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}-1}$ from the lattice 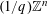 $(1/q)\mathbb{Z}^{n}$ for infinitely many
$(1/q)\mathbb{Z}^{n}$ for infinitely many 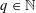 $q\in \mathbb{N}$. In pioneering work, Kleinbock and Margulis showed that for any non-degenerate submanifold
$q\in \mathbb{N}$. In pioneering work, Kleinbock and Margulis showed that for any non-degenerate submanifold 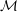 ${\mathcal{M}}$ of
${\mathcal{M}}$ of 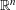 $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ and any
$\mathbb{R}^{n}$ and any 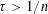 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}>1/n$ almost all points on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}>1/n$ almost all points on 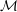 ${\mathcal{M}}$ are not
${\mathcal{M}}$ are not  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$-approximable. Numerous subsequent papers have been geared towards strengthening this result through investigating the Hausdorff measure and dimension of the associated null set
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$-approximable. Numerous subsequent papers have been geared towards strengthening this result through investigating the Hausdorff measure and dimension of the associated null set 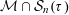 ${\mathcal{M}}\cap {\mathcal{S}}_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F})$. In this paper we suggest a new approach based on the Mass Transference Principle of Beresnevich and Velani [A mass transference principle and the Duffin–Schaeffer conjecture for Hausdorff measures. Ann. of Math. (2) 164(3) (2006), 971–992], which enables us to find a sharp lower bound for
${\mathcal{M}}\cap {\mathcal{S}}_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F})$. In this paper we suggest a new approach based on the Mass Transference Principle of Beresnevich and Velani [A mass transference principle and the Duffin–Schaeffer conjecture for Hausdorff measures. Ann. of Math. (2) 164(3) (2006), 971–992], which enables us to find a sharp lower bound for  $\dim {\mathcal{M}}\cap {\mathcal{S}}_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F})$ for any
$\dim {\mathcal{M}}\cap {\mathcal{S}}_{n}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F})$ for any 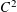 $C^{2}$ submanifold
$C^{2}$ submanifold 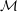 ${\mathcal{M}}$ of
${\mathcal{M}}$ of  $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ and any
$\mathbb{R}^{n}$ and any  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$ satisfying
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$ satisfying 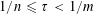 $1/n\leqslant \unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}<1/m$. Here
$1/n\leqslant \unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}<1/m$. Here 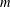 $m$ is the codimension of
$m$ is the codimension of 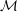 ${\mathcal{M}}$. We also show that the condition on
${\mathcal{M}}$. We also show that the condition on  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$ is best possible and extend the result to general approximating functions.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}$ is best possible and extend the result to general approximating functions.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © University College London 2017
References
- 6
- Cited by


