Article contents
AN EXTENSION OF A THEOREM OF HLAWKA
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 April 2010
Abstract
This paper extends Hlawka’s theorem (from the point of view of Siegel and Weil) on SL(n,ℝ)/SL(n,ℤ) to Sp(n,ℝ)/Sp(n,ℤ). Namely, if Vn=vol(Sp(n,ℝ)/Sp(n,ℤ), where the measure is the Sp(n,ℝ)-invariant measure on Sp(n,ℝ)/Sp(n,ℤ), then Vn can be expressed in terms of the Riemann zeta function by 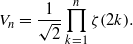 As a consequence, let D be a domain of a sufficiently regular set in ℝ2n. Then:
As a consequence, let D be a domain of a sufficiently regular set in ℝ2n. Then:
(i) if vol(D)>Vn, then some lattice in ℝ2n contains a non-zero point of D;
(ii) if vol(D)<Vn, then some lattice in ℝ2n contains only the zero point of D;
(iii) if D is star-shaped about the origin and vol(D)<ζ(2n)Vn, then some lattice in ℝ2n contains only the zero point of D.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © University College London 2010
References
- 4
- Cited by


