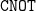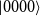Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Bataille, Marc
2022.
Quantum circuits of $$\texttt {CNOT}$$ gates: optimization and entanglement.
Quantum Information Processing,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 7,
Jaffali, Hamza
Holweck, Frédéric
and
Oeding, Luke
2024.
Maximally entangled real states and SLOCC invariants: the 3-qutrit case.
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 14,
p.
145301.