Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Roseblade, James E.
1963.
The automorphism group of McLain's characteristically simple group.
Mathematische Zeitschrift,
Vol. 82,
Issue. 4,
p.
267.
Hall, P.
1963.
On non-strictly simple groups.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 3,
p.
531.
Иванюта, И. Д.
1964.
О силовскихp-подгруппах топологической группы всех подстановок счетного множества.
Ukrainian Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 5,
p.
602.
Stonehewer, S. E.
1966.
Formations and a class of locally soluble groups.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 4,
p.
613.
Kopytov, V. M.
and
Mamaev, I. I.
1968.
The absolute convexity of certain subgroups of an ordered group.
Algebra and Logic,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 2,
p.
82.
Dark, R. S.
1968.
A prime Baer group.
Mathematische Zeitschrift,
Vol. 105,
Issue. 4,
p.
294.
Göbel, RÜdiger
1969.
Produkte von Gruppenklassen.
Archiv der Mathematik,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 2,
p.
113.
Rhemtulla, A. H.
1969.
A Property of Groups with No Central Factors.
Canadian Mathematical Bulletin,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 4,
p.
467.
Wilson, J. S.
1971.
Groups with every proper quotient finite.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 69,
Issue. 3,
p.
373.
Simonyan, L. A.
1972.
Some examples of Lie groups and Lie algebras.
Siberian Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 4,
p.
602.
1973.
Locally Finite Groups.
Vol. 3,
Issue. ,
p.
193.
Heineken, H.
and
Wilson, J. S.
1974.
Locally soluble groups with min-n..
Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 3,
p.
305.
Wells, Charles
1976.
Some Applications of the Wreath Product Construction.
The American Mathematical Monthly,
Vol. 83,
Issue. 5,
p.
317.
Neumann, Peter M.
1976.
The structure of finitary permutation groups.
Archiv der Mathematik,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 1,
p.
3.
Wilson, J. S.
1976.
On characteristically simple groups.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 80,
Issue. 1,
p.
19.
Silcock, Howard L.
1977.
Generalized wreath products and the lattice of normal subgroups of a group.
Algebra Universalis,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 1,
p.
361.
Wilson, J. S.
1979.
Groups with many characteristically simple subgroups.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 86,
Issue. 2,
p.
193.
Dixon, Martyn R.
and
Fournelle, Thomas A.
1984.
The indecomposability of certain wreath products indexed by partially ordered sets.
Archiv der Mathematik,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 3,
p.
193.
Behrendt, Gerhard
1986.
Systems of equivalence relations on countable sets.
Archiv der Mathematik,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 3,
p.
238.
Leinen, Felix
and
Phillips, Richard E.
1986.
Existentially closed central extensions of locally finite p-groups.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 100,
Issue. 2,
p.
281.


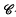 -groups; we also use
-groups; we also use 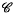 to denote the class of all characteristically simple groups.
to denote the class of all characteristically simple groups.