The Stopping Power of Hydrogen Atoms for α-Particles according to the New Quantum Theory
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 October 2008
Extract
An α-particle passing through a gas loses velocity because it gives up energy to the gaseous atoms. If we can calculate the average energy transferred to an atom, the stopping power of the gas follows immediately. The earlier theories, by Thomson and Darwin, took account of only the close collisions, in which the α-particle actually passes through the atom. Bohr, however, in 1913, took into account the transfers of energy to atoms at distances from the track considerably larger than atomic dimensions. His calculation was purely classical, and dealt with an atomic, model in which the electrons were capable of simple harmonic motions. The result was in very satisfactory agreement with experiment. For atoms containing each a single electron, with mass μ, charge ε, and natural period ω, Bohr's formula is
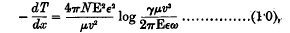
where − dT/dx is the rate of loss of energy by an α-particle whose charge is E, and velocity v; N is the number of atoms per c.c.; and γ = 1·123.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society , Volume 23 , Issue 6 , April 1927 , pp. 732 - 754
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge Philosophical Society 1927
References
* Thomson, , Conduction of Electricity through Gases, pp. 370–382.Google Scholar
† Darwin, , Phil, Mag. xxiii, p. 901 (1912).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
‡ Bohr, , Phil. Mag. xxv, p. 10 (1913).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
§ Fowler, , Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. xxii, p. 793 (1925).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
∥ Henderson, , Phil. Mag. xliv, p. 680 (1922).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
¶ See Fowler, , Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. xxi, p. 521 (1923).Google Scholar
* Fowler, , Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. xxii, p. 794 (1925).Google Scholar
† Gurney, , Proc. Roy. Soc. A, cvii, pp. 332, 340 (1925).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
* All this section is parallel to Dirac, , Proc. Roy. Soc. A, cxii, pp. 673–677. See also Born, Zeitschrift für Physik, 40, p. 167.Google Scholar
† See Oppenheimer, , Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. xxiii, p. 422 (1926).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
‡ See Fues, , Ann. der Physik, LXXXI, 19, pp. 295–303 (1926).Google Scholar
* Schrodinger, , Ann. der Phytik, LXXIX, p. 361 (1926).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
† See Schrodinger, loe. cit.
* See Oppenheimer, loc. cit. The second half of C(Wkm) was communicated to me by Dr. Oppenheimer, by letter.
* This approximation may break down. when u is nearly as large as λ. If so, we mast UBB the fact that u/λ is, in practice, small—see the text following equation (4·28).
† Watson, , Theory of Besstl Functions, Camb. Univ. Press, 1922, p. 185.Google Scholar
* Watson, P. 202.
* See Sohrodinger, , Zeit. f. Phys. LXXX, p. 437 (1926), Mathematischer Anhang.Google Scholar
* Thomson, loc. cit.
* Watson, p. 80.
- 27
- Cited by


