No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 October 2008
The following embedding theorem was proved in the paper (7). Let Π be a set of primes and P, H and K periodic Π-groups satisfying
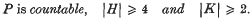
Then there is a period Π-group J generated by isomorphic copies of H and K such that P ≤ J.