Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Bouillot, Olivier
2015.
On Hurwitz multizeta functions.
Advances in Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 71,
Issue. ,
p.
68.
Nakamura, Takashi
and
Pańkowski, Łukasz
2016.
On complex zeros off the critical line for non-monomial polynomial of zeta-functions.
Mathematische Zeitschrift,
Vol. 284,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
23.
NAKAMURA, TAKASHI
2016.
Real zeros of Hurwitz–Lerch zeta and Hurwitz–Lerch type of Euler–Zagier double zeta functions.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 160,
Issue. 1,
p.
39.
Mehta, Jay
Saha, Biswajyoti
and
Viswanadham, G.K.
2016.
Analytic properties of multiple zeta functions and certain weighted variants, an elementary approach.
Journal of Number Theory,
Vol. 168,
Issue. ,
p.
487.
MEHTA, Jay
and
VISWANADHAM, G. K.
2017.
Analytic continuation of multiple Hurwitz zeta functions.
Journal of the Mathematical Society of Japan,
Vol. 69,
Issue. 4,
Gun, Sanoli
and
Saha, Biswajyoti
2018.
Multiple Lerch Zeta Functions and an Idea of Ramanujan.
Michigan Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 67,
Issue. 2,
Chen, Kwang-Wu
2020.
Generalized harmonic number sums and quasisymmetric functions.
Rocky Mountain Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 4,
Sadaoui, Boualem
Jarad, Fahd
Adjabi, Yacine
and
Türkan, Erkan Murat
2023.
A symbolic approach to multiple Hurwitz zeta values at non-positive integers.
Open Mathematics,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 1,


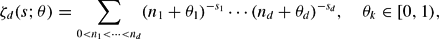
 , to locate the hyperplanes containing its possible poles and to compute the residues at the poles. We explain how to use the residues to locate trivial zeros of
, to locate the hyperplanes containing its possible poles and to compute the residues at the poles. We explain how to use the residues to locate trivial zeros of 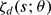 .
.