Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 October 2008
Sommerfeld has shown that the electromagnetic field set up by a Hertzian oscillator placed on the infinite plane surface separating two media normal to that surface may be obtained from the Hertzian function of cylindrical coordinates r, z,
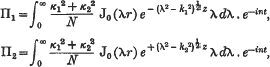
where the suffixes 1, 2 refer to the two media occupying the regions z>0, z<0,
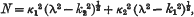
and
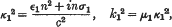
where ɛ1, μ1, σ1 are the dielectric constant, permeability, and conductivity (in Heaviside units) of the first medium, k2, k2 like expressions for the second, c is the velocity of light, and n the frequency in radians per second; +(λ2−k2)½ is taken to have its real part positive.
* Sommerfeld, A., Ann. der Phys. 28 (1909), p. 665;CrossRefGoogle Scholar see also Riemann-Weber's, Differential-gleichungen der Physik, II, p. 542 (1927 edition).Google Scholar