No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Revisiting the general cubic: a simplification of Cardano's solution
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 October 2023
Extract
Given a polynomial equation x3 + ax2 + bx + c = 0 of degree 3 with real coefficients, we may translate the variable by replacing x with x − 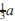 to make the quadratic term vanish. We then obtain a simpler equation x3 + px + q = 0 where
to make the quadratic term vanish. We then obtain a simpler equation x3 + px + q = 0 where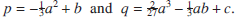 Therefore, in order to solve a polynomial equation of degree 3, it is sufficient to solve equations of the form x3 + px + q = 0.
Therefore, in order to solve a polynomial equation of degree 3, it is sufficient to solve equations of the form x3 + px + q = 0.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Authors, 2023 Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of The Mathematical Association
References
Harris, J. W., Stocker, H., Handbook of mathematics and computational science, Springer-Verlaine (1998).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Gilbert, L., Gilbert, J., Elementary modern algebra (8th edn), Cengage Learning (2015).Google Scholar
Sylvester, J. J., On a remarkable discovery in the theory of canonical forms and of hyperdeterminants, Math. Mag. 2 (1851) pp. 391–410.Google Scholar
Chen, W.Y.C., Cubic equations through the looking glass of Sylvester, College Math. J., 53(5) (2022) pp. 396–398.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Liao, H. C., Shiue, P. J. -S, Cubic equations revisited (in Chinese), Math Media, 46(1) (2022) pp. 33–39.Google Scholar



