Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 January 2015
Although it is an old one, the fascinating world of Fibonnaci numbers and Lucas numbers continues to provide rich areas of investigation for professional and amateur mathematicians. We revisit divisibility properties for t0hose numbers along with the closely related Pell numbers and Pell-Lucas numbers by providing a unified approach for our investigation.
For non-negative integers n, the recurrence relation defined by
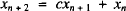
with initial conditions
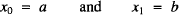
can be used to study the Pell (Pn), Fibonacci (Fn), Lucas (Ln), and Pell-Lucas (Qn) numbers in a unified way. In particular, if a = 0, b = 1 and c = 1, then (1) defines the Fibonacci numbers xn = Fn. If a = 2, b = 1 and c = 1, then xn = Ln. If a = 0, b = 1 and c = 2, then xn = Pn. If a =b = c = 2, then xn = Qn [1].