No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 February 2025
The goal of this paper is to derive a series expansion for standard normal probabilities F(b), where b ≥ 0 and the upper half of the cumulative distribution function (or CDF) of the standard normal is given by(1)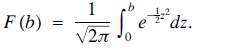 See [1, Chapter 4] for information and results about the normal distribution. It is known that this integral is not elementary, and the usual approach is to use the Taylor series expansion for ez in order to evaluate the integral. We know that
See [1, Chapter 4] for information and results about the normal distribution. It is known that this integral is not elementary, and the usual approach is to use the Taylor series expansion for ez in order to evaluate the integral. We know that 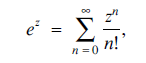 and therefore that (2)
and therefore that (2)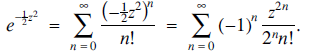 .
.