No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
A Simple Modification of the Binomial Distribution
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 August 2014
Extract
Given any probability distribution, new distributions can be derived from it by assuming its parameters to follow some specific probability distributions. A simple example of this process is provided by the Poisson distribution
P(r∣λ) = e-λλr/r! (r = o, 1, 2, …).
If the parameter λ is assumed to follow the Pearson's Type III law

then the probability of r successes is obtained as
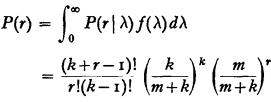
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Institute of Actuaries Students' Society 1960
References
REFERENCES
Kendall, M. G. (1948). The Advanced Theory of Statistics, vol. 1, 4th ed., p. 57. London: Charles Griffin and Co.
Google Scholar
Moore, P. G. (1958). Principles of Statistical Techniques, p. 138. Cambridge University Press.Google Scholar


