Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Matz, Jasmin
2016.
Families of Automorphic Forms and the Trace Formula.
p.
327.
Sarnak, Peter
Shin, Sug Woo
and
Templier, Nicolas
2016.
Families of Automorphic Forms and the Trace Formula.
p.
531.
Müller, Werner
2016.
Families of Automorphic Forms and the Trace Formula.
p.
477.
Abert, Miklos
Gelander, Tsachik
and
Nikolov, Nikolay
2017.
Rank, combinatorial cost, and homology torsion growth in higher rank lattices.
Duke Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 166,
Issue. 15,
Matz, Jasmin
and
Müller, Werner
2017.
Analytic torsion of arithmetic quotients of the symmetric space $${\rm SL} (n,\mathbb{R})/ {\rm SO}(n)$$ SL ( n , R ) / SO ( n ).
Geometric and Functional Analysis,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 6,
p.
1378.
Binder, John
2017.
Fields of rationality of cusp forms.
Israel Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 222,
Issue. 2,
p.
973.
Abert, Miklos
Bergeron, Nicolas
Biringer, Ian
Gelander, Tsachik
Nikolav, Nikolay
Raimbault, Jean
and
Samet, Iddo
2017.
On the growth of $L^2$-invariants for sequences of lattices in Lie groups.
Annals of Mathematics,
Vol. 185,
Issue. 3,
Finis, Tobias
and
Lapid, Erez
2018.
An approximation principle for congruence subgroups II: application to the limit multiplicity problem.
Mathematische Zeitschrift,
Vol. 289,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
1357.
Finis, Tobias
and
Lapid, Erez
2019.
On the analytic properties of intertwining operators II: Local degree bounds and limit multiplicities.
Israel Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 230,
Issue. 2,
p.
771.
Raimbault, Jean
2019.
Analytic, Reidemeister and homological torsion for congruence three–manifolds.
Annales de la Faculté des sciences de Toulouse : Mathématiques,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 3,
p.
417.
Binder, John
2019.
Fields of rationality of automorphic representations: The case of unitary groups.
Journal of Number Theory,
Vol. 203,
Issue. ,
p.
32.
Matz, Jasmin
and
Müller, Werner
2020.
APPROXIMATION OF -ANALYTIC TORSION FOR ARITHMETIC QUOTIENTS OF THE SYMMETRIC SPACE.
Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 2,
p.
307.
Beuzart-Plessis, Raphaël
2021.
Relative Trace Formulas.
p.
1.
Finis, Tobias
and
Matz, Jasmin
2021.
On the asymptotics of Hecke operators for reductive groups.
Mathematische Annalen,
Vol. 380,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
1037.
Chen, Shih-Yu
2021.
Gamma factors for the Asai cube representation.
Mathematische Zeitschrift,
Vol. 297,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
747.
Frączyk, Mikołaj
2021.
Strong limit multiplicity for arithmetic hyperbolic surfaces and 3-manifolds.
Inventiones mathematicae,
Vol. 224,
Issue. 3,
p.
917.
Dalal, Rahul
2022.
Sato–Tate equidistribution for families of
automorphic representations through the stable trace formula.
Algebra & Number Theory,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 1,
p.
59.
Matz, Jasmin
and
Müller, Werner
2023.
Analytic torsion for arithmetic locally symmetric manifolds and approximation of L2-torsion.
Journal of Functional Analysis,
Vol. 284,
Issue. 1,
p.
109727.
Müller, Werner
2024.
The Weyl law for congruence subgroups and arbitrary K∞-types.
Journal of Functional Analysis,
Vol. 287,
Issue. 1,
p.
110444.
Jana, Subhajit
and
Kamber, Amitay
2024.
On the local -Bound of the Eisenstein series.
Forum of Mathematics, Sigma,
Vol. 12,
Issue. ,
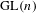 $\text{GL}(n)$ AND
$\text{GL}(n)$ AND 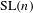 $\text{SL}(n)$
$\text{SL}(n)$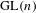 $\text{GL}(n)$ and
$\text{GL}(n)$ and 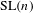 $\text{SL}(n)$ we show that the suitably normalized spectra converge to the Plancherel measure (the limit multiplicity property). For general reductive groups we obtain a substantial reduction of the problem. Our main tool is the recent refinement of the spectral side of Arthur’s trace formula obtained in [Finis, Lapid, and Müller, Ann. of Math. (2) 174(1) (2011), 173–195; Finis and Lapid, Ann. of Math. (2) 174(1) (2011), 197–223], which allows us to show that for
$\text{SL}(n)$ we show that the suitably normalized spectra converge to the Plancherel measure (the limit multiplicity property). For general reductive groups we obtain a substantial reduction of the problem. Our main tool is the recent refinement of the spectral side of Arthur’s trace formula obtained in [Finis, Lapid, and Müller, Ann. of Math. (2) 174(1) (2011), 173–195; Finis and Lapid, Ann. of Math. (2) 174(1) (2011), 197–223], which allows us to show that for 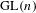 $\text{GL}(n)$ and
$\text{GL}(n)$ and 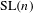 $\text{SL}(n)$ the contribution of the continuous spectrum is negligible in the limit.
$\text{SL}(n)$ the contribution of the continuous spectrum is negligible in the limit.

