Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 January 2021
We say that a group G of local (maybe formal) biholomorphisms satisfies the uniform intersection property if the intersection multiplicity
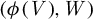 $(\phi (V), W)$
takes only finitely many values as a function of G for any choice of analytic sets V and W of complementary dimension. In dimension
$(\phi (V), W)$
takes only finitely many values as a function of G for any choice of analytic sets V and W of complementary dimension. In dimension
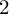 $2$
we show that G satisfies the uniform intersection property if and only if it is finitely determined – that is, if there exists a natural number k such that different elements of G have different Taylor expansions of degree k at the origin. We also prove that G is finitely determined if and only if the action of G on the space of germs of analytic curves has discrete orbits.
$2$
we show that G satisfies the uniform intersection property if and only if it is finitely determined – that is, if there exists a natural number k such that different elements of G have different Taylor expansions of degree k at the origin. We also prove that G is finitely determined if and only if the action of G on the space of germs of analytic curves has discrete orbits.