Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 April 2009
Consider an m × n rectangular array whose m rows are permutations of 1, 2, …, n. Such an array will be called a constant-sum array if the sum of the elements in each column is the same (and equal to ½m (n+1)). An example of a 3×9 constant-sum array is 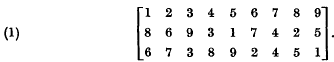 In contrast to a Latin rectangle, elements in the same column of a constantsum array may be equal. It will be convenient to assume arrays normalised in the sense that the columns are arranged so that, as in (1), the first row is in the standard order 1, 2, …, n.
In contrast to a Latin rectangle, elements in the same column of a constantsum array may be equal. It will be convenient to assume arrays normalised in the sense that the columns are arranged so that, as in (1), the first row is in the standard order 1, 2, …, n.