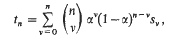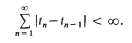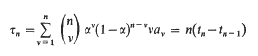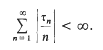Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Ray, B. K.
and
Sahoo, A. K.
1996.
Application of the absolute Euler method to some series related to Fourier series and its conjugate series.
Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences - Section A,
Vol. 106,
Issue. 1,
p.
13.
Chandra, Prem
2001.
Multipliers for the absolute euler summability of fourier series.
Proceedings Mathematical Sciences,
Vol. 111,
Issue. 2,
p.
203.


 is said to be summable |
is said to be summable |