No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
ALGEBRAIC CUNTZ–KRIEGER ALGEBRAS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 September 2019
Abstract
We show that a directed graph 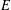 $E$ is a finite graph with no sinks if and only if, for each commutative unital ring
$E$ is a finite graph with no sinks if and only if, for each commutative unital ring 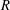 $R$, the Leavitt path algebra
$R$, the Leavitt path algebra 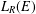 $L_{R}(E)$ is isomorphic to an algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebra if and only if the
$L_{R}(E)$ is isomorphic to an algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebra if and only if the 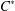 $C^{\ast }$-algebra
$C^{\ast }$-algebra 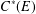 $C^{\ast }(E)$ is unital and
$C^{\ast }(E)$ is unital and 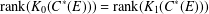 $\text{rank}(K_{0}(C^{\ast }(E)))=\text{rank}(K_{1}(C^{\ast }(E)))$. Let
$\text{rank}(K_{0}(C^{\ast }(E)))=\text{rank}(K_{1}(C^{\ast }(E)))$. Let 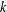 $k$ be a field and
$k$ be a field and 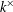 $k^{\times }$ be the group of units of
$k^{\times }$ be the group of units of 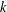 $k$. When
$k$. When 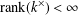 $\text{rank}(k^{\times })<\infty$, we show that the Leavitt path algebra
$\text{rank}(k^{\times })<\infty$, we show that the Leavitt path algebra 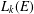 $L_{k}(E)$ is isomorphic to an algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebra if and only if
$L_{k}(E)$ is isomorphic to an algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebra if and only if  $L_{k}(E)$ is unital and
$L_{k}(E)$ is unital and 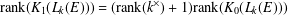 $\text{rank}(K_{1}(L_{k}(E)))=(\text{rank}(k^{\times })+1)\text{rank}(K_{0}(L_{k}(E)))$. We also show that any unital
$\text{rank}(K_{1}(L_{k}(E)))=(\text{rank}(k^{\times })+1)\text{rank}(K_{0}(L_{k}(E)))$. We also show that any unital  $k$-algebra which is Morita equivalent or stably isomorphic to an algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebra, is isomorphic to an algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebra. As a consequence, corners of algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebras are algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebras.
$k$-algebra which is Morita equivalent or stably isomorphic to an algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebra, is isomorphic to an algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebra. As a consequence, corners of algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebras are algebraic Cuntz–Krieger algebras.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2019 Australian Mathematical Publishing Association Inc.
Footnotes
This research was in part supported by a grant from IPM (no. 95170419).



