Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 March 2014
We study some generalized notions of cohesiveness which arise naturally in connection with effective versions of Ramsey's Theorem. An infinite set A of natural numbers is n-cohesive (respectively, n-r-cohesive) if A is almost homogeneous for every computably enumerable (respectively, computable) 2-coloring of the n-element sets of natural numbers. (Thus the 1-cohesive and 1-r-cohesive sets coincide with the cohesive and r-cohesive sets, respectively.) We consider the degrees of unsolvability and arithmetical definability levels of n-cohesive and n-r-cohesive sets. For example, we show that for all n ≥ 2, there exists a 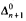 n-cohesive set. We improve this result for n = 2 by showing that there is a
n-cohesive set. We improve this result for n = 2 by showing that there is a 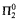 2-cohesive set. We show that the n-cohesive and n-r-cohesive degrees together form a linear, non-collapsing hierarchy of degrees for n ≥ 2. In addition, for n ≥ 2 we characterize the jumps of n-cohesive degrees as exactly the degrees ≥ 0(n+1) and also characterize the jumps of the n-r-cohesive degrees.
2-cohesive set. We show that the n-cohesive and n-r-cohesive degrees together form a linear, non-collapsing hierarchy of degrees for n ≥ 2. In addition, for n ≥ 2 we characterize the jumps of n-cohesive degrees as exactly the degrees ≥ 0(n+1) and also characterize the jumps of the n-r-cohesive degrees.