Article contents
THE POSET OF ALL LOGICS I: INTERPRETATIONS AND LATTICE STRUCTURE
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 June 2021
Abstract
A notion of interpretation between arbitrary logics is introduced, and the poset 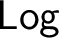 $\mathsf {Log}$
of all logics ordered under interpretability is studied. It is shown that in
$\mathsf {Log}$
of all logics ordered under interpretability is studied. It is shown that in 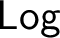 $\mathsf {Log}$
infima of arbitrarily large sets exist, but binary suprema in general do not. On the other hand, the existence of suprema of sets of equivalential logics is established. The relations between
$\mathsf {Log}$
infima of arbitrarily large sets exist, but binary suprema in general do not. On the other hand, the existence of suprema of sets of equivalential logics is established. The relations between 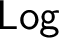 $\mathsf {Log}$
and the lattice of interpretability types of varieties are investigated.
$\mathsf {Log}$
and the lattice of interpretability types of varieties are investigated.
Keywords
MSC classification
Primary:
03G27: Abstract algebraic logic
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Association for Symbolic Logic 2021
References
REFERENCES
Albuquerque, H., Font, J. M., Jansana, R., and Moraschini, T., Assertional logics, truth-equational logics, and the hierarchies of abstract algebraic logic, Don Pigozzi on Abstract Algebraic Logic and Universal Algebra, (Czelakowski, J., editor), Springer-Verlag, Cham, 2018.Google Scholar
Baldwin, J. T. and Berman, J., A model theoretic approach to Malcev conditions, this Journal, vol. 42 (1977), no. 2, pp. 277–288.Google Scholar
Bergman, C., Universal Algebra: Fundamentals and Selected Topics, Chapman & Hall Pure and Applied Mathematics. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2011.10.1201/9781439851302CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Blok, W. J. and Pigozzi, D., Protoalgebraic logics. Studia Logica, vol. 45 (1986), pp. 337–369.10.1007/BF00370269CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Blok, W. J. and Pigozzi, D., Algebraizable Logics, Memoirs of the American Mathematical Society, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 1989.Google Scholar
Blok, W. J. and Pigozzi, D., Algebraic semantics for universal Horn logic without equality, Universal Algebra and Quasigroup Theory (Romanowska, A. and Smith, J. D. H., editors), Heldermann, Berlin, 1992, pp. 1–56.Google Scholar
Burris, S. and Sankappanavar, H. P., A course in universal algebra, 2012, The millennium edition. Available at https://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/~snburris/htdocs/ualg.html.Google Scholar
Czelakowski, J., Reduced products of logical matrices. Studia Logica, vol. 39 (1980), pp. 19–43.10.1007/BF00373095CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Czelakowski, J., Equivalential logics, I, II. Studia Logica, vol. 40 (1981), pp. 227–236 and 355–372.10.1007/BF02584057CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Czelakowski, J., Protoalgebraic Logics, Trends in Logic—Studia Logica Library, vol. 10, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 2001.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Czelakowski, J., The Suszko operator. Part I. Studia Logica, Special Issue on Abstract Algebraic Logic, Part II, vol. 74 (2003), no. 5, pp. 181–231.10.1023/A:1024678007488CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Czelakowski, J. and Jansana, R., Weakly algebraizable logics, this Journal, vol. 65 (2000), no. 2, pp. 641–668.Google Scholar
Davey, B. A. and Werner, H., Dualities and equivalences for varieties of algebras, Contributions to Lattice Theory (Szeged, 1980) (Bolyai, J., editor), North-Holland, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1983, pp. 101–275.Google Scholar
Dellunde, P. and Jansana, R., Some characterization theorems for infinitary universal Horn logic without equality, this Journal, vol. 61 (1996), no. 4, pp. 1242–1260.Google Scholar
Font, J. M., Abstract Algebraic Logic - An Introductory Textbook, Studies in Logic - Mathematical Logic and Foundations, vol. 60, College Publications, London, 2016.Google Scholar
Font, J. M. and Jansana, R., A General Algebraic Semantics for Sentential Logics, second ed., Lecture Notes in Logic. vol. 7, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2017. First edition 1996. Electronic version freely available through Project Euclid at projecteuclid.org/euclid.lnl/1235416965.Google Scholar
Font, J. M., Jansana, R., and Pigozzi, D., A survey on abstract algebraic logic. Studia Logica, Special Issue on Abstract Algebraic Logic, Part II, vol. 74 (2003), no. 1–2, pp. 13–97, With an “Update” in 91 (2009), 125–130.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Font, J. M. and Moraschini, T., Logics of varieties, logics of semilattices, and conjunction. Logic Journal of the IGPL, vol. 22 (2014), pp. 818–843.10.1093/jigpal/jzu003CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Font, J. M. and Moraschini, T., A note on congruences of semilattices with sectionally finite height. Algebra Universalis, vol. 72 (2014), no. 3, pp. 287–293.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
García, O. C. and Taylor, W., The Lattice of Interpretability Types of Varieties, Memoirs of the American Mathematical Society, vol. 50, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 1984.Google Scholar
Grätzer, G., Two Mal’cev-type theorems in universal algebra. Journal of Combinatorial Theory, vol. 8 (1970), pp. 334–342.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Herrmann, B., Algebraizability and Beth’s theorem for equivalential logics. Bulletin of the Section of Logic, vol. 22 (1993), no. 2, pp. 85–88.Google Scholar
Herrmann, B., Equivalential and algebraizable logics. Studia Logica, vol. 57 (1996), pp. 419–436.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Herrmann, B., Characterizing equivalential and algebraizable logics by the Leibniz operator. Studia Logica, vol. 58 (1997), pp. 305–323.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Hobby, D. and McKenzie, R., The Structure of Finite Algebras, Contemporary Mathematics, vol. 76, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 1988.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Jansana, R. and Moraschini, T., Relational semantics and ordered algebras for deductive systems, Manuscript, 2021.Google Scholar
Jansana, R. and Moraschini, T., The poset of all logics II: Leibniz classes and hierarchy, this Journal, to appear, 2021.10.1017/jsl.2021.49CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Jansana, R. and Moraschini, T., The poset of all logics III: Finitely presentable logics. Studia Logica, vol. 109 (2021), pp. 539–580.10.1007/s11225-020-09916-zCrossRefGoogle Scholar
Kearnes, K. A. and Kiss, E. W., The Shape of Congruences Lattices, Memoirs of the American Mathematical Society, vol. 222, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 2013.Google Scholar
Lawvere, F. W.,
Functorial semantics for algebraic theories
, Ph.D. thesis, Columbia University, 1963.10.1073/pnas.50.5.869CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Mal’cev, A. I., On the general theory of algebraic system. Matematicheskii Sbornik, vol. 77 (1954), no. 35, pp. 3–20.Google Scholar
Malinowski, J., Modal equivalential logics. Journal of Non-Classical Logic, vol. 3 (1986), pp 13–35.Google Scholar
McKenzie, R., An algebraic version of categorical equivalence for varieties and more general algebraic categories, Logic and Algebra (Aglianò, P. and Magari, R., editors), Lecture Notes in Pure and Applied Mathematics, vol. 180, Dekker, New York, 1996, pp. 211–243.Google Scholar
Moraschini, T., On everywhere strongly logifiable algebras. Reports on Mathematical Logic, vol. 50 (2015), pp. 83–107.Google Scholar
Moraschini, T., A logical and algebraic characterization of adjunctions between generalized quasi-varieties. Journal of Symbolic Logic, vol. 83 (2018), no. 3, pp. 899–919.10.1017/jsl.2018.47CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Moraschini, T., A study of the truth predicates of matrix semantics. Review of Symbolic Logic, vol. 11 (2018), no. 4, pp. 780–804.10.1017/S175502031800014XCrossRefGoogle Scholar
Moraschini, T., On the complexity of the Leibniz hierarchy. Annals of Pure and Applied Logic, vol. 170 (2019), no. 7, pp. 805–824.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Moraschini, T. and Raftery, J. G., On prevarieties of logic. Algebra Universalis, vol. 80 (2019), no. 3, pp. 1–11.10.1007/s00012-019-0611-7CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Neumann, W., On Mal’cev conditions. Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society, vol. 17 (1974), pp. 376–384.10.1017/S1446788700017122CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Neumann, W. D., Representing varieties of algebras by algebras. Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society, vol. 11 (1970), pp. 1–8.10.1017/S1446788700005899CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Pixley, A. F., Local Mal’cev conditions. Canadian Mathematical Bulletin, vol. 15 (1972), pp. 559–568.10.4153/CMB-1972-098-8CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Přenosil, A., Constructing natural extensions of propositional logics. Studia Logica, vol. 82 (2015), pp. 1–12.Google Scholar
Raftery, J. G., Correspondences between Gentzen and Hilbert systems, this Journal, vol. 71 (2006), no. 3, pp. 903–957.Google Scholar
Raftery, J. G., The equational definability of truth predicates. Reports on Mathematical Logic, vol. 41 (2006), pp. 95–149.Google Scholar
Raftery, J. G., A perspective on the algebra of logic. Quaestiones Mathematicae, vol. 34 (2011), pp. 275–325.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Raftery, J. G., Admissible rules and the Leibniz hierarchy. Notre Dame Journal of Formal Logic, vol. 57 (2016), no. 4, pp. 569–606.10.1215/00294527-3671151CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Taylor, W., Characterizing Mal’cev conditions. Algebra Universalis, vol. 3 (1973), pp. 351–397.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Taylor, W., The fine spectrum of a variety. Algebra Universalis, vol. 5 (1975), no. 2, pp. 263–303.10.1007/BF02485261CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Taylor, W., Varieties obeying homotopy laws. Canadian Journal of Mathematics, vol. 29 (1977), pp. 498–527.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Wille, R., Kongruenzklassengeometrien, Springer Lecture Notes, vol. 113, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1970.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Wójcicki, R., Theory of Logical Calculi. Basic Theory of Consequence Operations, Synthese Library, vol. 199, Reidel, Dordrecht, 1988.10.1007/978-94-015-6942-2CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- 5
- Cited by



