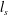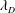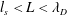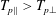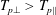Research Article
Three-dimensional magnetic reconnection and its application to solar flares
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2017, 535830101
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
- NASA ADS Abstract Service
Ion reflection by shock waves and pulse generation by cross-field ion beams
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2017, 595830101
Differential formulation of the gyrokinetic Landau operator
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2017, 595830102
Conceptual design of initial opacity experiments on the national ignition facility
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2017, 595830103
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
- NASA ADS Abstract Service
Fast magnetic field penetration into low resistivity plasma
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2017, 595830104
Studies of challenge in lower hybrid current drive capability at high density regime in experimental advanced superconducting tokamak
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2017, 595830105
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
- NASA ADS Abstract Service
Debye length and plasma skin depth: two length scales of interest in the creation and diagnosis of laboratory pair plasmas
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2017, 595830106
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
- NASA ADS Abstract Service
Ion angular distribution simulation of the Highly Efficient Multistage Plasma Thruster
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2017, 595830107
Effective factors on twisted terahertz radiation generation in a rippled plasma
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2017, 655830101
Vlasov models for kinetic Weibel-type instabilities
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2017, 705830101
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
- NASA ADS Abstract Service
Tutorial
Plasma waves as a benchmark problem
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2017, 707830101
Research Article
Diagnosing collisionless energy transfer using field–particle correlations: Vlasov–Poisson plasmas
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2017, 705830102
A pressure tensor description for the time-resonant Weibel instability
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2017, 705830103
Three-dimensional simulations of sheared current sheets: transition to turbulence?
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2017, 705830104
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
- NASA ADS Abstract Service
Proton fire hose instabilities in the expanding solar wind
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2017, 705830105
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
- NASA ADS Abstract Service
Phase mixing importance for both Landau instability and damping
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2017, 705830106
Alternating direction implicit type preconditioners for the steady state inhomogeneous Vlasov equation
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2017, 705830107
Colliding Alfvénic wave packets in magnetohydrodynamics, Hall and kinetic simulations
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2017, 705830108
Explicitly covariant dispersion relations and self-induced transparency
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2017, 905830101
Cyclotron auto resonance maser and free electron laser devices: a unified point of view
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2017, 905830102