Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Priest, E R
1985.
The magnetohydrodynamics of current sheets.
Reports on Progress in Physics,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 7,
p.
955.
Mondt, J. P.
and
Goedert, J.
1985.
Dissipative instabilities at the edge of reversed-field pinches driven by a combination of plasma gradients and a parallel current.
The Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 6,
p.
1816.
Simnett, G. M.
1986.
A dominant role for protons at the onset of solar flares.
Solar Physics,
Vol. 106,
Issue. 1,
p.
165.
Vilmer, N.
1987.
Hard X-ray emission processes in solar flares.
Solar Physics,
Vol. 111,
Issue. 1,
p.
207.
Vilmer, N.
1987.
Particle Acceleration and Trapping in Solar Flares.
p.
207.
Hinata, Satoshi
1988.
Microscopic filamentation due to electrothermal instability and plasma heating in time-dependent solar transition layer.
Solar Physics,
Vol. 116,
Issue. 2,
p.
239.
Cardozo, N J Lopes
and
Schuller, F C
1992.
Deterministic chaos and filamentation in plasmas.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 13,
p.
1939.
Cardozo, N J Lopes
Schuller, F C
Barth, C J
Chu, C C
Pijper, F J
Lok, J
Montvai, A
Oomens, A A M
Peters, M
and
Rover, M de
1994.
Evidence for small scale magnetic structures in the RTP tokamak.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 12B,
p.
B133.
Urrutia, J. M.
and
Stenzel, R. L.
1996.
Pulsed currents carried by whistlers. VI. Nonlinear effects.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 7,
p.
2589.
Cardozo, Niek Lopes
1998.
Anomalous Transport Due to Magnetic Turbulence.
Fusion Technology,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 2T,
p.
165.
Davies, J. R.
Bell, A. R.
and
Tatarakis, M.
1999.
Magnetic focusing and trapping of high-intensity laser-generated fast electrons at the rear of solid targets.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 5,
p.
6032.
Cardozo, Niek Lopes
2000.
Anomalous Transport Due to Magnetic Turbulence.
Fusion Technology,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 2T,
p.
296.
Davies, J. R.
2003.
Electric and magnetic field generation and target heating by laser-generated fast electrons.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 68,
Issue. 5,
Cardozo, Lopes Cardozo
2004.
Anomalous Transport due to Magnetic Turbulence.
Fusion Science and Technology,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 2T,
p.
321.
Khorashadizadeh, S. M.
Rastbood, E.
and
Niknam, A. R.
2014.
Filamentation instability of nonextensive current-driven plasma in the ion acoustic frequency range.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 12,
Khorashadizadeh, S. M.
Rastbood, E.
and
Niknam, A. R.
2015.
Kinetic theory of the filamentation instability in a collisional current-driven plasma with nonextensive distribution.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 7,
Auluck, Sunil
Kubes, Pavel
Paduch, Marian
Sadowski, Marek J.
Krauz, Vyacheslav I.
Lee, Sing
Soto, Leopoldo
Scholz, Marek
Miklaszewski, Ryszard
Schmidt, Hellmut
Blagoev, Alexander
Samuelli, Maurizio
Seng, Yeow Sing
Springham, Stuart Victor
Talebitaher, Alireza
Pavez, Cristian
Akel, Mohammad
Yap, Seong Ling
Verma, Rishi
Kolacek, Karel
Keat, Paul Lee Choon
Rawat, Rajdeep S.
Abdou, Ali
Zhang, Guixin
and
Laas, Tõnu
2021.
Update on the Scientific Status of the Plasma Focus.
Plasma,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 3,
p.
450.
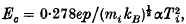 where the electrical conductivity is
where the electrical conductivity is 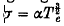 and the total pressure is p. Under this condition it is found that there are two /Futions for Te/Ti which satisfy the steady electron energy balance equation in a homogeneous, fully ionized plasma. One of these /Futions always has values above the critical value of Te/Ti (= 132 in absence of bremsstrahlung) for the onset of the electrothermal instability in a fully ionized gas. Inclusion of electron thermal conduction transverse to the magnetic field (with Hall parameter
and the total pressure is p. Under this condition it is found that there are two /Futions for Te/Ti which satisfy the steady electron energy balance equation in a homogeneous, fully ionized plasma. One of these /Futions always has values above the critical value of Te/Ti (= 132 in absence of bremsstrahlung) for the onset of the electrothermal instability in a fully ionized gas. Inclusion of electron thermal conduction transverse to the magnetic field (with Hall parameter 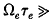 ) yields a wavelength for maximum growth of the instability of about
) yields a wavelength for maximum growth of the instability of about 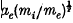 , where ae is the electron Larmor radius. The steady non linear profiles showing current filamentation have been calculated. Runaway electrons and ion-acoustic instabilities can occur in the spatial maximum of the current density and electron temperature. Inclusion of bremsstrahlung loss reduces the value of Te/Ti for the onset of the instability, and at Te = Ti yields a maximum ion temperature obtainable by Ohmic heating in a stable plasma.
, where ae is the electron Larmor radius. The steady non linear profiles showing current filamentation have been calculated. Runaway electrons and ion-acoustic instabilities can occur in the spatial maximum of the current density and electron temperature. Inclusion of bremsstrahlung loss reduces the value of Te/Ti for the onset of the instability, and at Te = Ti yields a maximum ion temperature obtainable by Ohmic heating in a stable plasma.