Article contents
Stability of relativistic anisotropic plasmas to perpendicular magnetosonic waves
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2009
Abstract
The stability of relativistic anisotropic plasmas to the magnetosonic (or righthand compressional Alfvén) wave, near the ion cyclotron frequency, propagating perpendicular to the magnetic field, is investigated. For this case, and for wavelengths larger than the ion Larmor radius and large ion plasma frequency (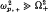 ) the dispersion relation is obtained in a simple form and solved. It is shown that for T‖ ╪ T⊥ (even T‖ ≥ T⊥) no instability occurs. This conclusion applies also to the case of the anisotropic interplanetary medium.
) the dispersion relation is obtained in a simple form and solved. It is shown that for T‖ ╪ T⊥ (even T‖ ≥ T⊥) no instability occurs. This conclusion applies also to the case of the anisotropic interplanetary medium.
We note a peculiarity of the dispersion relation. Zero-order and first-order terms cancel so that the relation is of second order in our expansion parameter. The non-relativistic numerical results of Fredricks and Kennel are recovered.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 1970
References
REFERENCE
- 7
- Cited by


